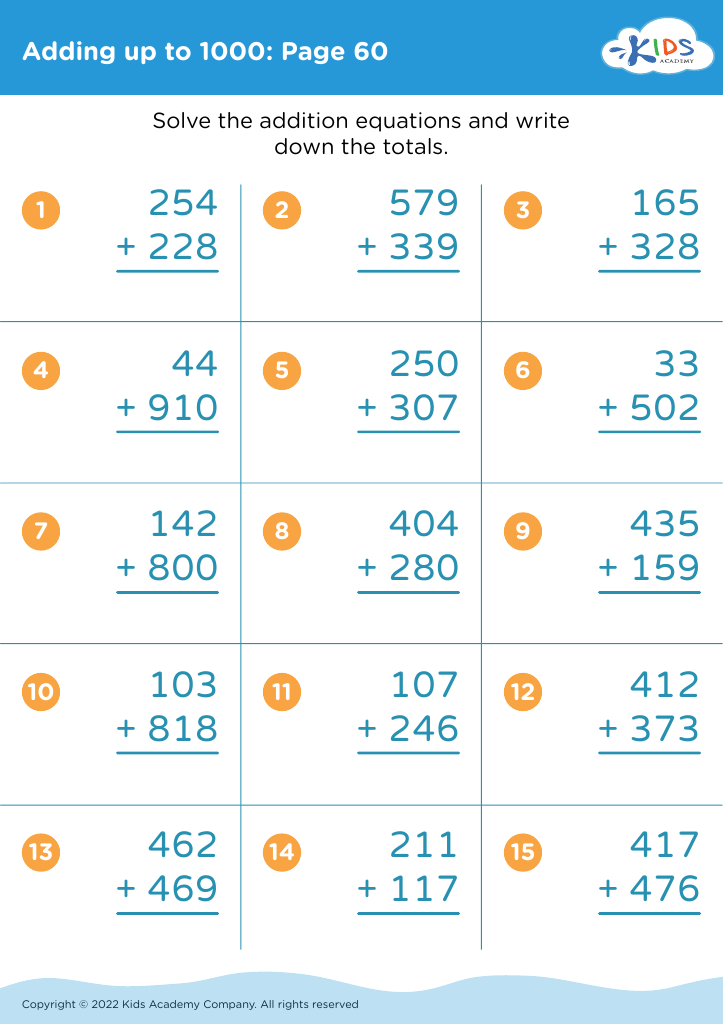
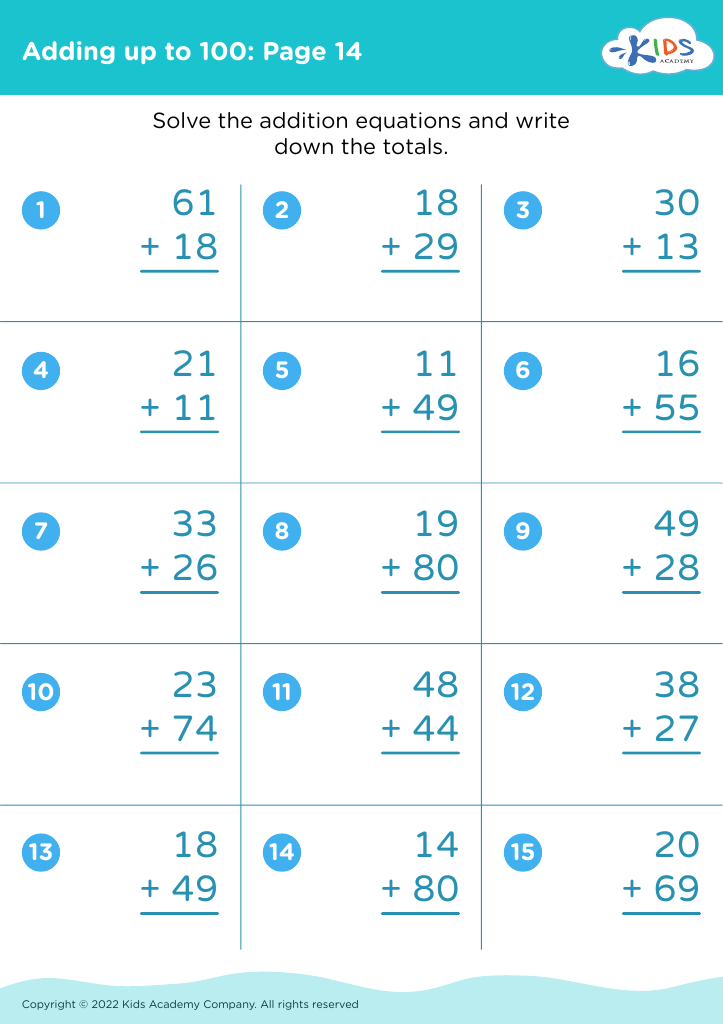
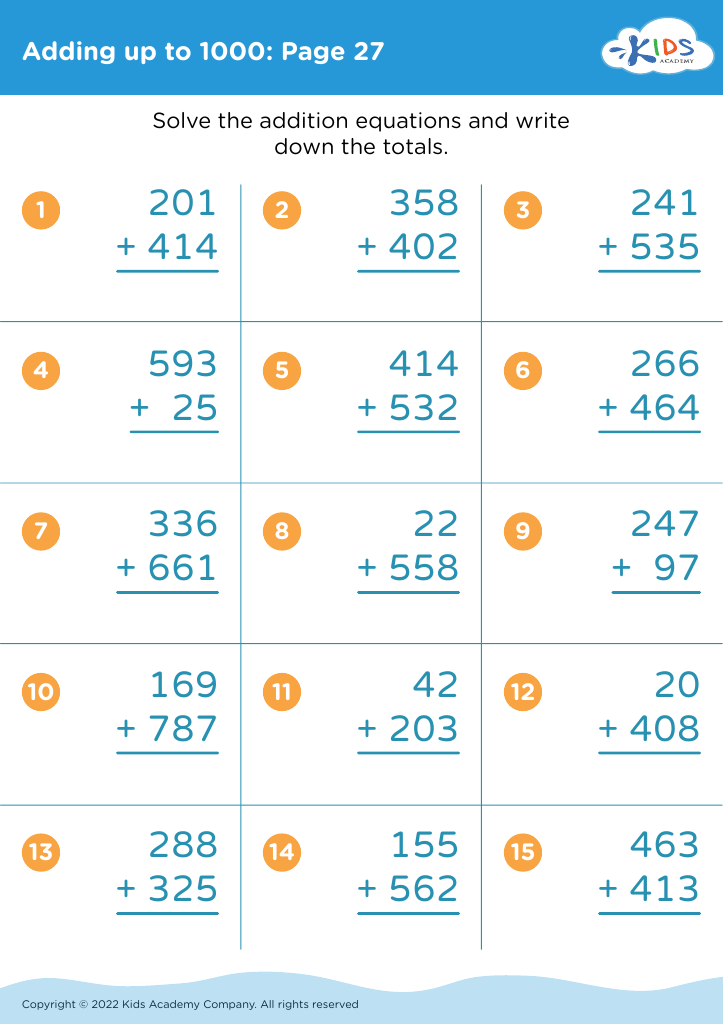
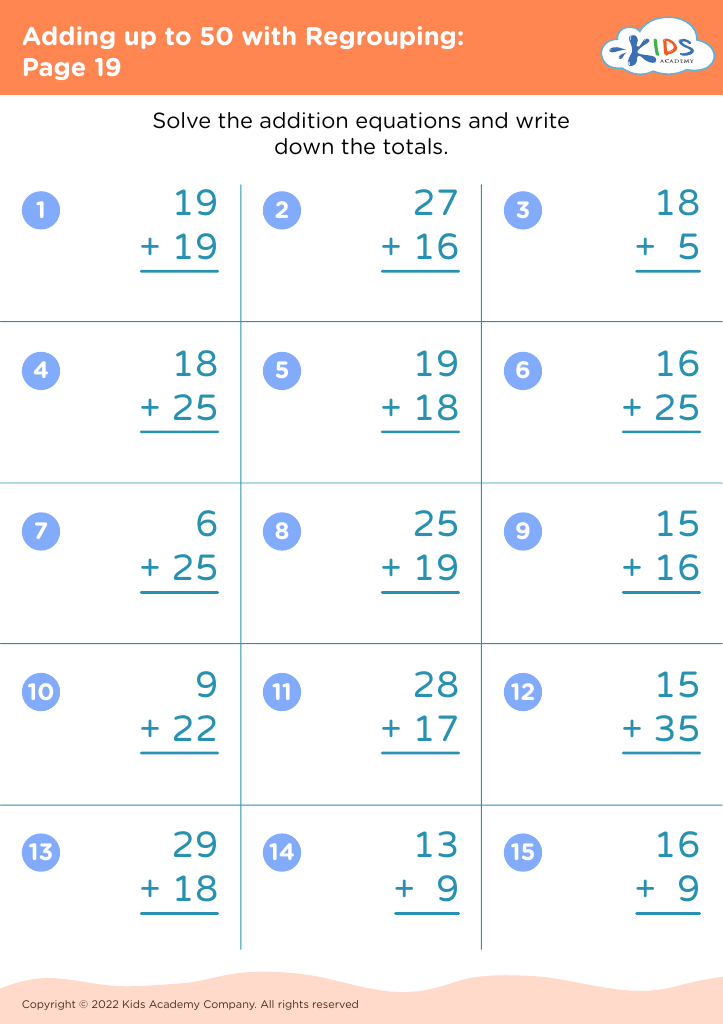
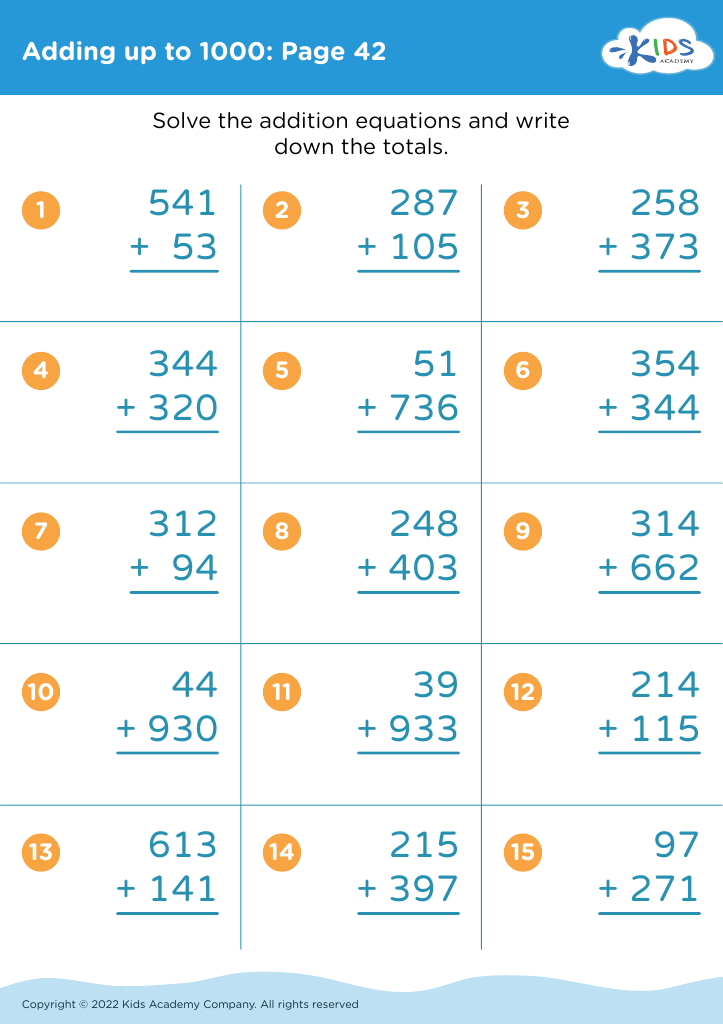
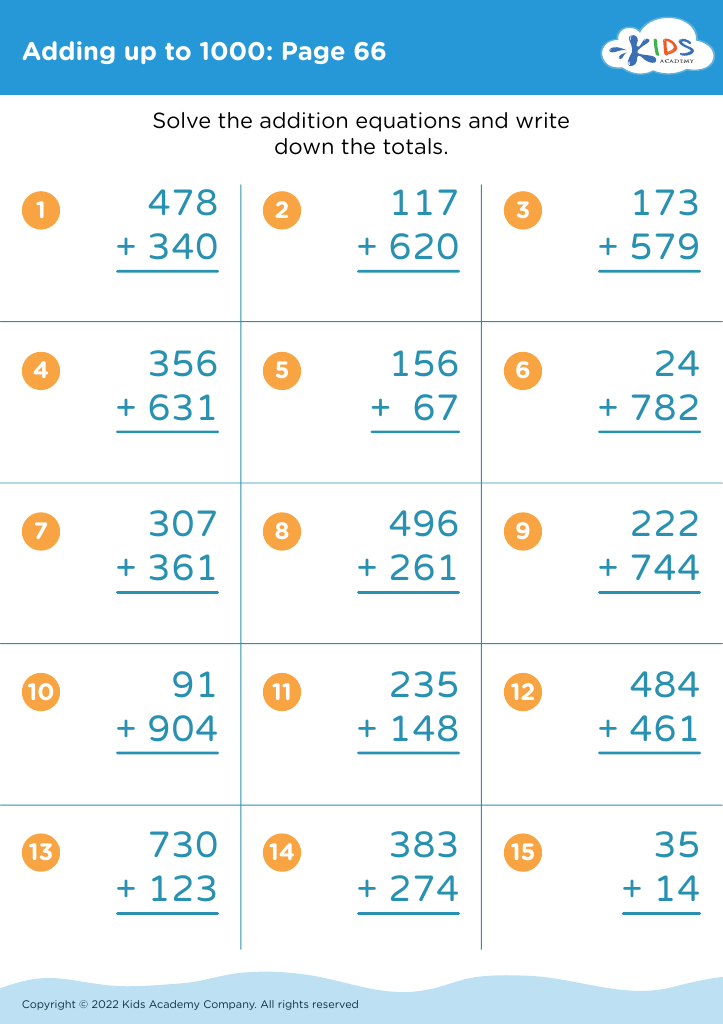
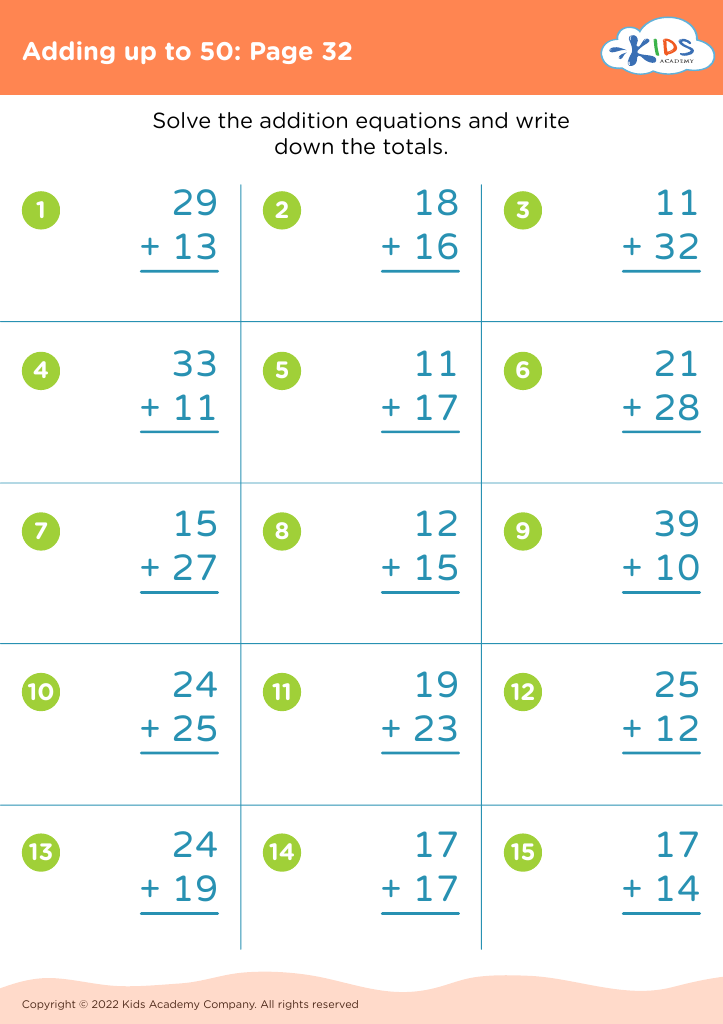
Parents and teachers should prioritize addition practice for children aged 7 to 9 as it forms a crucial foundation for later mathematical concepts. During this developmental stage, children build on basic arithmetic skills, enabling them to tackle more complex number operations. Mastery of addition enhances problem-solving abilities, fostering analytical thinking that can benefit academic performance across subjects.
Moreover, consistent addition practice cultivates confidence. As children become more proficient, they gain a sense of achievement that encourages them to approach challenges with a positive mindset. Additionally, these skills support real-life applications, such as managing money, understanding time, and making measurements, thus improving everyday decision-making abilities.
In this age group, children often learn in a social context, leveraging peer interactions to enhance their skills. Group activities centered on addition can make learning enjoyable and engaging, promoting a collaborative environment where children learn from one another. By fostering a solid understanding of addition, parents and teachers not only prepare children for future success in mathematics but also instill lifelong skills that extend beyond the classroom. Ultimately, prioritizing addition practice contributes to well-rounded cognitive development and equips children with essential tools for navigating the world around them.