Fine Motor Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 6-8 - Page 2
40 filtered results
-
From - To


Help the Bee Find 16 Flowers Worksheet


Planting Seeds for 11 Worksheet


Addition Robot Sorter Worksheet
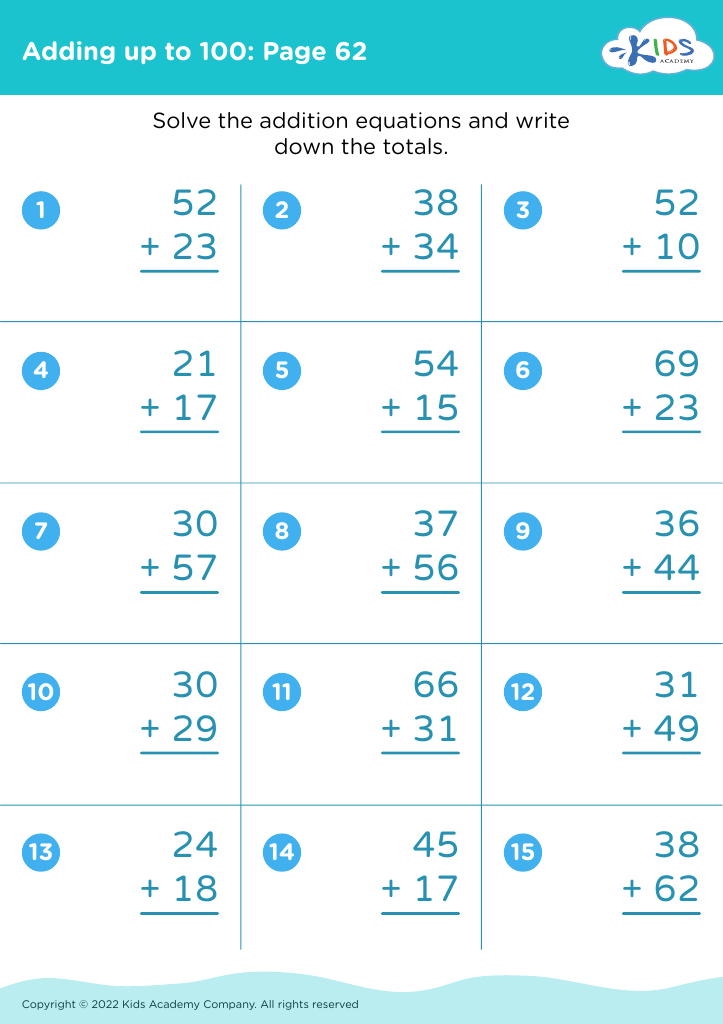
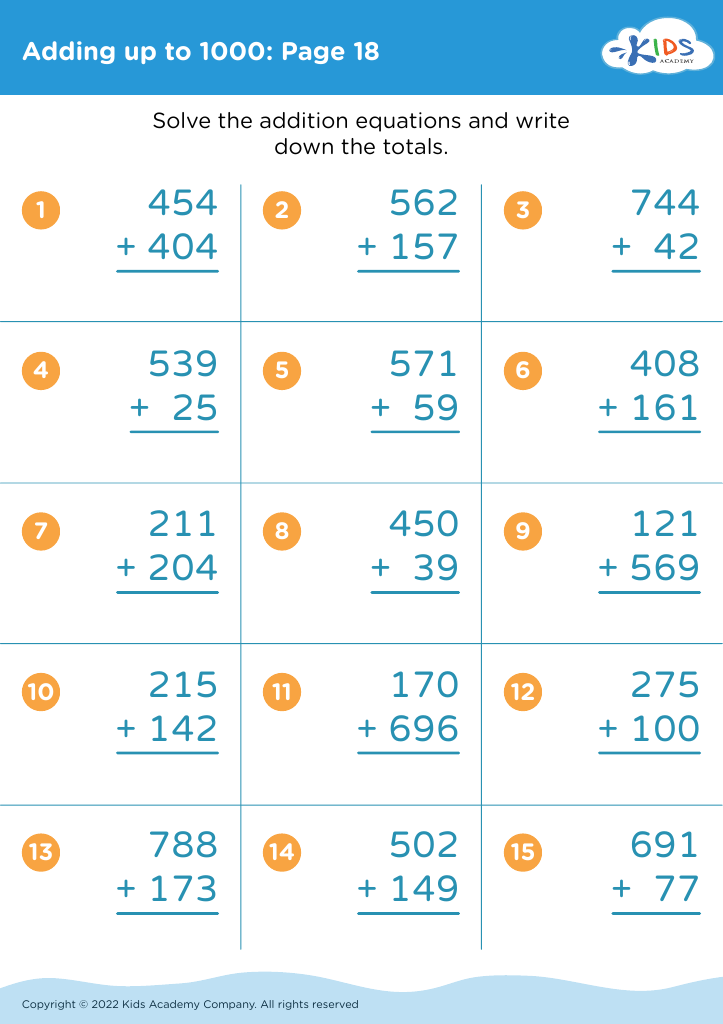
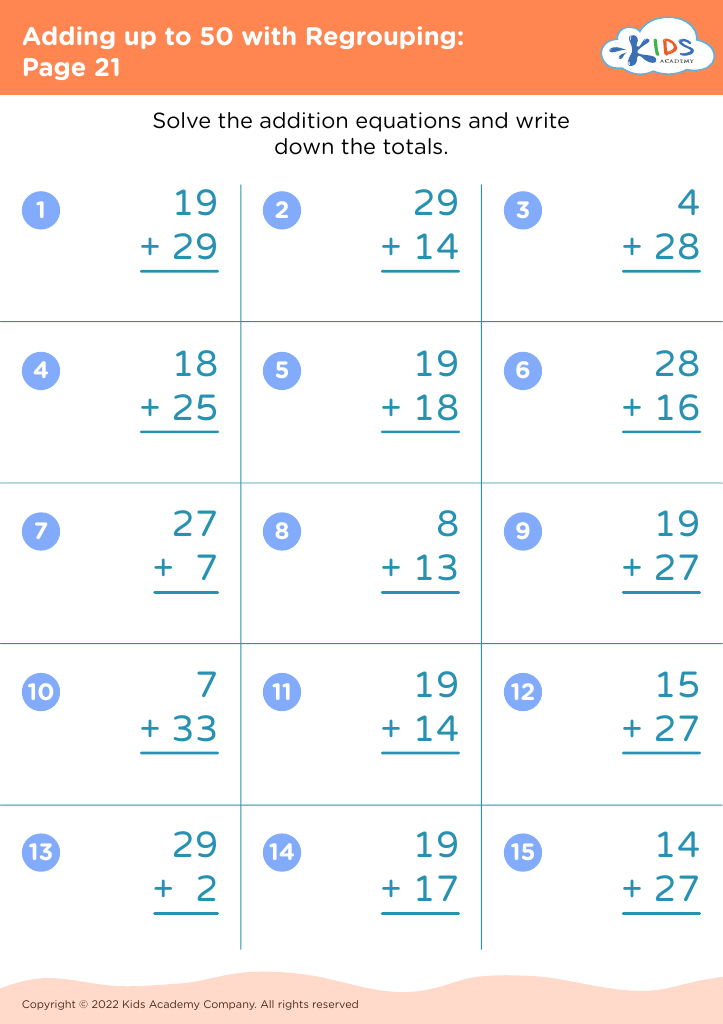
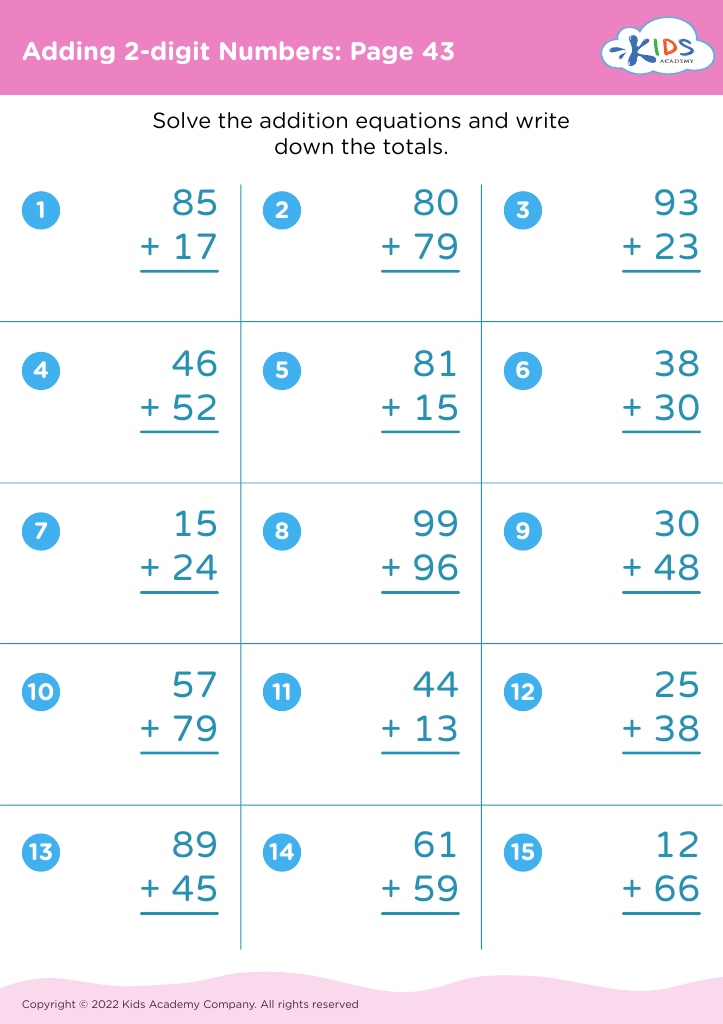
Parents and teachers should pay attention to the development of fine motor skills in children aged 6-8 because these skills are foundational for academic success and everyday tasks. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, essential for activities like writing, cutting with scissors, and manipulating small objects. At this age, children transition from simple, large movements to more precise actions, making fine motor development crucial for school-related tasks.
A strong grip and dexterity enable children to write legibly, complete puzzles, and perform detailed artwork, which are often integral parts of the curriculum. Additionally, improving fine motor skills boosts hand-eye coordination, concentration, and cognitive processing, further aiding academic performance. These skills also promote independence in personal tasks such as dressing, tying shoelaces, and feeding themselves, which contributes to a child's confidence and sense of achievement.
Early intervention in the form of activities and exercises can address any delays or difficulties, ensuring that children do not fall behind their peers. By encouraging activities like playing with building blocks, drawing, or using tweezers, adults can foster a child’s development, setting a strong foundation for future success in both school and everyday tasks.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students