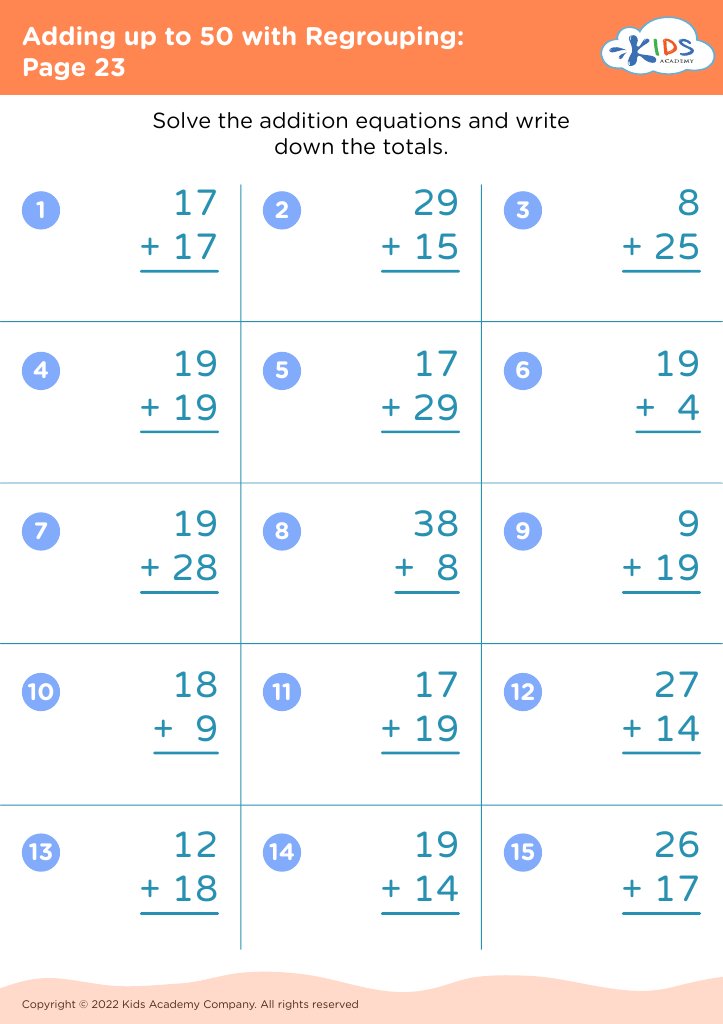
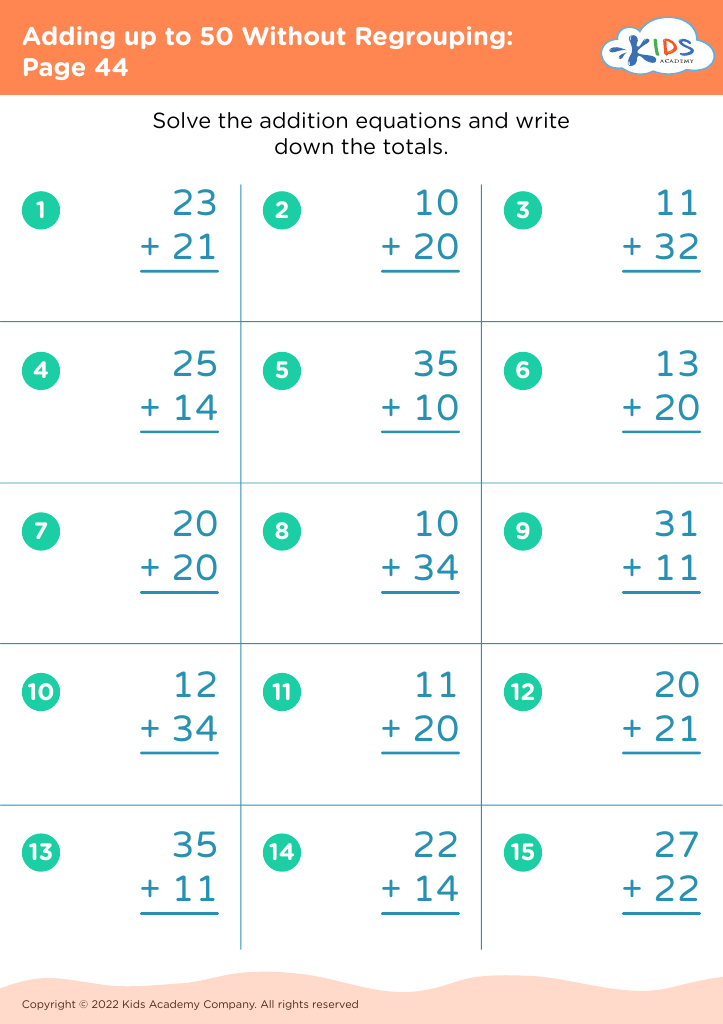
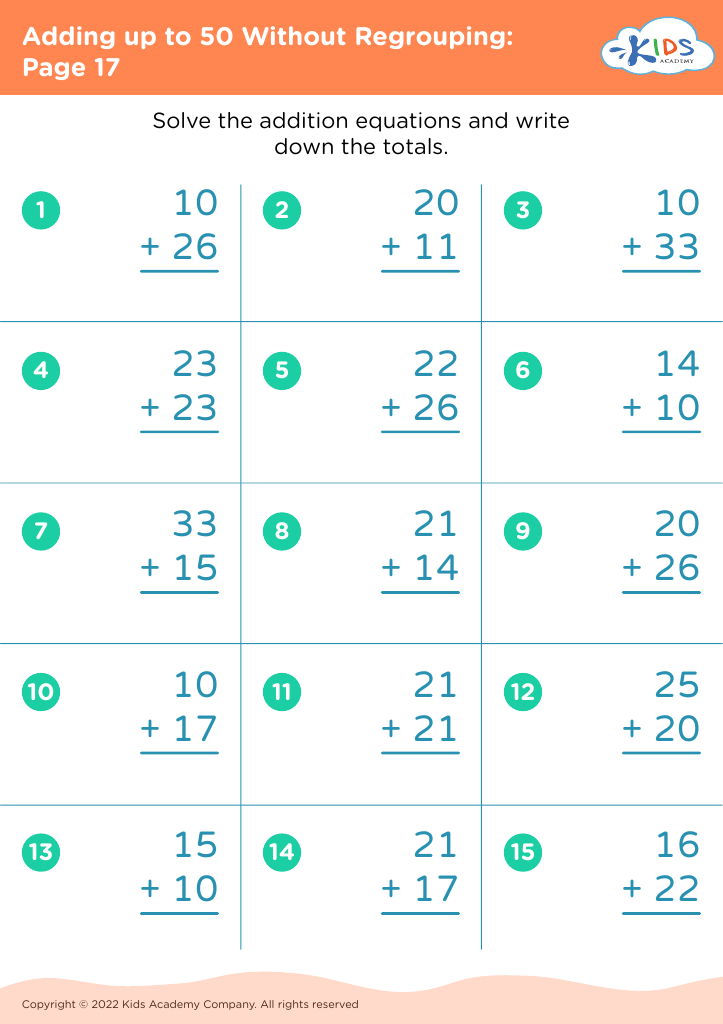
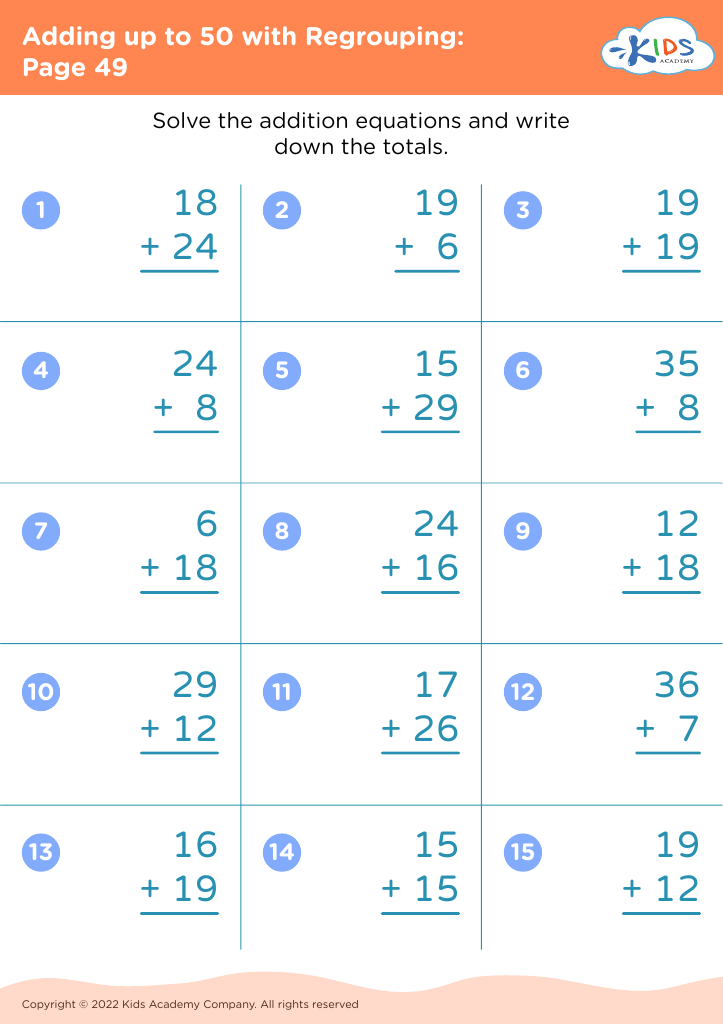
Develop fine motor skills Adding up to 50 Worksheets for 8-Year-Olds
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills while mastering addition with our engaging "Adding Up to 50" worksheets designed for 8-year-olds. This collection of 50 fun and interactive worksheets encourages young learners to practice their math skills while refining their hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Through tracing numbers, coloring activities, and thoughtful exercises, children will not only gain confidence in addition but also foster essential fine motor skills crucial for their development. Perfect for home or classroom use, these worksheets offer an exciting way to make learning math enjoyable and interactive. Unlock your child's potential today with our comprehensive and entertaining resources!
Developing fine motor skills is crucial for 8-year-olds as these skills lay the groundwork for various everyday tasks, academic success, and overall development. As children engage in activities that require precise hand movements—such as writing, drawing, or using scissors—they enhance their coordination and dexterity. This age marks an essential time for refining these skills, as children are beginning to tackle more complex tasks, both in school and at home.
Fine motor development is strongly linked to larger cognitive abilities. Improved coordination can boost a child's confidence, encouraging them to express themselves through art and writing, which are significant parts of the curriculum. Furthermore, as children start to perform simple calculations like adding numbers up to 50, a strong foundation in fine motor skills becomes essential for efficiently using tools like pencils, calculators, or manipulatives.
Parents and teachers should focus on providing opportunities for practice—like crafting, puzzles, or cooking—ensuring children can successfully engage in activities that build both fine motor skills and mathematical understanding. The intersection of these skills not only supports academic achievement but also promotes independence and a sense of accomplishment in children, contributing to their emotional well-being and fostering a love for learning.