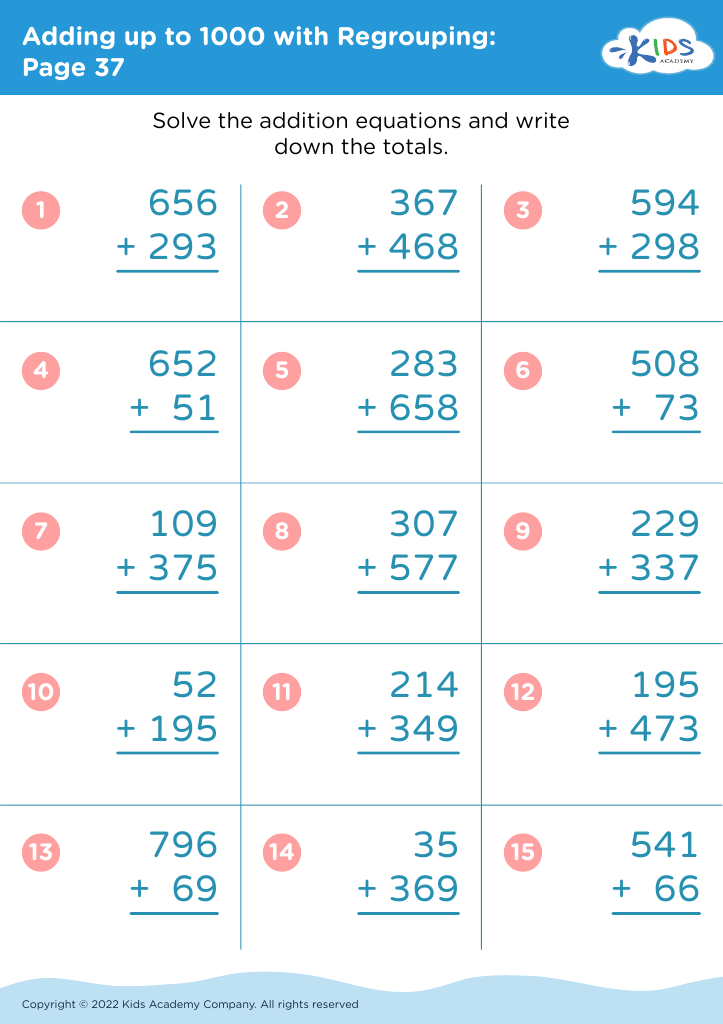
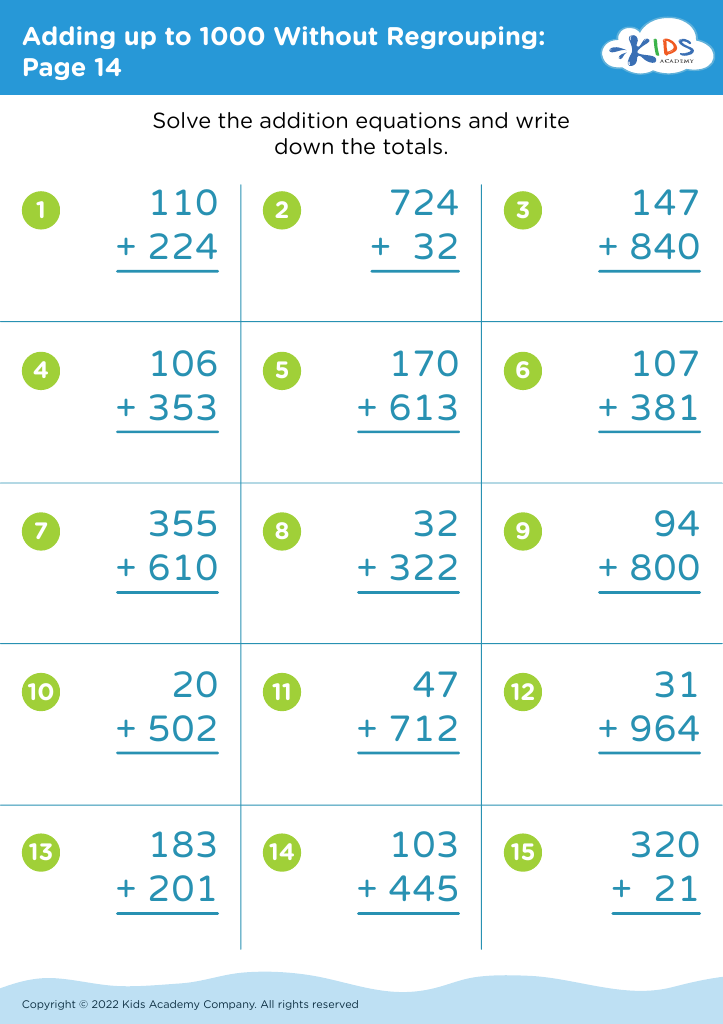
Fine motor skills development Addition Worksheets for Ages 5-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills while mastering addition with our engaging worksheets designed for ages 5-8! These interactive printables seamlessly blend important math concepts with fun activities that promote hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and grip strength. Each worksheet features colorful illustrations and creative tasks that make learning enjoyable, helping young learners practice counting, number recognition, and basic addition skills. Perfect for both home and classroom settings, our Fine Motor Skills Development Addition Worksheets create a stimulating learning environment. Watch your child build confidence and skills as they progress through each level, setting a strong foundation for future mathematical success!
Fine motor skills are essential for children aged 5-8 as they lay the foundation for academic success and daily living. These skills, which involve the use of smaller muscle groups for tasks requiring precision, are crucial for writing, drawing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. Parents and teachers need to care about fine motor development because it significantly impacts a child’s learning experience.
Strong fine motor skills enhance a child's ability to express themselves through writing and art. At this age, children begin formal schooling, where tasks such as holding a pencil, completing worksheets, and participating in craft activities become routine. Inadequate fine motor skills can lead to frustration and lack of confidence, hindering academic progress.
Moreover, fine motor skills contribute to self-help abilities, such as buttoning shirts, tying shoes, and using utensils, fostering independence. Delayed development in this area can affect a child's social interactions and participation in group activities.
Engaging in activities like puzzles, arts and crafts, and interactive games benefits fine motor development. Parents and teachers should prioritize these skills to help children thrive academically and socially, setting them on a path toward lasting success and confidence.