Basic counting skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 5-8
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Help your child master the essentials with our Basic Counting Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets designed for ages 5-8. Perfectly crafted to build a strong mathematical foundation, these worksheets blend fun and learning, engaging young minds with colorful, interactive exercises that simplify addition and subtraction concepts. Tailored to develop basic counting skills, they encourage critical thinking, problem-solving, and numerical fluency. Our worksheets are an excellent resource for both classroom and at-home learning, boosting confidence and ensuring your child excels in early math education. Explore our collection today and watch your little mathematician flourish!


Community Helpers: 1 less Worksheet
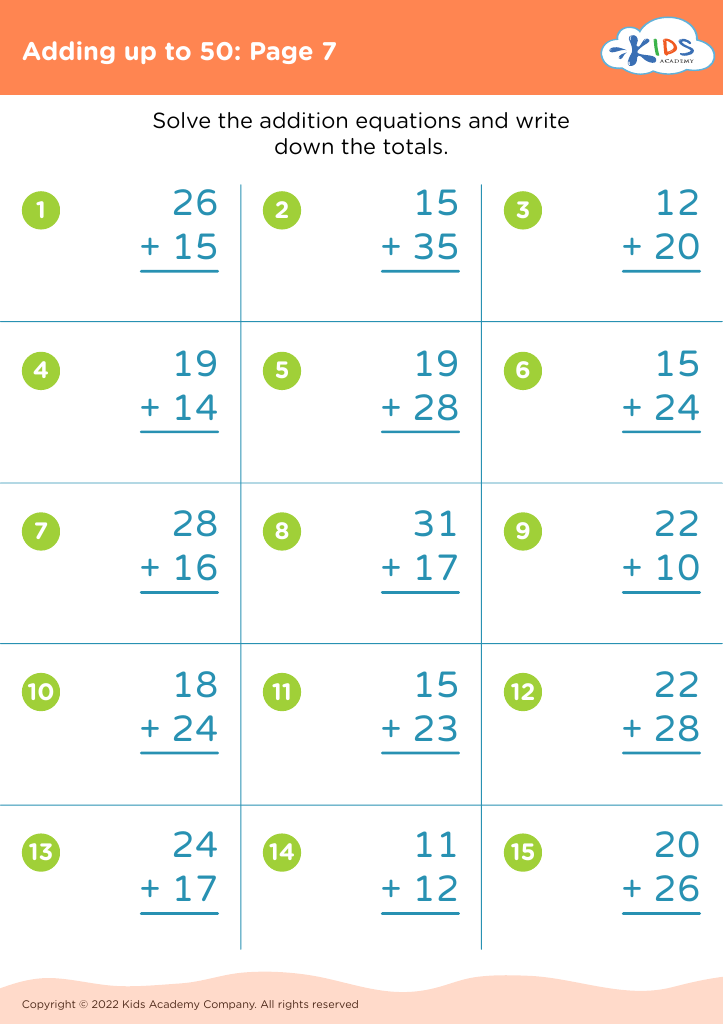
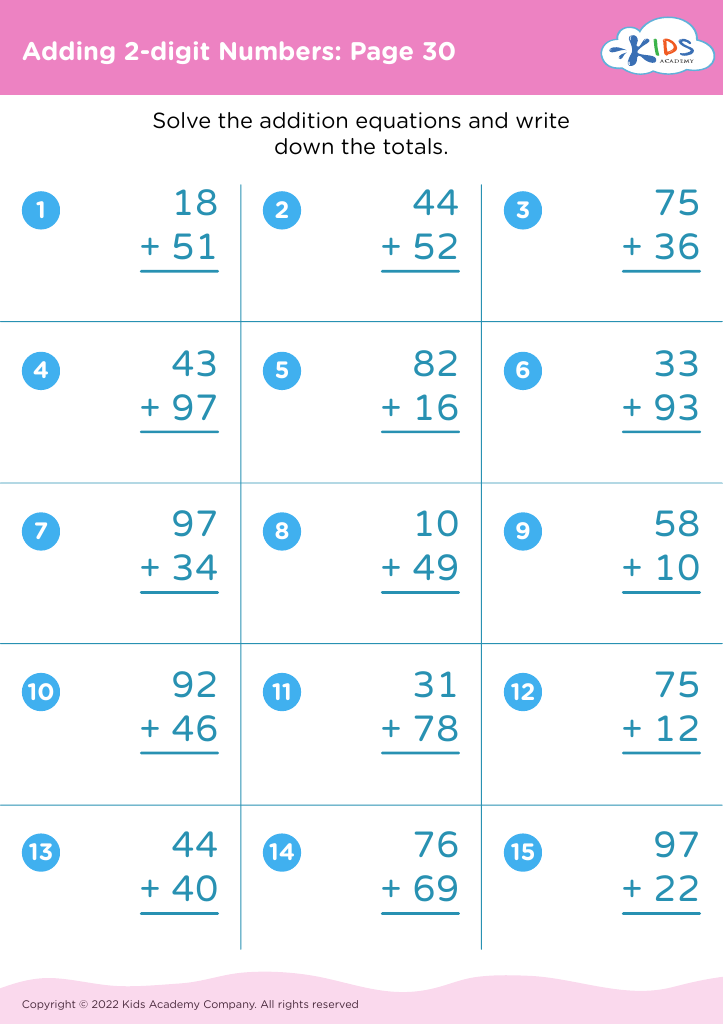
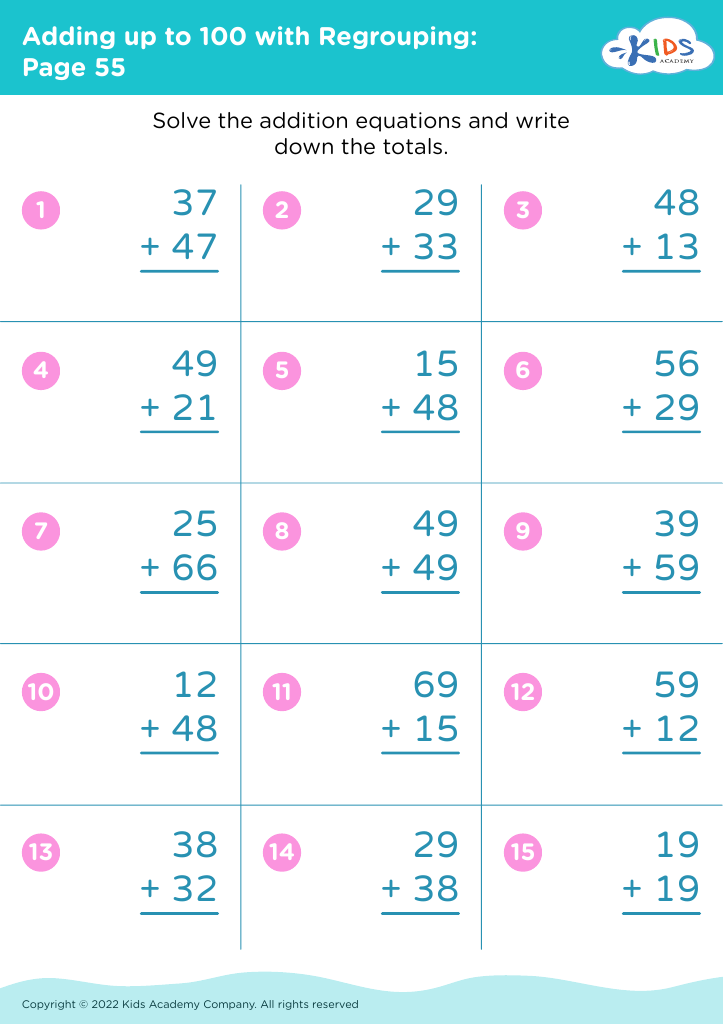
Basic counting skills, addition, and subtraction form the foundational building blocks of a child's mathematical education. By ages 5-8, children are in a critical developmental stage where they can grasp these fundamental concepts that pave the way for more advanced arithmetic, problem-solving, and logical thinking.
For parents and teachers, prioritizing these skills is essential. First, basic counting teaches children about number recognition and sequence, essential components in understanding the world mathematically. Counting often serves as a primary introduction to more complex mathematical procedures and aids in everyday tasks like telling time and managing money.
Addition and subtraction build on counting. Mastery of these operations means children can begin to perform basic calculations mentally, a skill used throughout life in grocery shopping, cooking measurements, and even time management. These operations also promote analytical thinking and enhance memory, which benefit all areas of learning.
Moreover, early proficiency in these areas fosters confidence and a positive attitude towards mathematics. When children see that they can solve problems and understand basic math concepts, they're more likely to be encouraged to tackle more challenging subjects later on.
Ultimately, neglecting these basic skills can lead to gaps in understanding, making it harder for children to catch up later and potentially developing math anxiety. Thus, both parents and teachers play a crucial role in nurturing these early mathematical abilities.


 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students