Basic Math Skills Adding up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 8-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
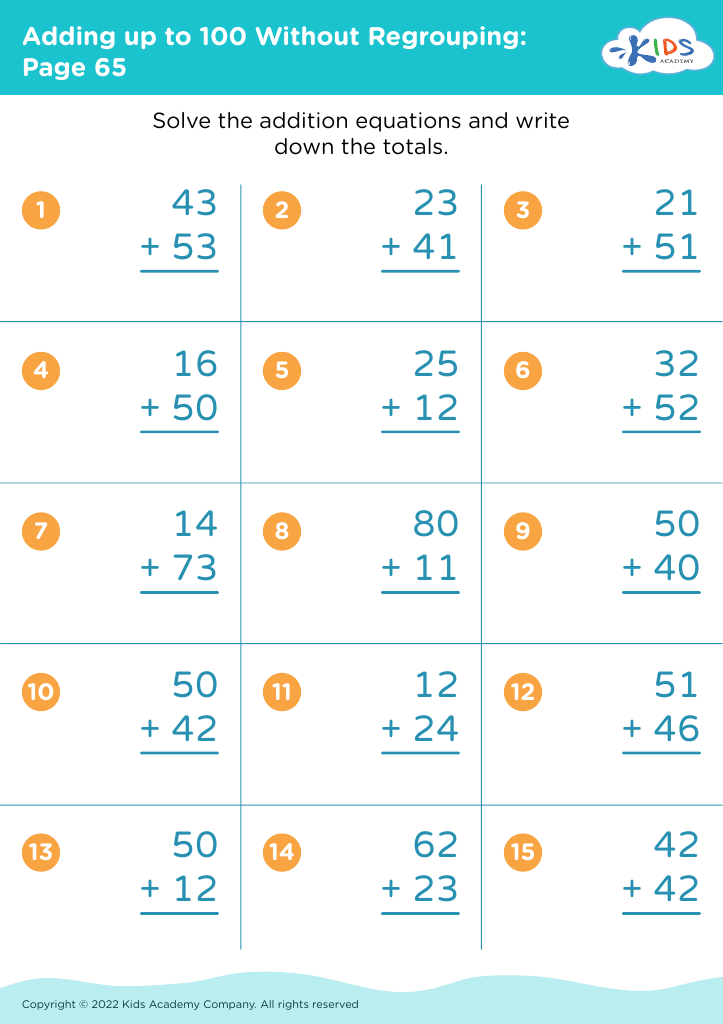
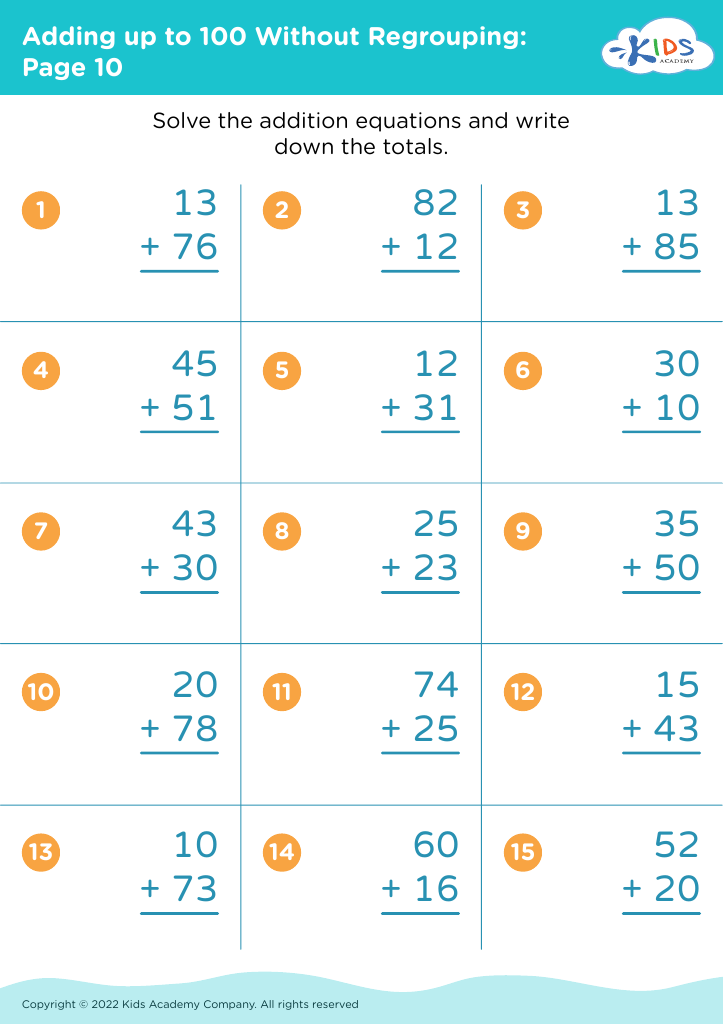
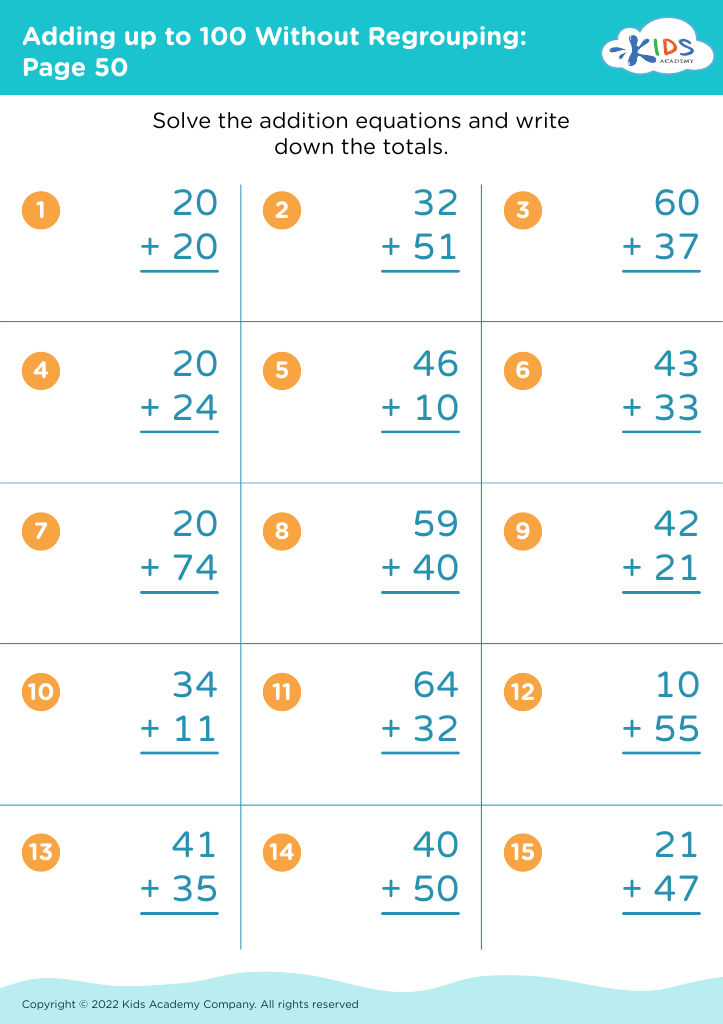
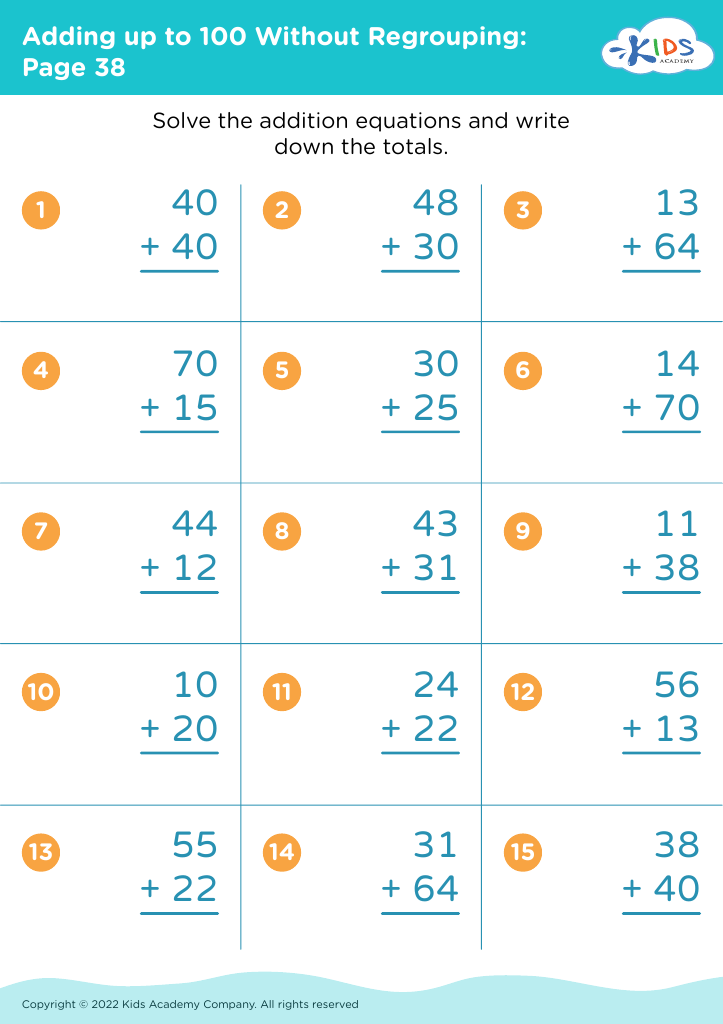
Discover our engaging "Basic Math Skills: Adding Up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets" designed specifically for children ages 8-9. These worksheets provide a friendly and supportive environment for young learners to enhance their addition skills while fostering confidence in their mathematical abilities. With a focus on adding numbers up to 100 without regrouping, each worksheet features a variety of exercises that promote practice and mastery in a fun way. Perfect for reinforcing classroom learning at home, our resources will help your child develop essential math skills that set the foundation for future success. Unlock their potential today!
Parents and teachers should prioritize basic math skills, such as adding up to 100 without regrouping, for children aged 8-9 because these foundational skills are critical for future mathematical understanding and everyday problem-solving. Mastery of addition within 100 helps solidify number sense, enables confidence in handling larger numbers, and prepares students for more complex operations, such as subtraction and multiplication.
At this age, children are transitioning from concrete to more abstract mathematical thinking. Proficiency in basic addition promotes cognitive development, fostering logical reasoning and analytical thinking. The ability to add numbers effectively without regrouping minimizes errors and encourages efficiency in calculations, helping children develop problem-solving strategies that will serve them throughout their education.
Moreover, strong math skills are linked to academic success in other subjects. Familiarity with numbers and operations enhances comprehension in science and economics and even builds skills critical for daily activities, such as budgeting and shopping.
Finally, fostering these skills can boost students' confidence, as mastery often leads to enjoyment in learning. Encouraging practice in a supportive environment nurtures positive attitudes towards mathematics that can last a lifetime, making it essential for parents and teachers to invest in their development.