Counting skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 6-9 - Page 7
146 filtered results
-
From - To


One Less: Assessment 2 Worksheet
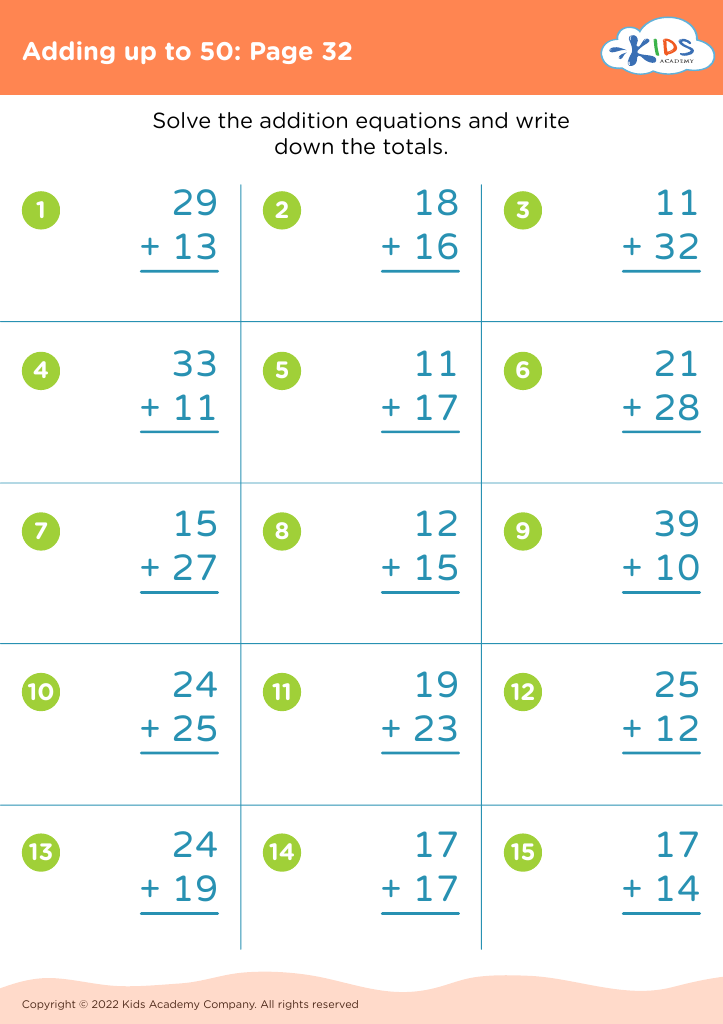
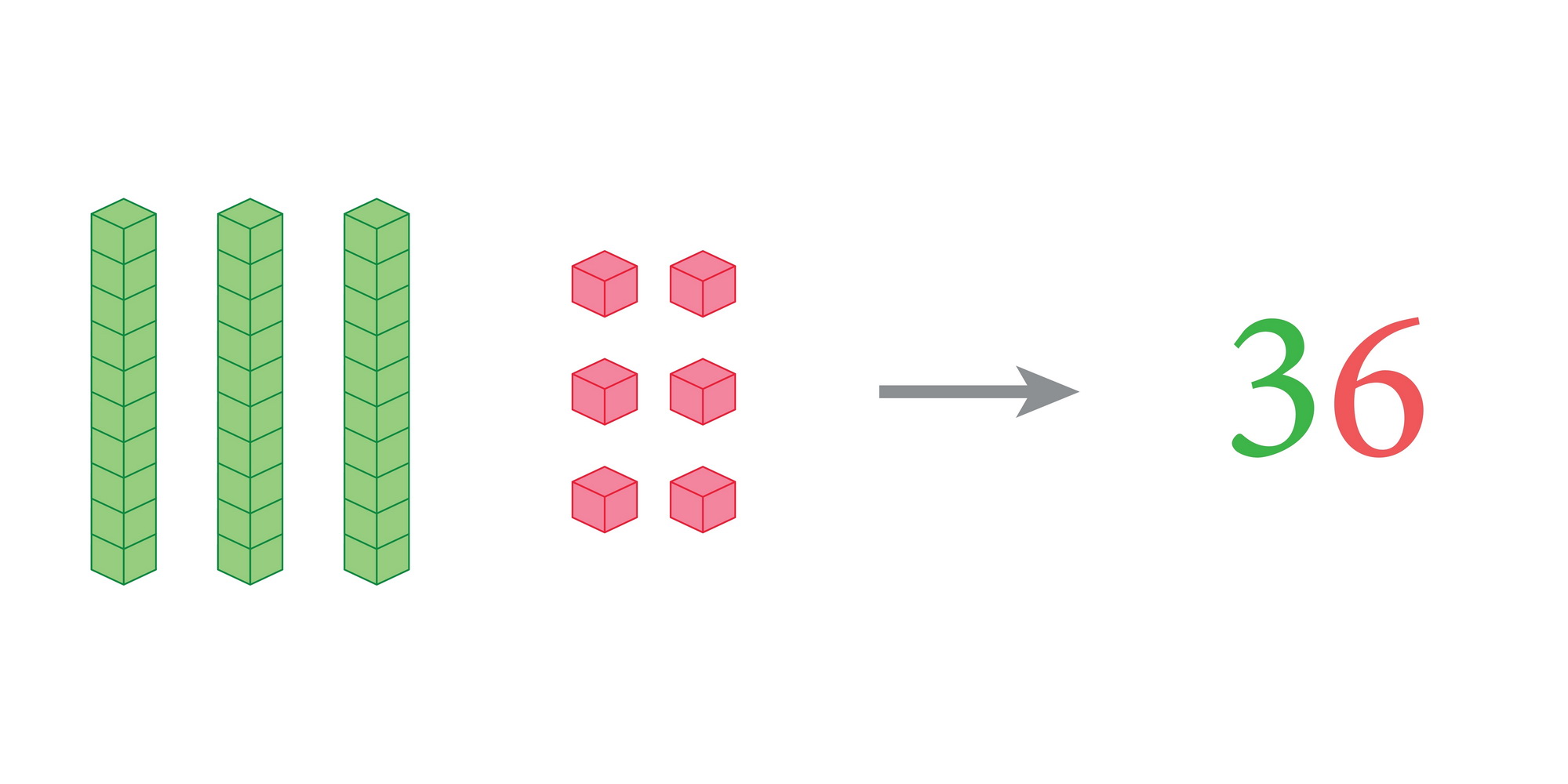
Counting skills, along with addition and subtraction, form the foundation for a child's mathematical development, making it essential for parents and teachers to prioritize these skills in children aged 6-9. At this developmental stage, children are not just learning numbers; they are also building essential problem-solving abilities and critical thinking skills.
Mastering counting leads to a better understanding of quantity, order, and relationships between numbers. When children grasp addition and subtraction, they gain confidence in their mathematical abilities, which sets a positive tone for future learning. These foundational math skills are crucial for everyday life, helping children manage simple transactions, understand time, and solve basic puzzles.
Additionally, supporting the development of these skills fosters a growth mindset. Children learn persistence through practice, enhancing their self-esteem as they conquer challenges. Engaging with counting games, story problems, and hands-on activities cultivates a love for learning, making math fun and relevant.
Ultimately, by emphasizing counting skills and basic arithmetic, parents and teachers equip children for academic success, ensuring they are proficient in the skills necessary for more complex mathematical concepts later on. This preparation not only aids their education but also promotes critical cognitive and social skills essential for overall growth.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students