Letter recognition Normal ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-7
16 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child’s early literacy skills with our "Letter Recognition Normal ABC Letters Worksheets" designed for ages 3-7. These engaging worksheets support young learners in identifying and recognizing both uppercase and lowercase letters. With fun activities, including tracing, coloring, and matching exercises, your child will build a strong foundation in the alphabet. Our resources are perfect for enhancing fine motor skills while promoting letter familiarity in a playful and interactive way. Whether at home or in the classroom, these worksheets make learning letters enjoyable, setting the stage for future reading success. Start your child’s literacy journey today!


Letter E Coloring Sheet
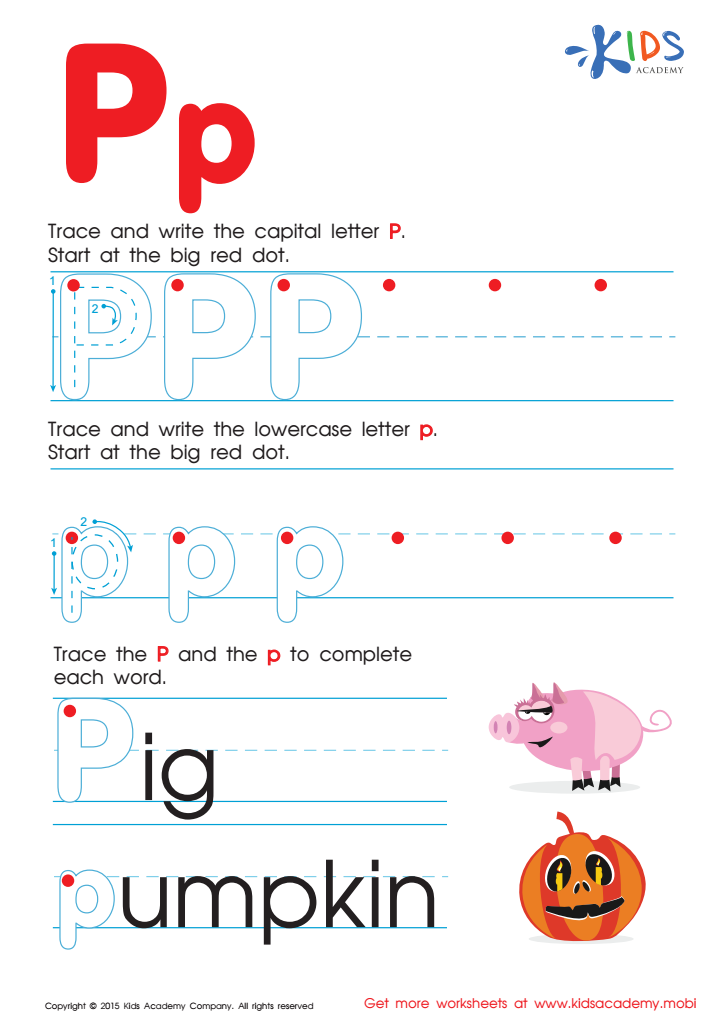

Letter P Tracing Page


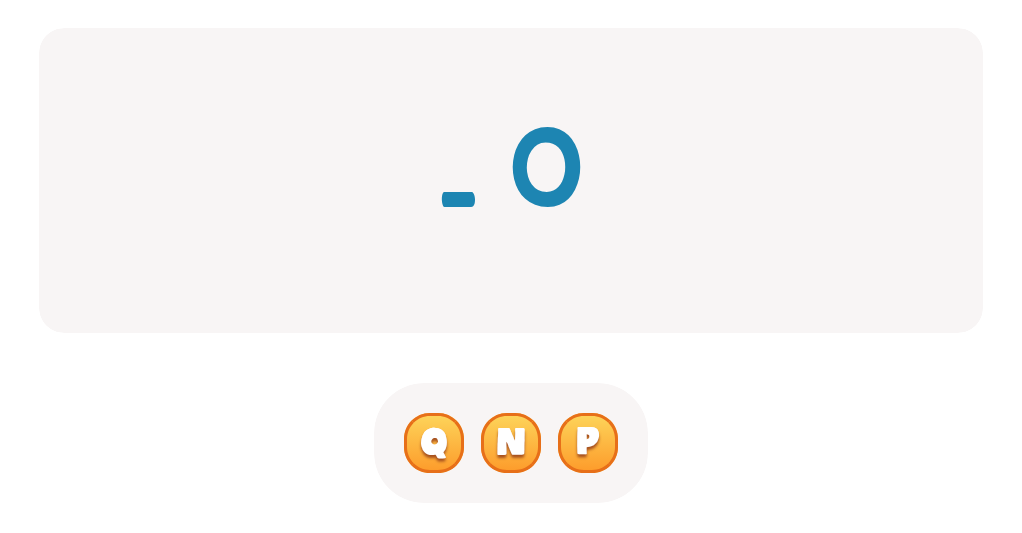
Letter Q Tracing Page

Letter H Tracing Page


Letter G Tracing Page

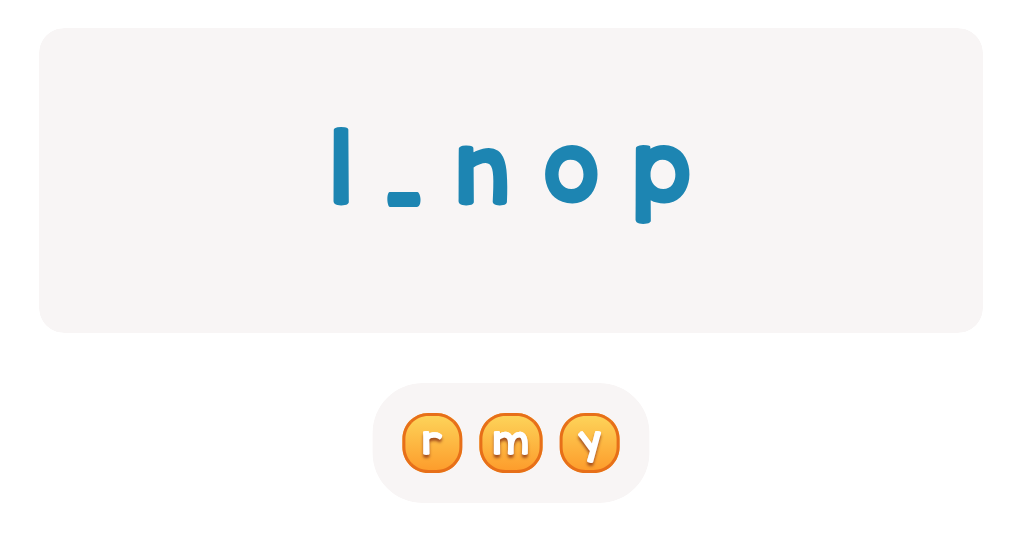
Recognize Letters l and i Worksheet

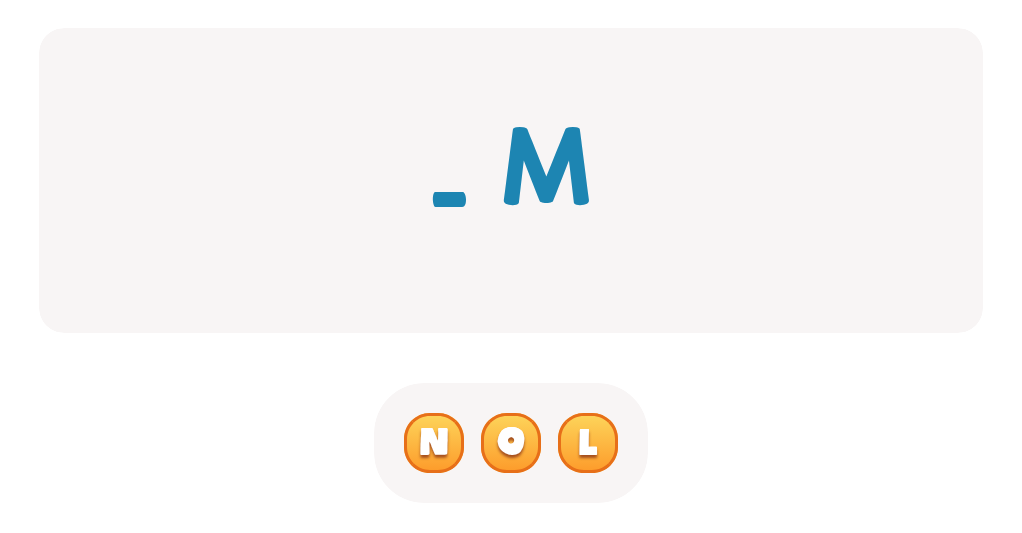
Letter L Tracing Page


Letter I Coloring Sheet


Letter G Coloring Sheet


Letter J Coloring Sheet


Letter K Tracing Page


Letter K Coloring Sheet


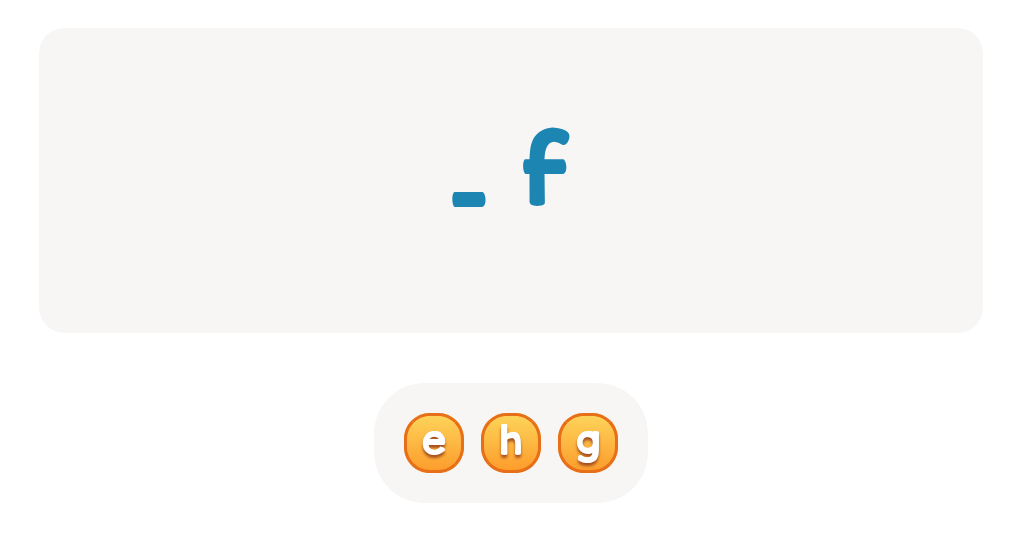
Letter F Tracing Page


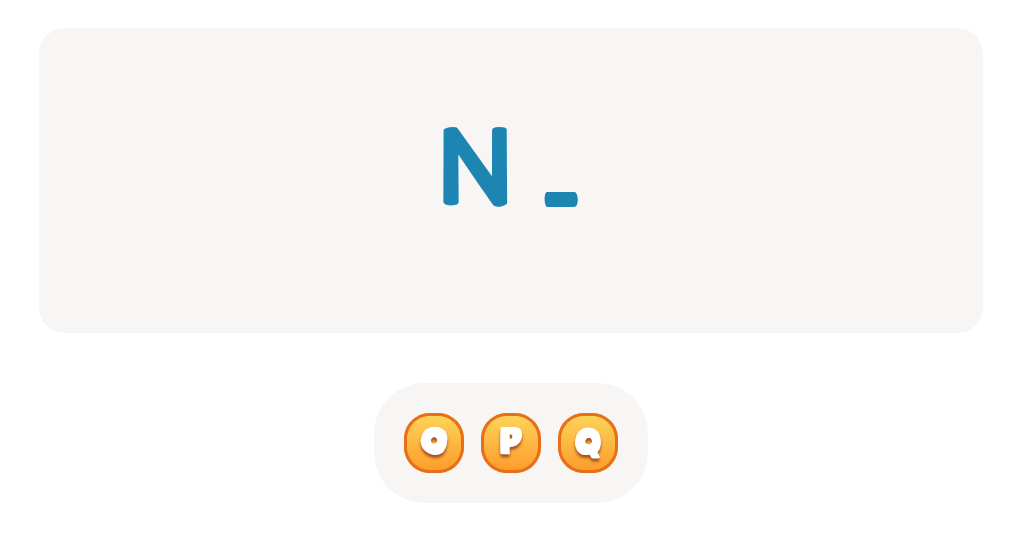
Letter N Coloring Sheet


Letter D Tracing Page


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet
Letter recognition is a foundational skill for young children, typically developing between the ages of 3 and 7. Parents and teachers should prioritize this skill because it plays a critical role in early literacy development. Recognizing letters helps children understand that letters represent sounds and that these sounds combine to form words. This awareness is essential for later reading and writing success.
When children can recognize letters, they gain confidence and motivation to engage with books and written materials. Early letter recognition contributes to vocabulary expansion and language comprehension, setting the stage for effective communication.
Additionally, letter recognition supports cognitive development by encouraging children to make connections and enhances fine motor skills through writing activities. For cognitively stimulating environments, engaging children in activities like letter games, storytelling, and crafts helps reinforce learning.
Creating a positive atmosphere around letters—such as labeling objects in the home or classroom, playing with letter-based toys, or reading books with letters—fosters a love for learning. Thus, by caring about letter recognition, parents and teachers can equip children with essential skills for higher academic achievement, enriching their educational journey and daily interactions.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students