Counting skills Addition Worksheets for 8-Year-Olds - Page 2
104 filtered results
-
From - To


Counting Birds Worksheet
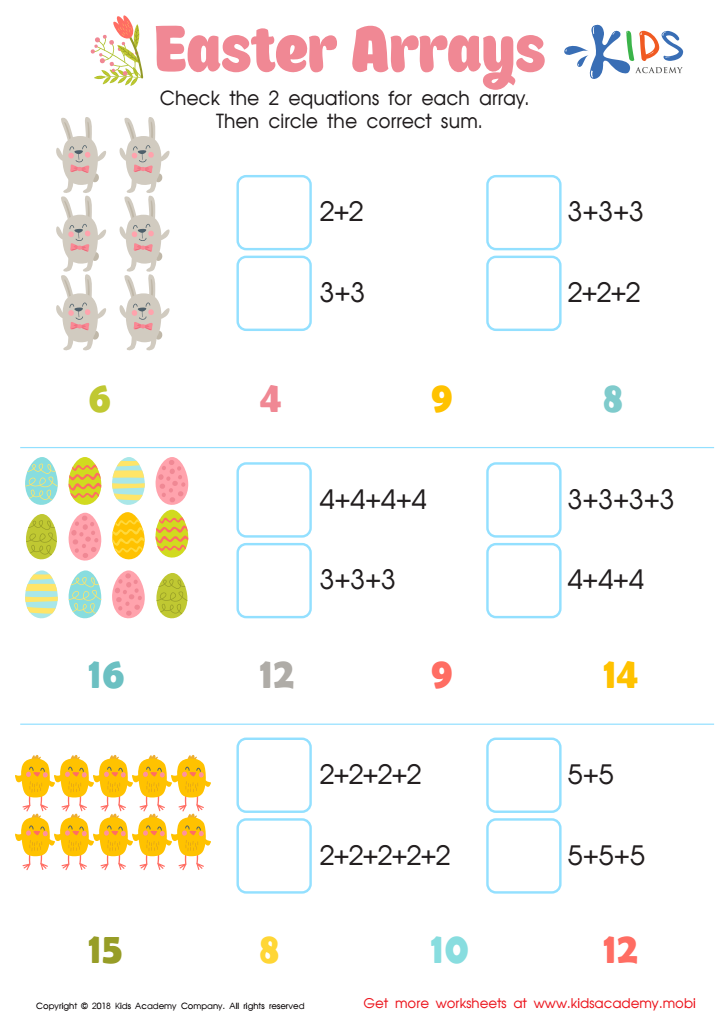

Easter Arrays Worksheet


Adding Flower Petals Worksheet
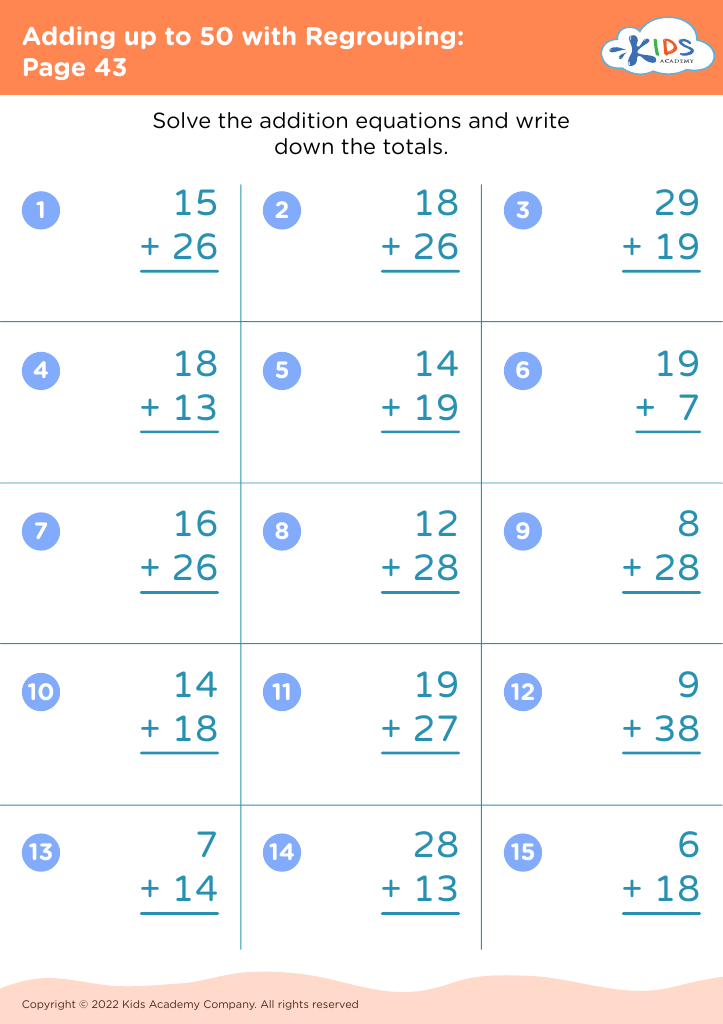
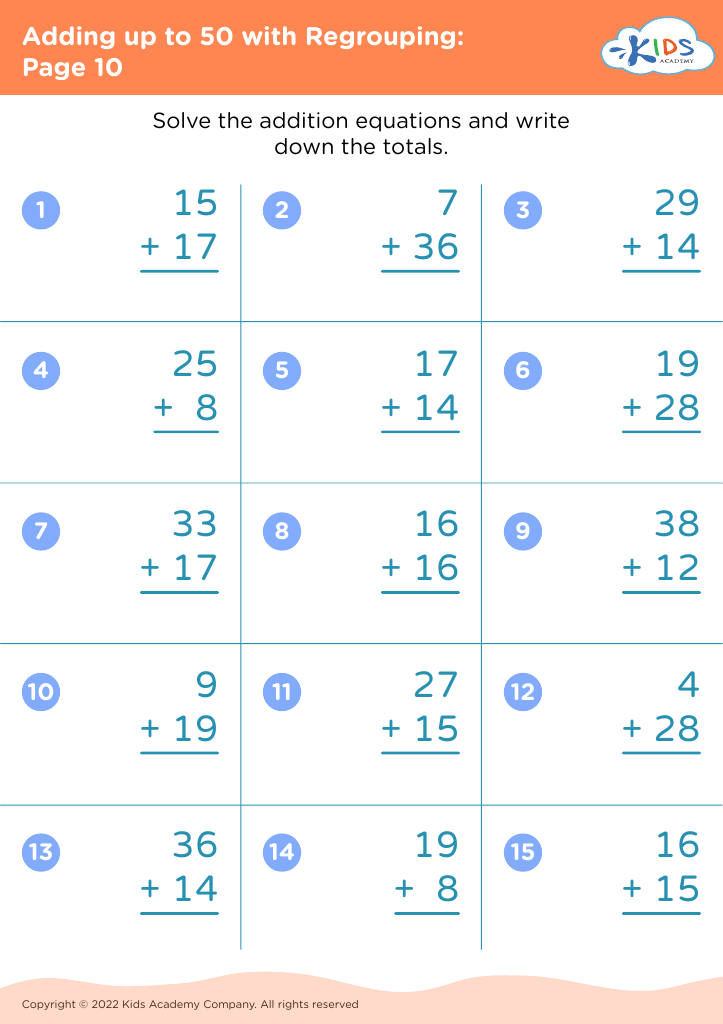
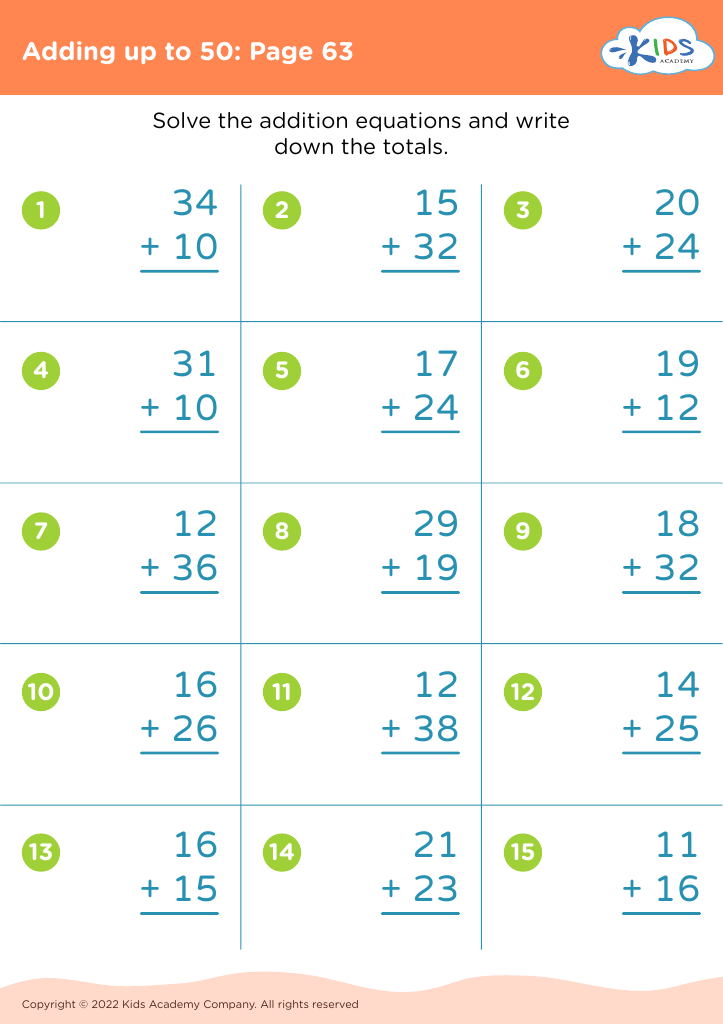
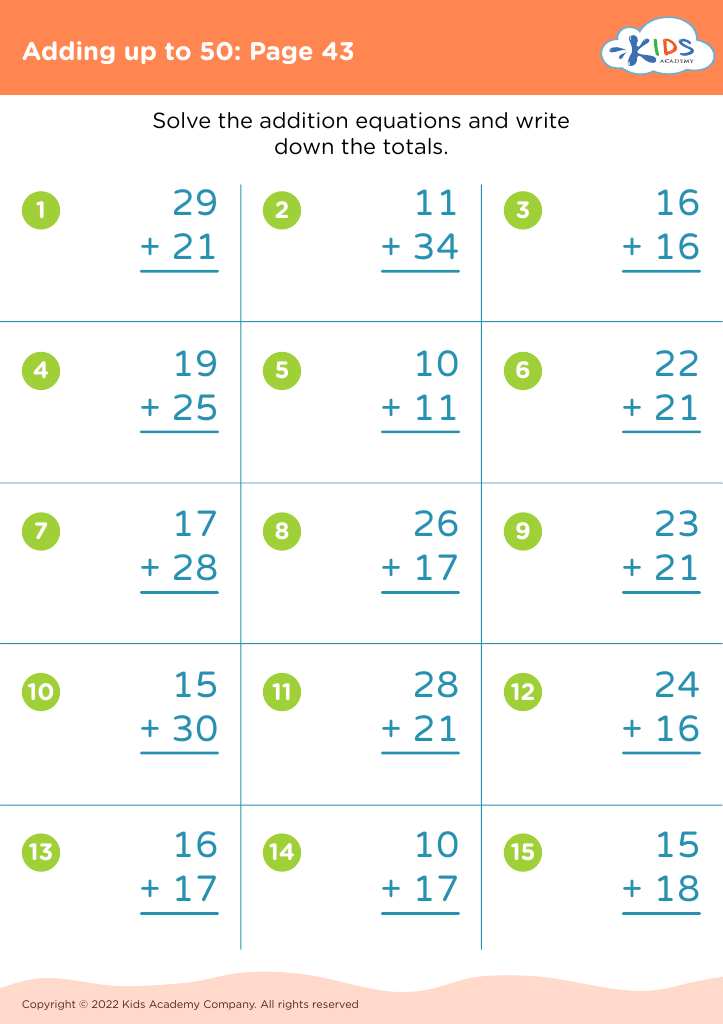
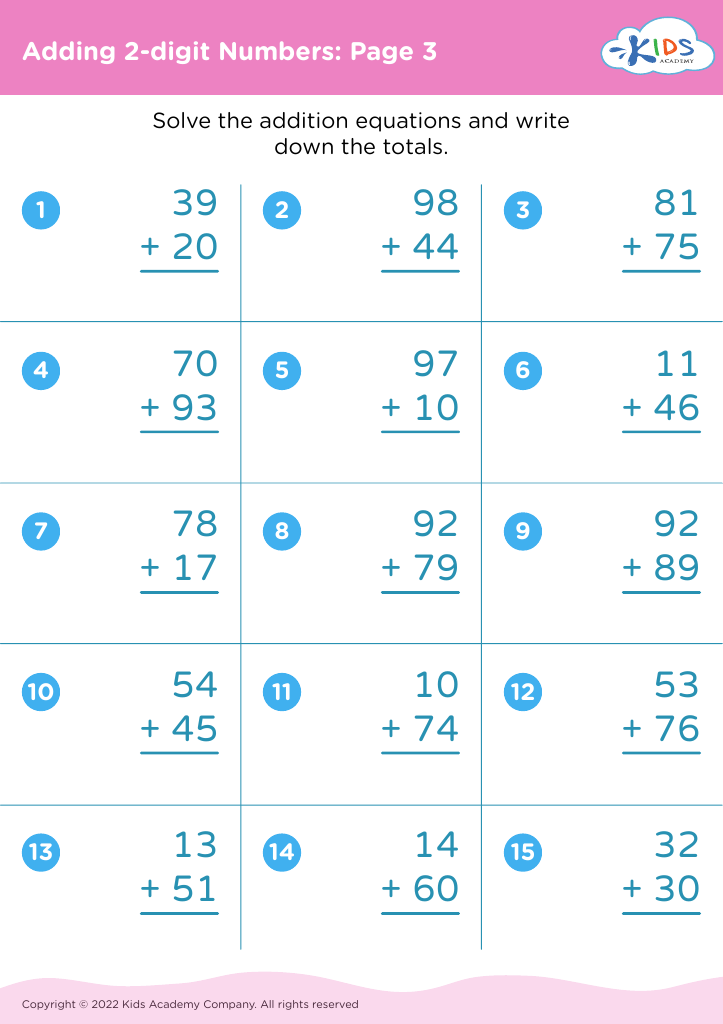
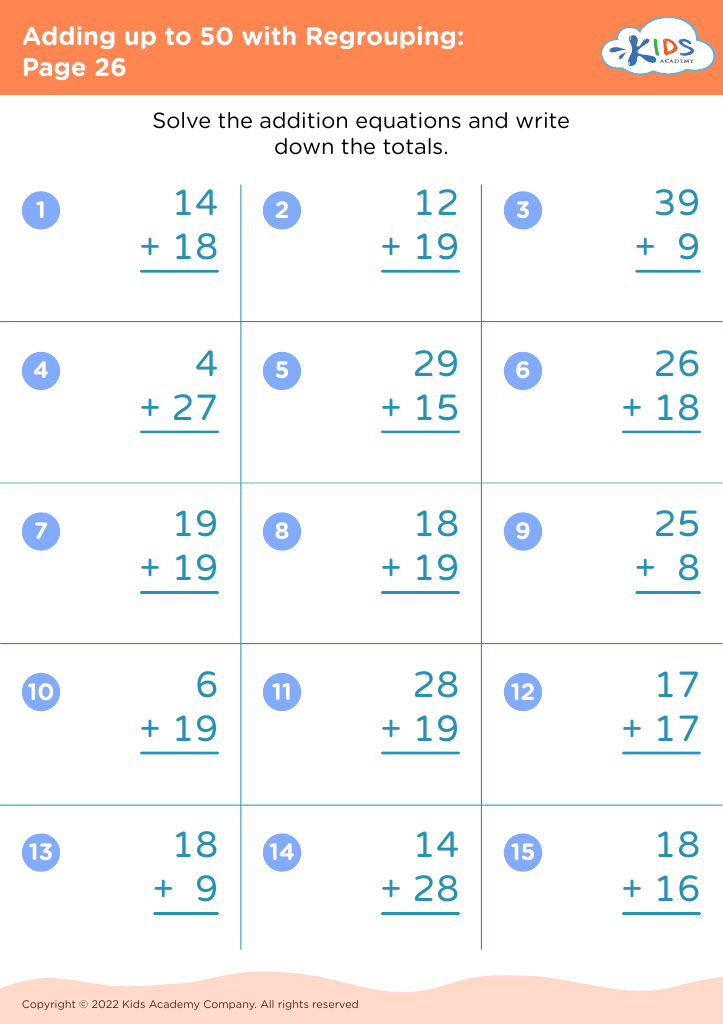
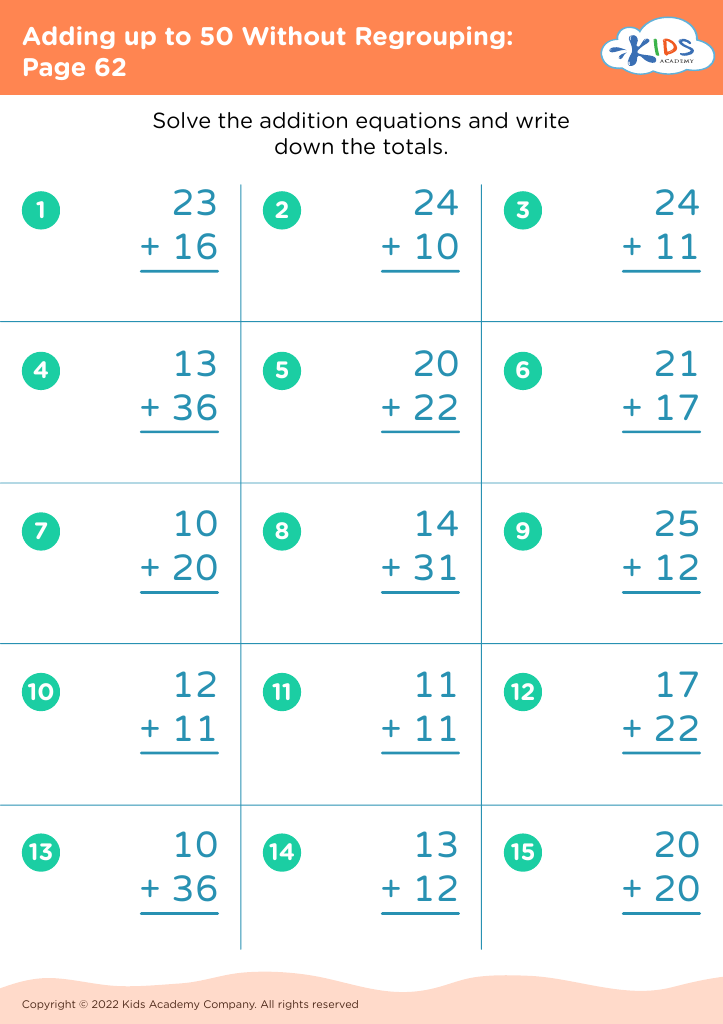
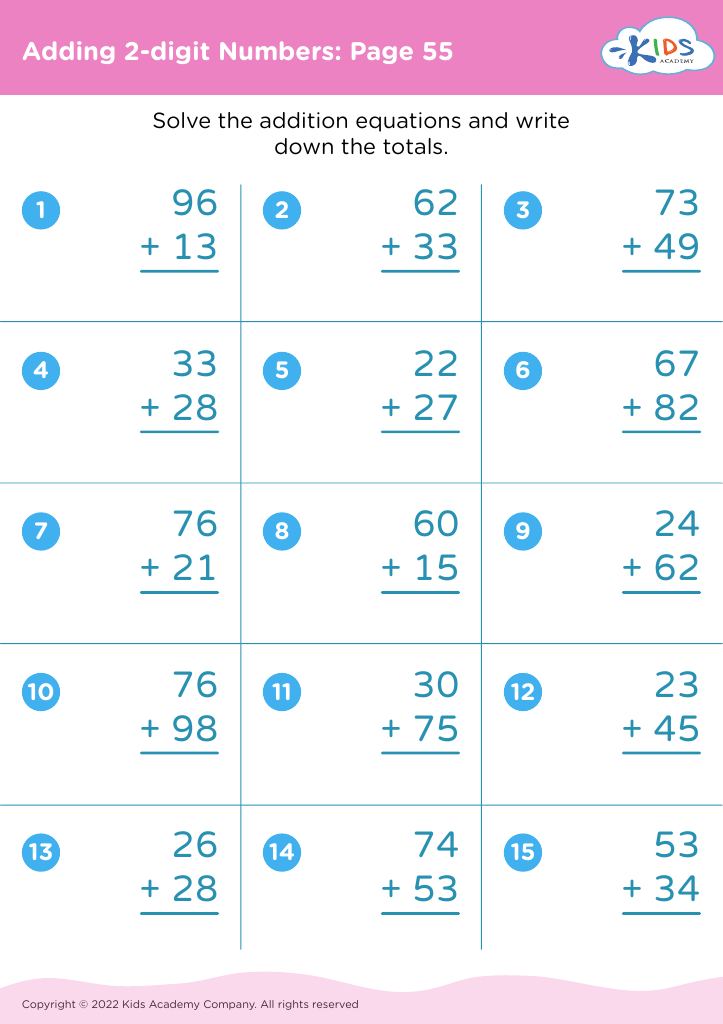
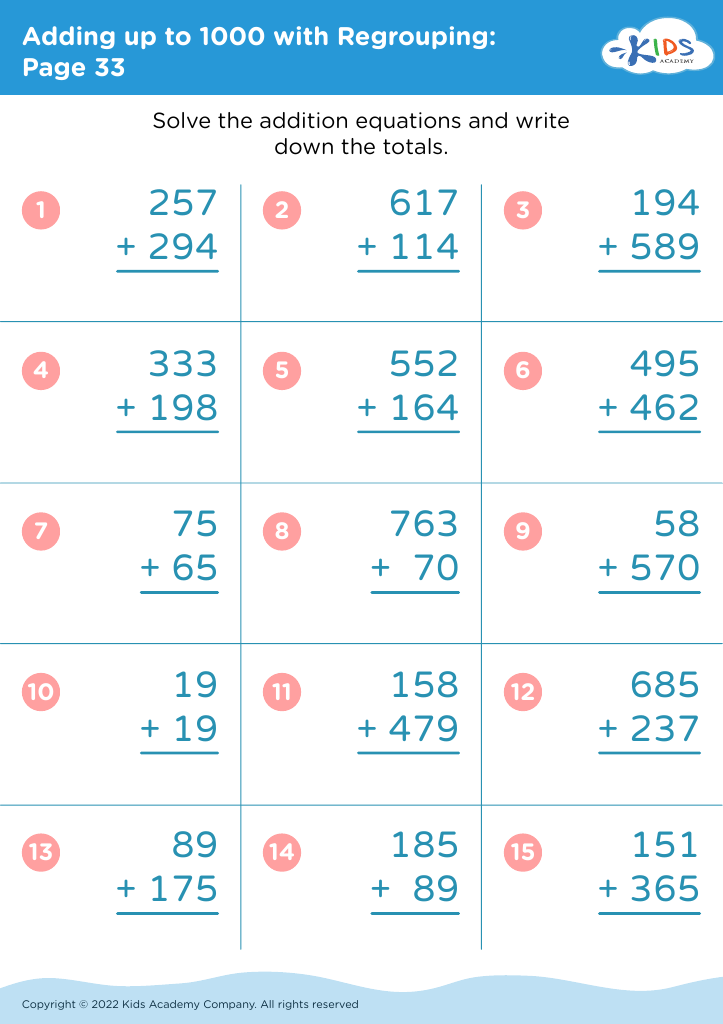
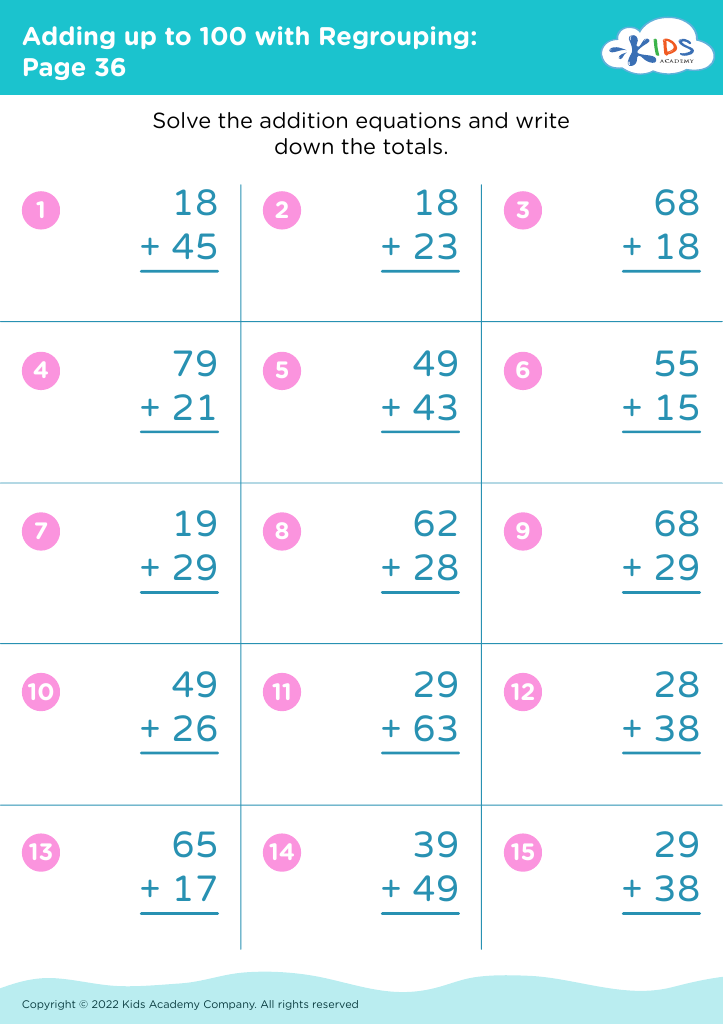
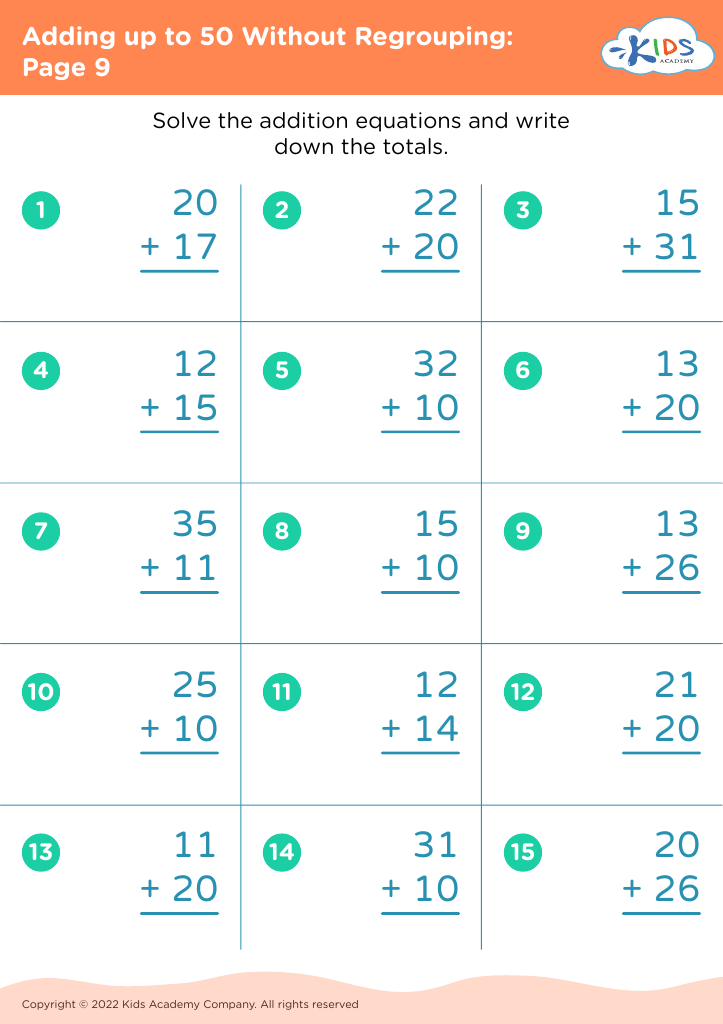
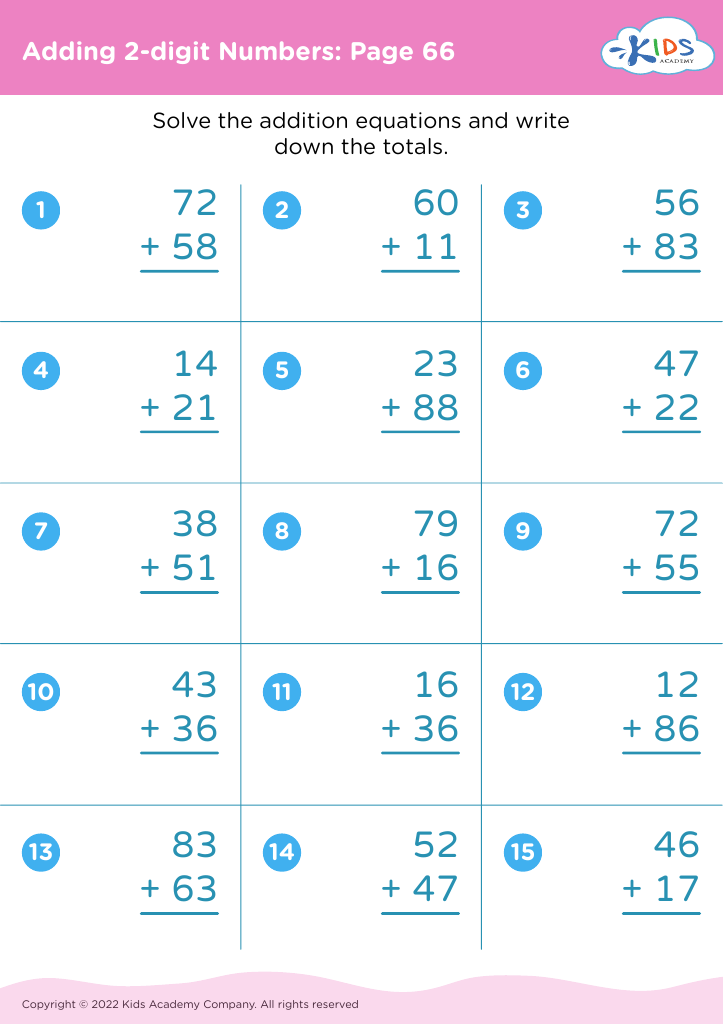
Counting skills and addition are fundamental components of a child's early mathematical education, particularly for 8-year-olds. At this age, children are typically in the 2nd or 3rd grade and are expected to achieve fluency in basic arithmetic, which supports more advanced mathematical concepts later on.
First, confidence and proficiency in counting and addition form the bedrock for other mathematical operations such as subtraction, multiplication, and division. Mastery in these areas allows children to approach more complex problems with ease, encouraging a smoother academic journey in mathematics.
Second, these skills build critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. When children practice counting and addition, they develop logical thinking and pattern recognition. These cognitive skills extend beyond math, aiding in overall intellectual development and the capability to tackle various academic and everyday challenges.
Additionally, early success in math enhances self-confidence. Struggling with basic math operations can lead to frustration and anxiety, negatively impacting a child's overall attitude toward learning. Ensuring that children are proficient in counting and addition fosters a positive relationship with mathematics, promoting a lifelong appreciation and curiosity for the subject.
In essence, focusing on these skills at the age of eight is crucial. It lays down a solid educational foundation, cultivates important cognitive abilities, and nurtures a positive attitude toward future learning endeavors. This holistic benefit underscores the importance for parents and teachers to prioritize these basic, yet essential, mathematical skills.

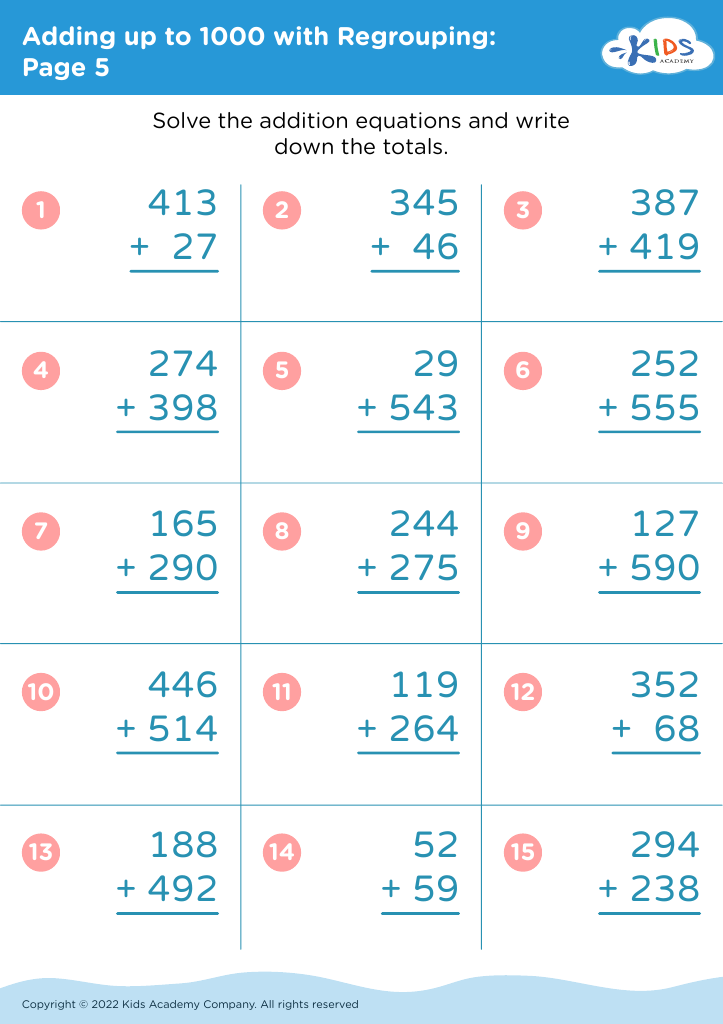
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students