Hand-eye Coordination Adding up to 100 Worksheets for Ages 7-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's math proficiency and motor skills with our "Hand-eye Coordination Adding up to 100 Worksheets for Ages 7-9." Designed to make math enjoyable, these printables blend visual and kinesthetic learning to aid in the seamless integration of interactive and educational experiences. As kids work through these engaging exercises, they'll improve their addition skills and develop critical hand-eye coordination. Perfectly tailored for young learners, these worksheets provide targeted practice that supports cognitive development while making math comprehension more intuitive. Give your child the tools to excel in both math and essential life skills through fun, hands-on activities.
Hand-eye coordination is crucial for children aged 7-9, particularly when learning to add up to 100. This skill involves the synchronization of visual input with hand movement, essential for efficient and accurate academic performance. Parents and teachers should prioritize activities enhancing this coordination because it directly impacts a child's ability to engage in tasks such as writing, drawing, and, critically, math operations.
Mathematics requires children to focus on numbers while controlling pencil movements to solve problems on paper. Poor hand-eye coordination can lead to mistakes, incorrect number formation, or slow problem-solving speeds, which may frustrate the child and hinder their learning process. Furthermore, proficiency in adding up to 100 lays a foundational understanding of number relationships and arithmetic needed for more advanced math concepts, critical in later education stages.
Additionally, fine motor skills, a subset of hand-eye coordination, support cognitive development. When children can seamlessly write or draw their calculations, they can focus more mental energy on understanding and solving the problem, fostering confidence and academic success. Therefore, engaging children in activities like sports, puzzles, or handwriting practice can significantly boost their coordination skills, creating a cascade of positive effects on their overall educational experience.
Prioritizing hand-eye coordination not only improves math capabilities but also enhances broader academic and daily skills, crucial for holistic growth and development.

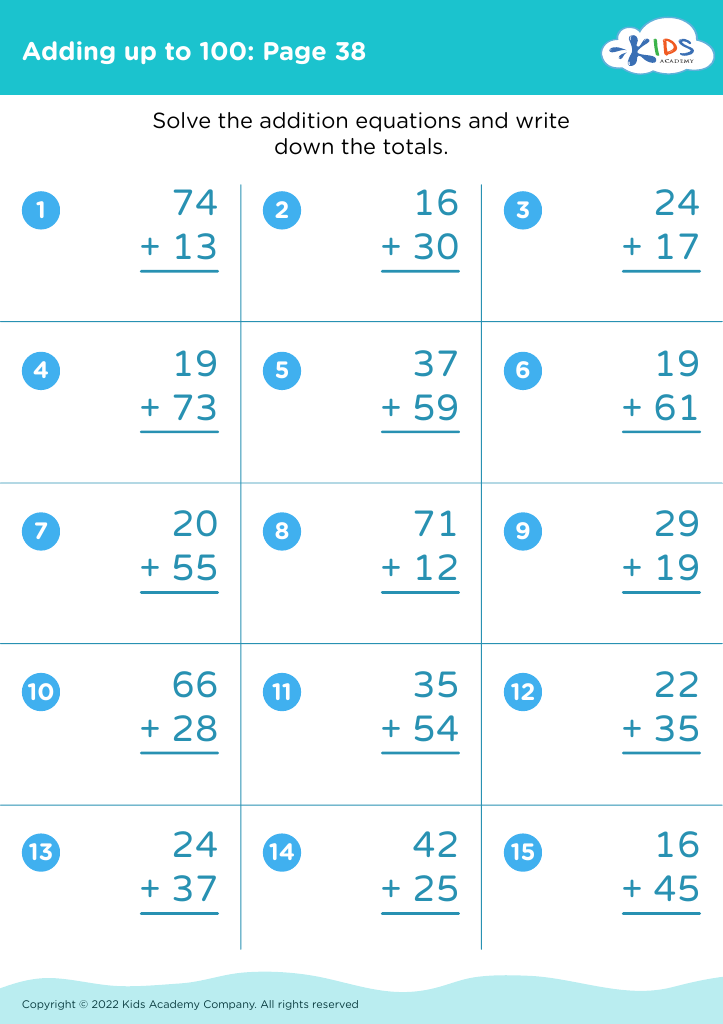
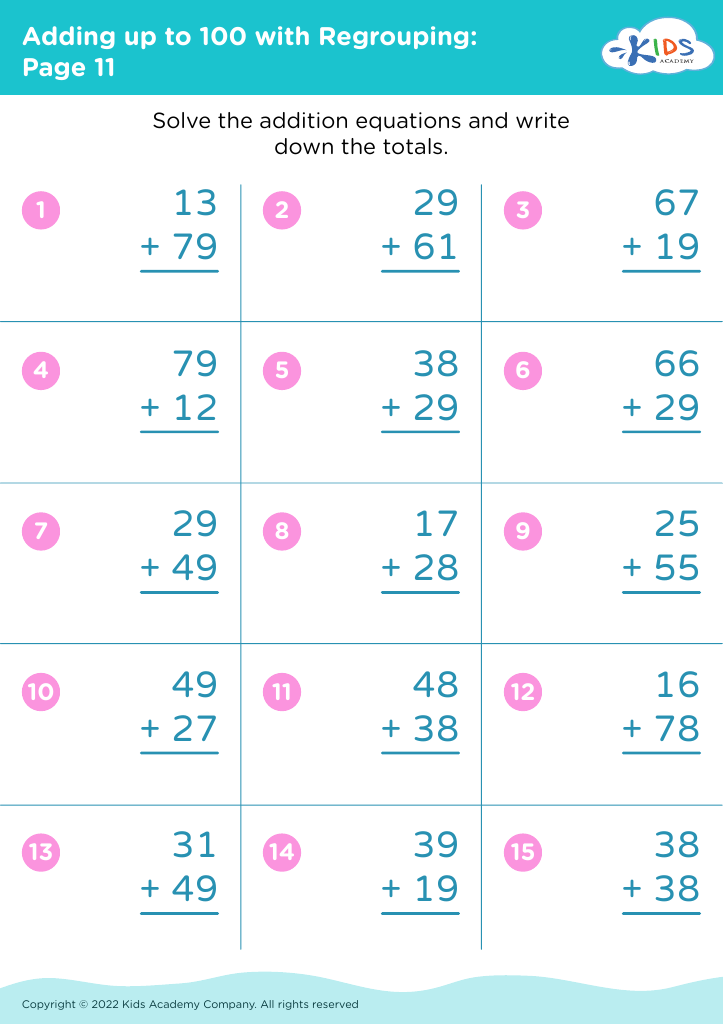
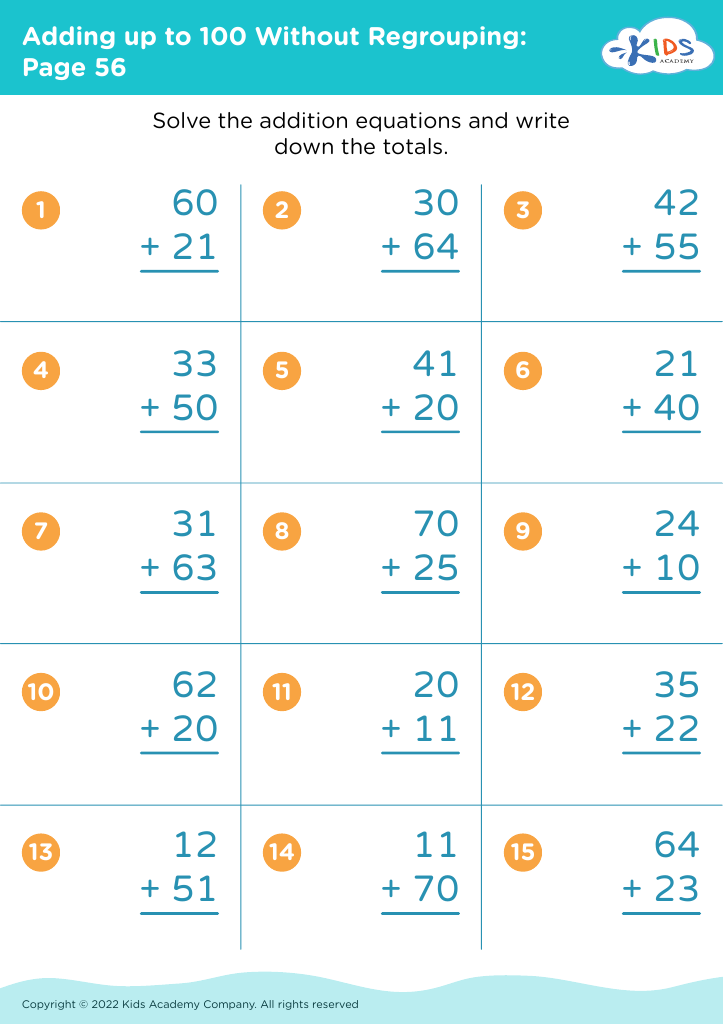




%20(1).jpg)










