Financial literacy Extra Challenge Worksheets for Ages 4-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your child's financial savvy early with our "Financial Literacy Extra Challenge Worksheets for Ages 4-9." Tailored for young learners, these worksheets offer engaging and interactive activities that teach essential money management skills. From recognizing coins and bills to understanding needs versus wants and basic budgeting, our worksheets provide a fun yet educational experience. Ideal for both classroom and at-home learning, they raise critical awareness about spending, saving, and planning. Equip your children with the tools they need for a financially responsible future, all while enjoying creative and thought-provoking challenges. Tags: kids financial literacy, printable worksheets, educational activities.
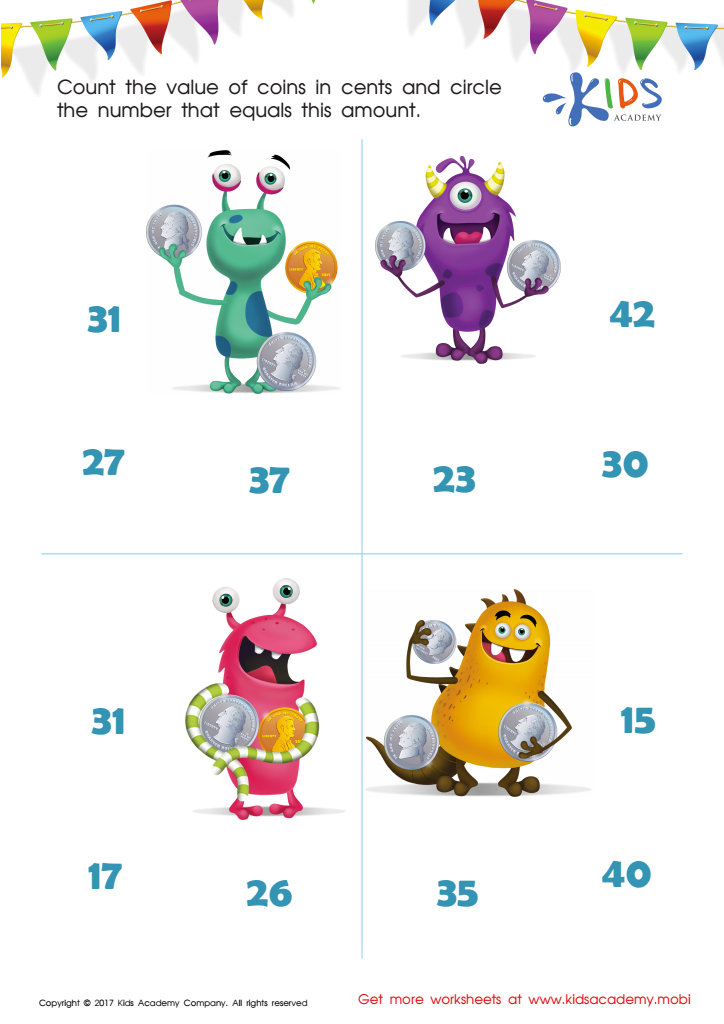


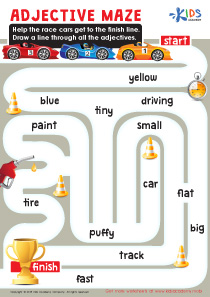
How Many Coins Money Worksheet
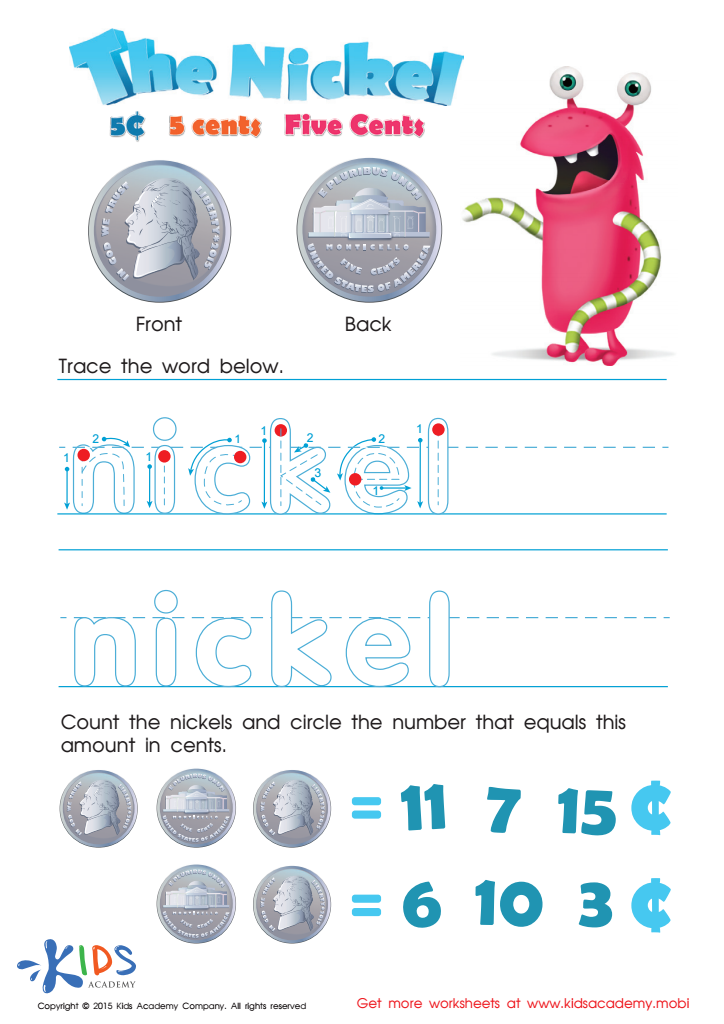

Five Cents or the Nickel Money Worksheet
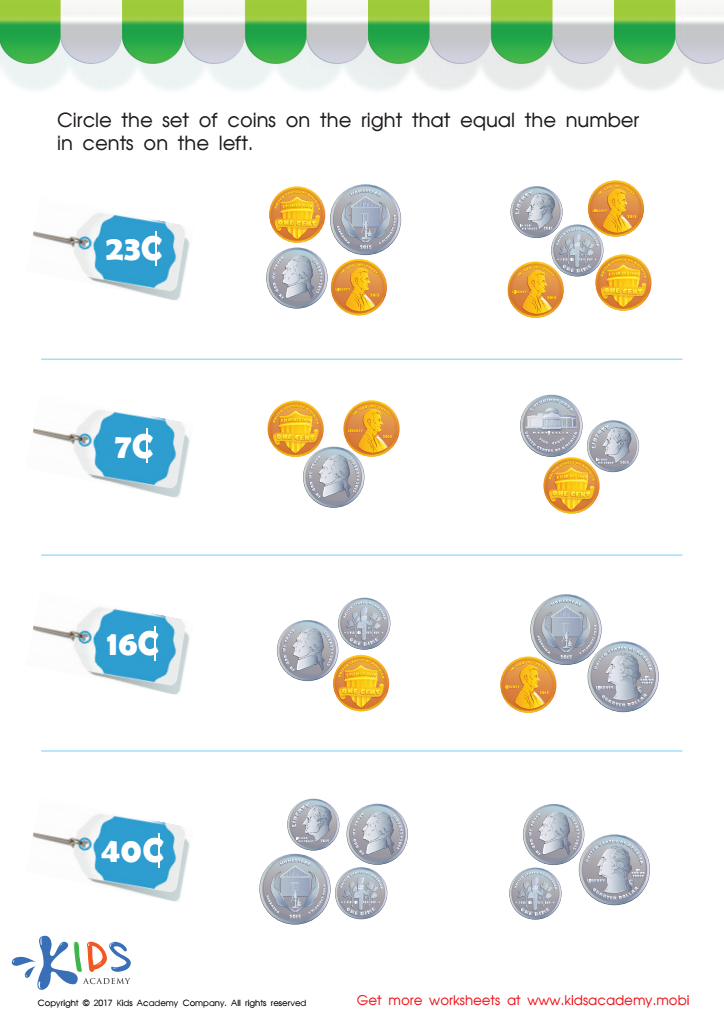

Picking the Coins You Need Money Worksheet
Financial literacy for children aged 4-9 is foundational for their future financial well-being. Introducing basic financial concepts at an early age helps shape responsible money habits that can last a lifetime. One of the key reasons for fostering financial literacy early is that it helps children understand the value of money and the importance of budgeting. When children learn to differentiate between needs and wants, they are better equipped to make informed spending decisions.
Parents and teachers play essential roles in guiding children through these early educational experiences. By incorporating financial literacy into everyday activities, such as allowing children to handle small sums of money, engaging in simple saving and spending exercises, and encouraging them to set achievable financial goals, adults can make learning about money practical and relevant.
This early exposure can also improve math skills, as counting coins and making change involve arithmetic practice. More so, learning about saving fosters patience and delayed gratification, critical skills for future success. It underscores that financial literacy is not just about managing money; it’s also about building character traits like discipline and responsibility.
Moreover, addressing financial literacy at an early age can close knowledge gaps that might otherwise widen over time, leading to more equitable financial futures for all children, regardless of their socio-economic background.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students




.jpg)