Fine Motor Skills Easy Math Worksheets for Ages 4-9 - Page 2
44 filtered results
-
From - To

Eight Geese Worksheet


Number 8 Printable


Planting Seeds for 11 Worksheet


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet


Let's Pick Fruit Worksheet

Cutting in Halves Worksheet


Build with 9 Worksheet

Drawing Ovals And Triangles with Fun Printable

Scottish Sewing Part 2 Worksheet


Patchwork Math Worksheet


Adding in the Arctic Worksheet

Build and Match Worksheet
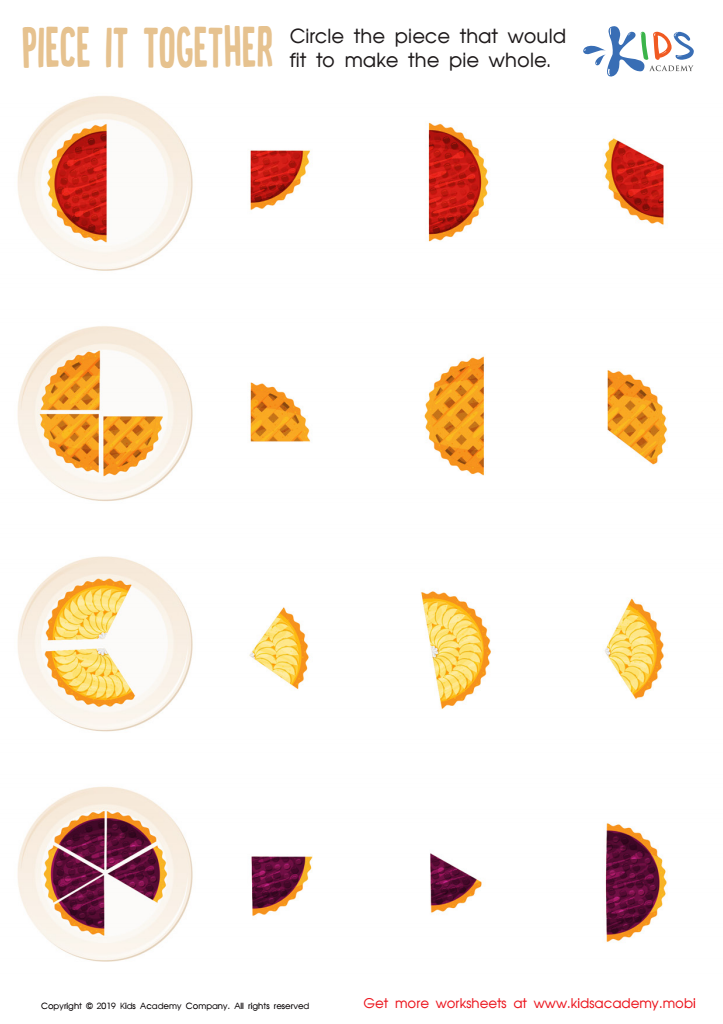


Piece it together Worksheet


Ordering 11–20: Dot–to–dot Seashell Printable


Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet


Counting on the City Skyline: Dot-to-Dot Worksheet


Counting Big City Buildings Worksheet

Construction Shapes Worksheet


Night Sky Numbers Worksheet
Fine motor skills are essential for children ages 4-9, as they significantly influence their ability to perform tasks that require hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Teachers and parents should prioritize these skills since they lay the foundation for academic success, especially in mathematics. Engaging children in activities that develop fine motor skills—such as cutting, drawing, or assembling puzzles—enhances their capability to manipulate objects, which is crucial for handling math tools like rulers and counters.
Moreover, connecting fine motor activities with easy math concepts helps reinforce learning. For instance, while threading beads to create patterns, children can learn about sequencing and counting. These playful interactions foster a positive attitude towards math, making it enjoyable rather than intimidating.
Furthermore, refining fine motor skills benefits children's overall development, promoting confidence, concentration, and creativity. As they gain proficiency in tasks that require dexterity, they feel empowered to tackle more complex challenges in learning.
In conclusion, parents and teachers should care about integrating fine motor skills into early math education to set a strong foundation for children's future academic endeavors and instill a sense of joy and achievement in their learning experiences.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students



.jpg)

.jpg)