Fine Motor Skills Easy Math Worksheets for Ages 4-8 - Page 2
44 filtered results
-
From - To

Eight Geese Worksheet


Number 8 Printable


Planting Seeds for 11 Worksheet


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet


Let's Pick Fruit Worksheet

Cutting in Halves Worksheet


Build with 9 Worksheet

Drawing Ovals And Triangles with Fun Printable
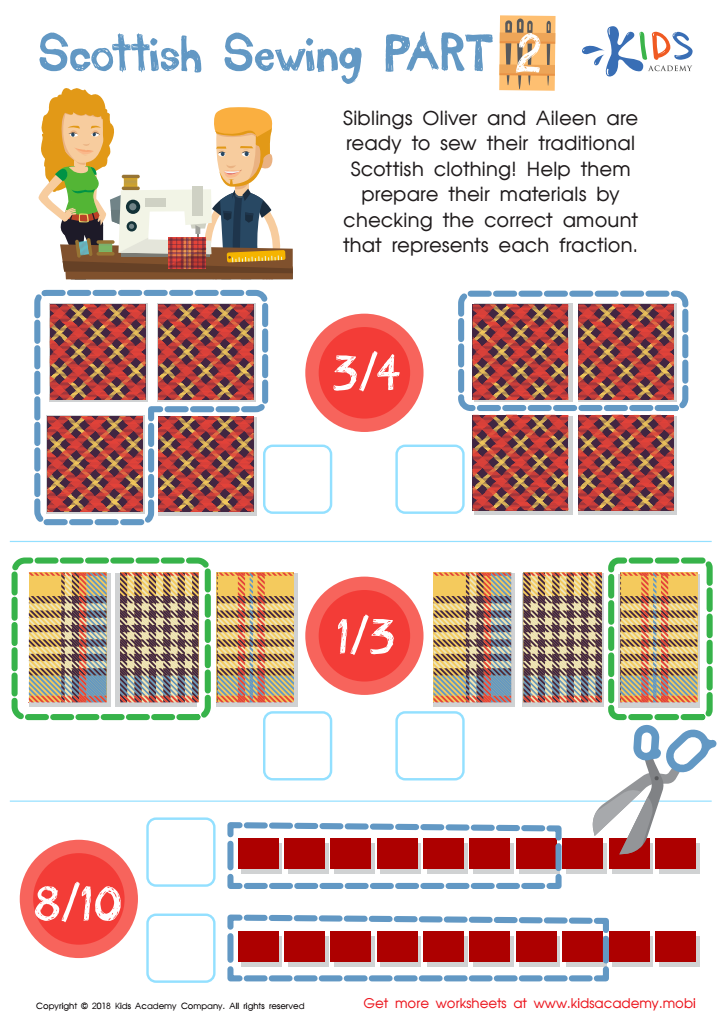

Scottish Sewing Part 2 Worksheet


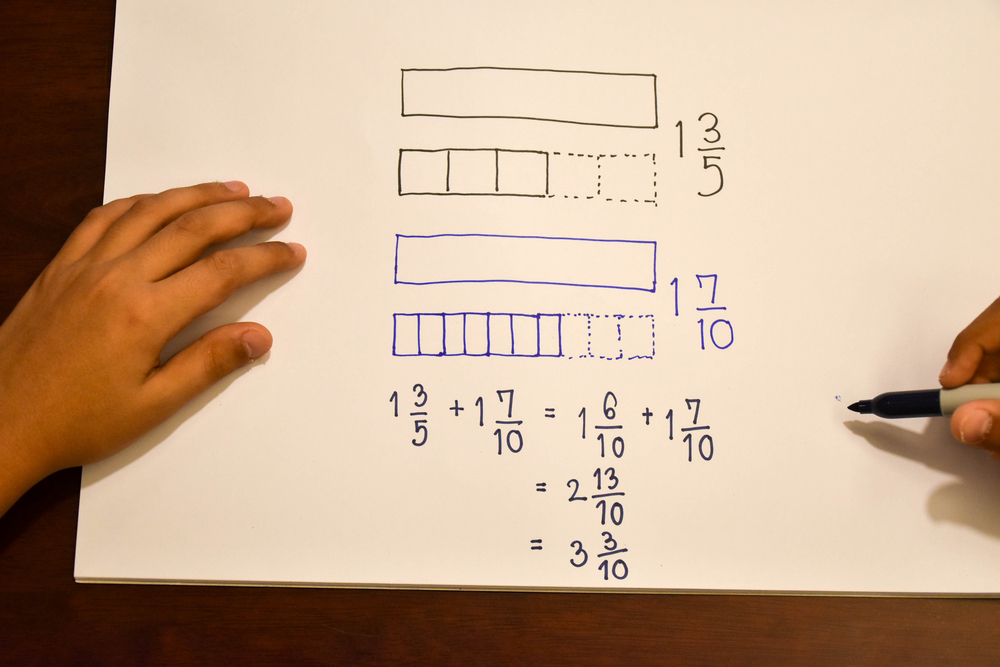
Patchwork Math Worksheet


Adding in the Arctic Worksheet
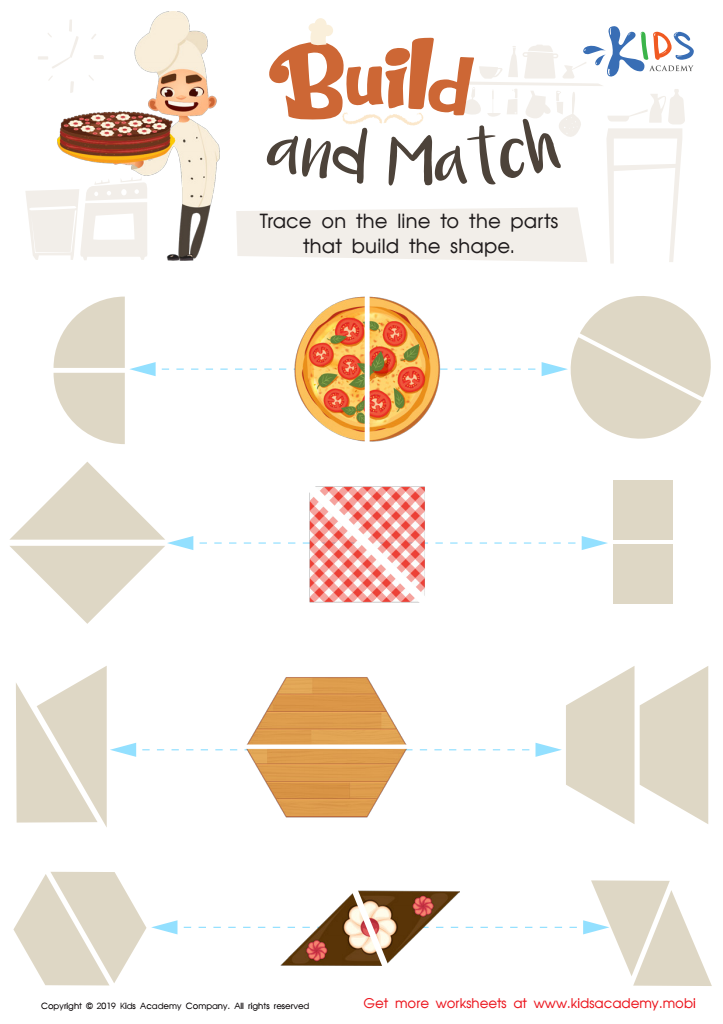

Build and Match Worksheet
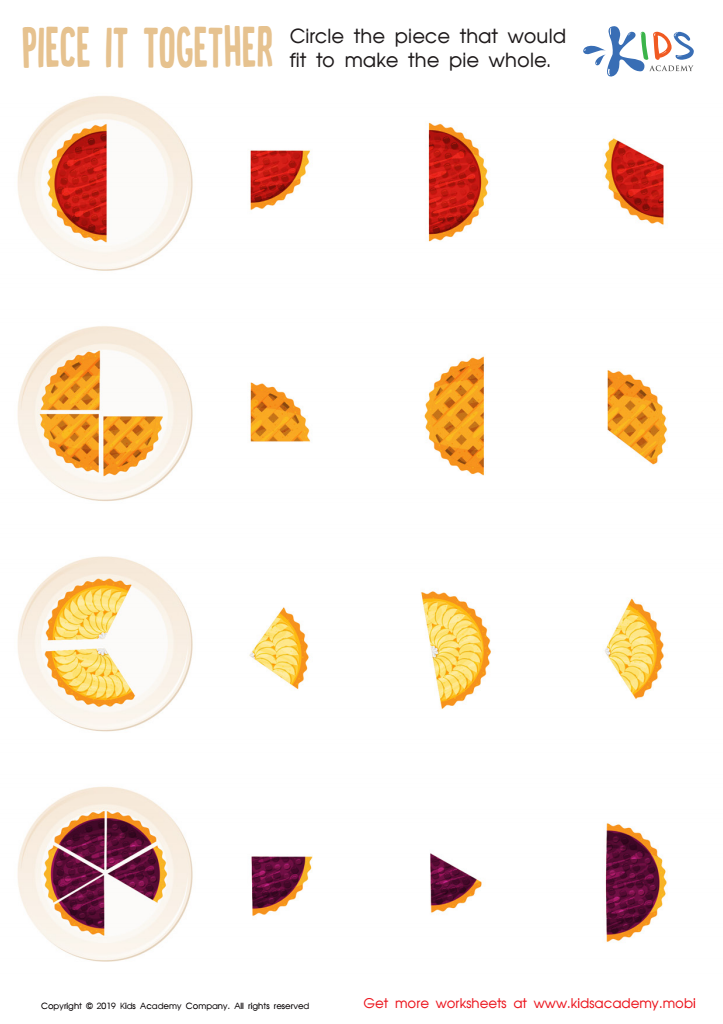


Piece it together Worksheet


Ordering 11–20: Dot–to–dot Seashell Printable


Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet


Counting on the City Skyline: Dot-to-Dot Worksheet


Counting Big City Buildings Worksheet
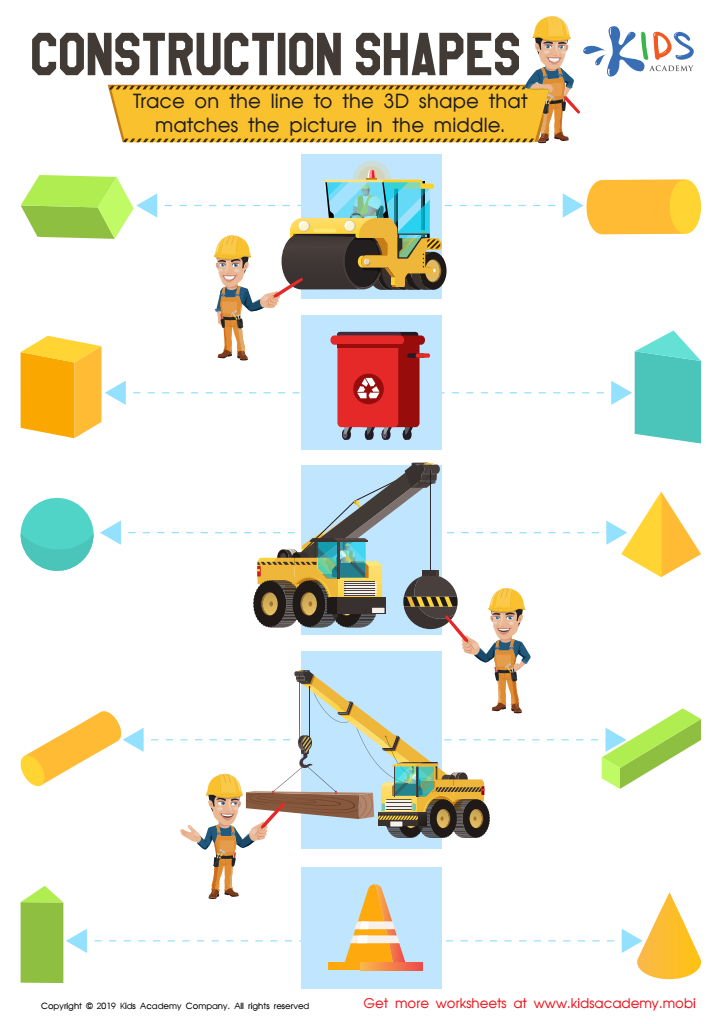

Construction Shapes Worksheet


Night Sky Numbers Worksheet
Fine motor skills and early math abilities are foundational for children aged 4-8, influencing their academic and everyday life success. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, which are crucial for tasks like writing, drawing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. These skills not only support literacy development but also enhance a child's ability to perform basic math tasks, such as counting, sorting, and recognizing shapes.
Encouraging fine motor skills and easy math together creates a synergistic effect; for instance, when children use counting beads or shape blocks, they refine their dexterity while also learning mathematical concepts. Moreover, engaging in playful activities, like drawing geometric shapes or playing with puzzles, promotes problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
Parents and teachers who foster these abilities help develop a child's confidence and enthusiasm for learning, laying the groundwork for more complex skills in the future. Additionally, early mastery of these skills can lead to better performance in standardized assessments and classroom settings. Ultimately, prioritizing fine motor skills and easy math equips children with foundational tools essential for lifelong learning and success.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students