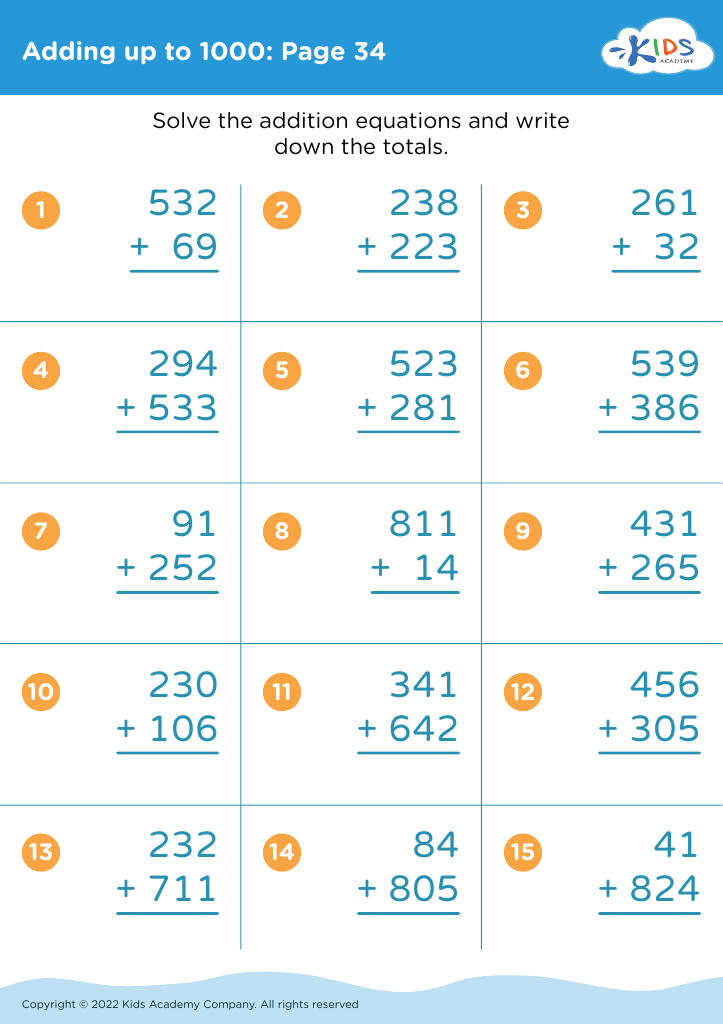
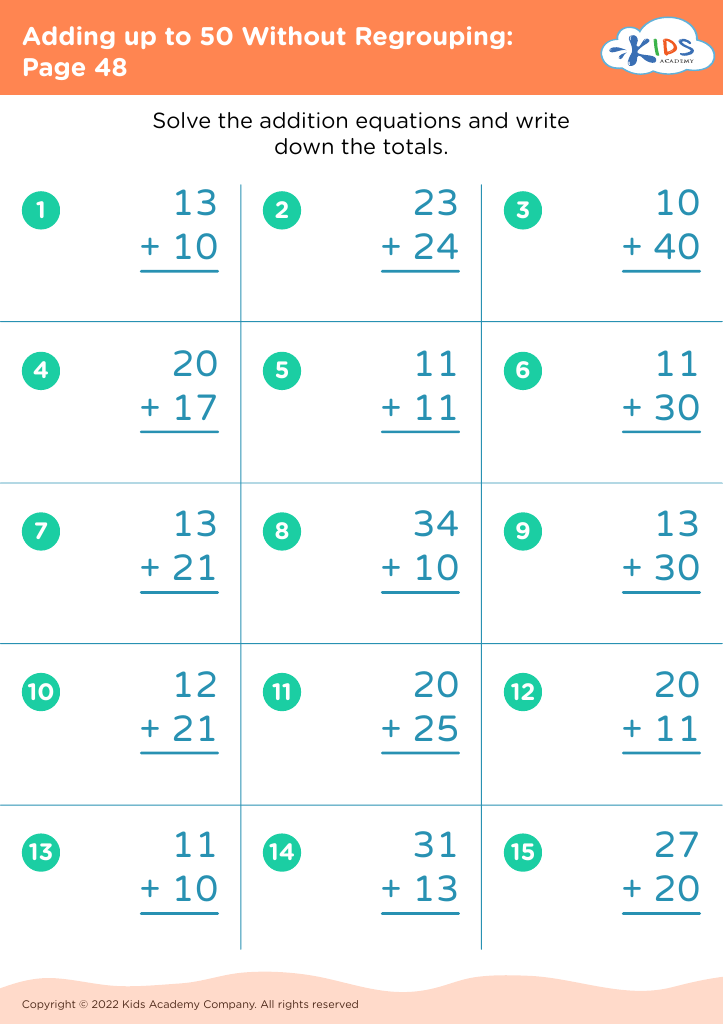
Fine motor skills (writing) Addition Worksheets for Ages 8-9
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills while mastering addition with our engaging worksheets designed for ages 8-9. Our printable activities seamlessly blend writing practice with math, helping to strengthen hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Each worksheet features fun, age-appropriate addition problems that encourage children to develop confident handwriting alongside their mathematical abilities. Perfect for supplemental learning at home or in the classroom, our resources support not just numerical understanding but also the necessary skill of writing neatly. Explore these creative worksheets today to make learning enjoyable and effective, paving the way for academic success in math and beyond!
Fine motor skills, especially related to writing, are crucial for children aged 8-9 as they significantly influence academic success and daily living. At this age, children are refining their ability to hold pencils, control their movements, and express thoughts in written form. Strong fine motor skills enhance handwriting legibility, which is essential for completing assignments and participating in classroom activities.
Moreover, developing fine motor skills directly correlates with cognitive development. As children practice writing, they strengthen their hand-eye coordination and dexterity, which are vital for tasks beyond academics, such as typing, arts and crafts, or even self-care routines. Improved fine motor skills can also boost their confidence during assessments and encourage a sense of achievement when they can articulate their thoughts clearly.
Additionally, nurturing these skills helps foster discipline, patience, and persistence as children engage in repetitive but rewarding tasks. For parents and teachers, focusing on fine motor development through fun exercises or activities not only supports intellectual growth but also prepares children for future academic challenges, ultimately forming a foundation for lifelong learning and success. Thus, fine motor skills are not just about writing; they shape a child’s ability to navigate the world confidently.