Basic arithmetic skills Adding up to 100 Worksheets for Ages 6-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Introduce your child to the world of math with our "Basic Arithmetic Skills: Adding up to 100 Worksheets." Tailored for ages 6-7, these engaging worksheets build essential addition skills through fun and interactive activities. Each sheet is carefully designed to enhance number sense, boost confidence, and develop problem-solving abilities. Ideal for classroom use or extra practice at home, our printable worksheets provide clear instructions and progressive challenges to support your child's learning journey. Help your student master the basics with effective, enjoyable exercises that make arithmetic an exciting and rewarding experience.
Basic arithmetic skills, particularly the ability to add up to 100, are foundational for children aged 6-7, serving as a cornerstone for their future academic and everyday success. At this age, children are developing cognitive, problem-solving, and critical-thinking skills that are essential for learning more complex mathematical concepts later on, such as subtraction, multiplication, and division.
For parents and teachers, emphasizing these skills supports cognitive development and helps children develop a sense of numerical awareness. Mastering addition up to 100 helps build confidence and reduces math-related anxiety, promoting a positive attitude toward learning. It also provides practical benefits, as basic arithmetic is used in daily activities such as counting money, telling time, and understanding quantities and measurements.
Importantly, early arithmetic skills form the basis for higher-order thinking. Solving addition problems encourages logical reasoning, attention to detail, and the ability to focus on a task. It also fosters perseverance as children learn to work through challenges and find solutions.
By caring about and actively supporting arithmetic skill development, parents and teachers set students on a path toward academic achievement and practical competence, laying a solid foundation for lifelong learning and critical thinking skills.
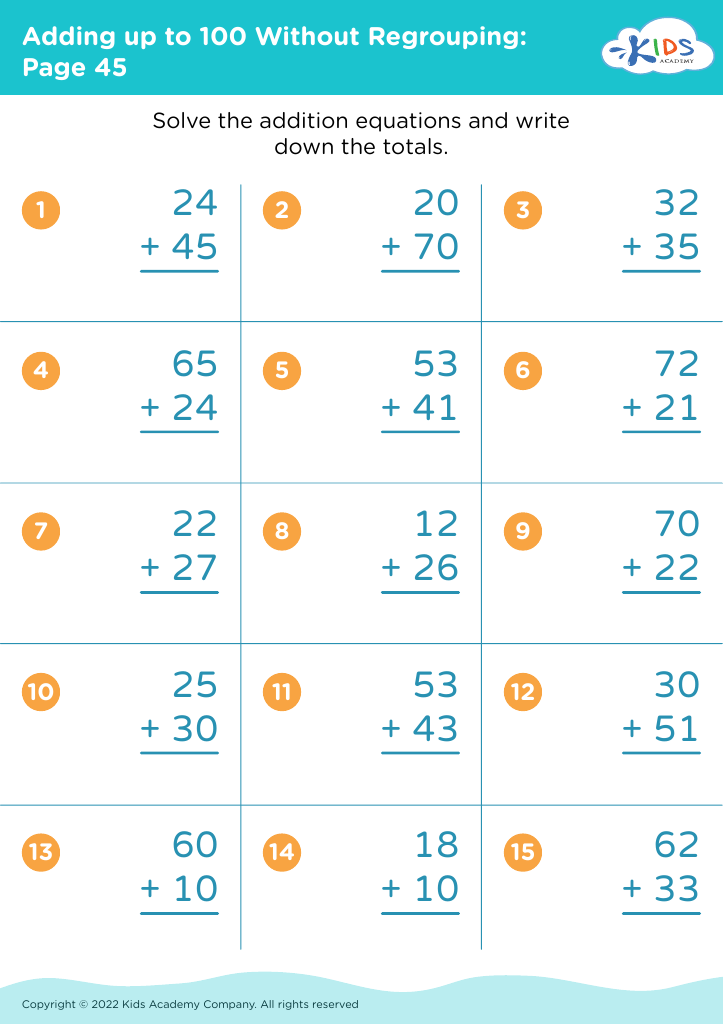
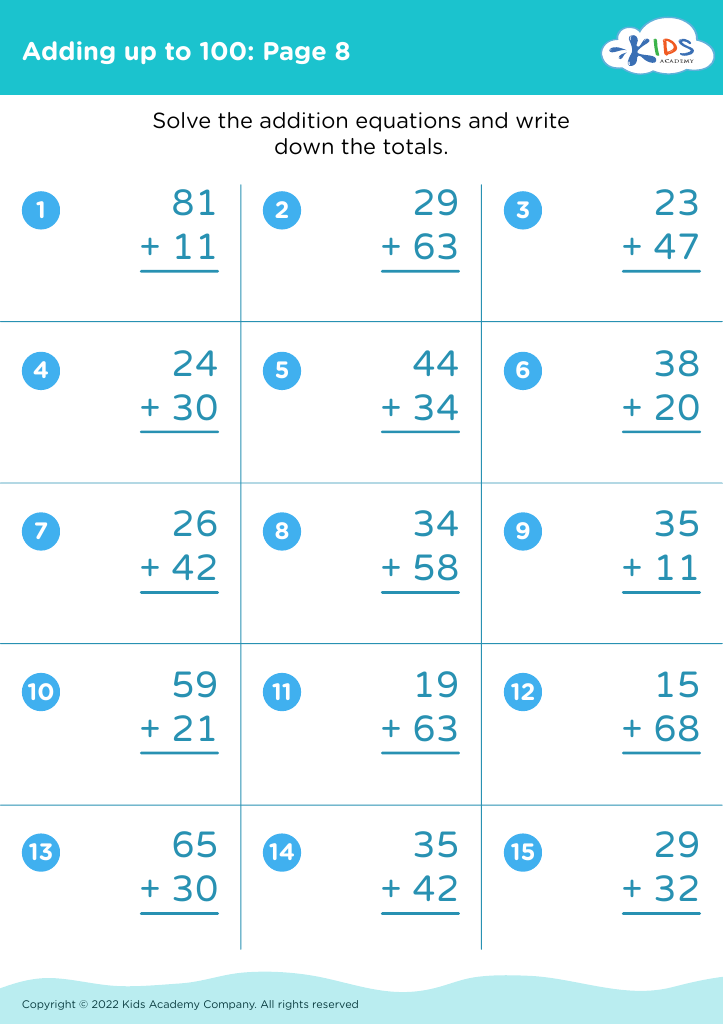
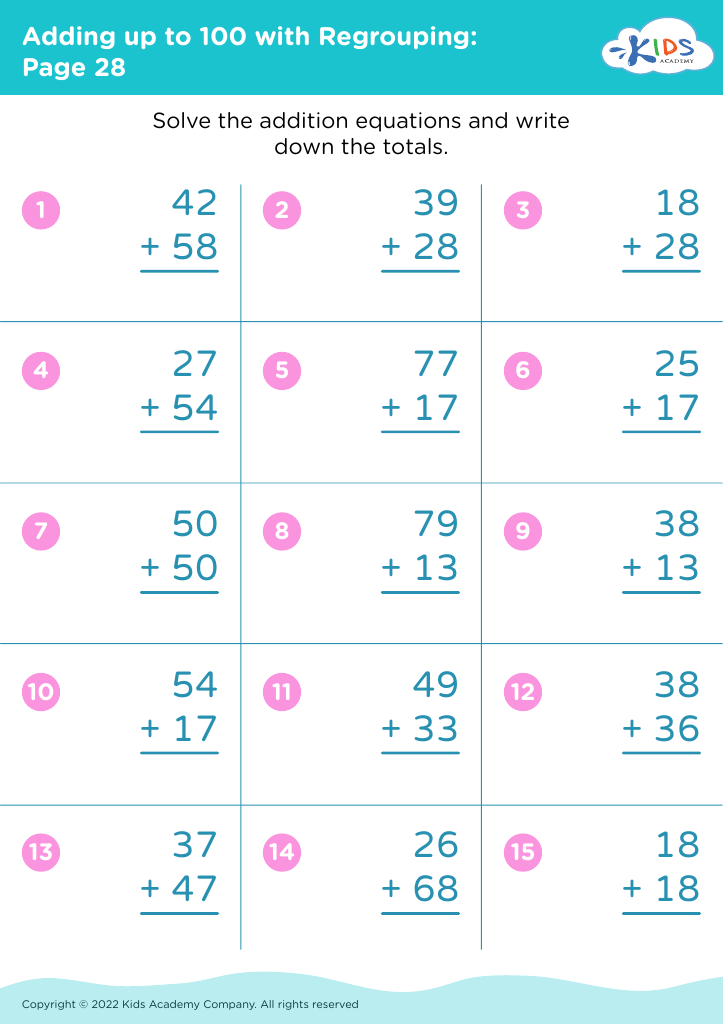



%20(1).jpg)











