Addition Practice Normal Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 2
39 filtered results
-
From - To
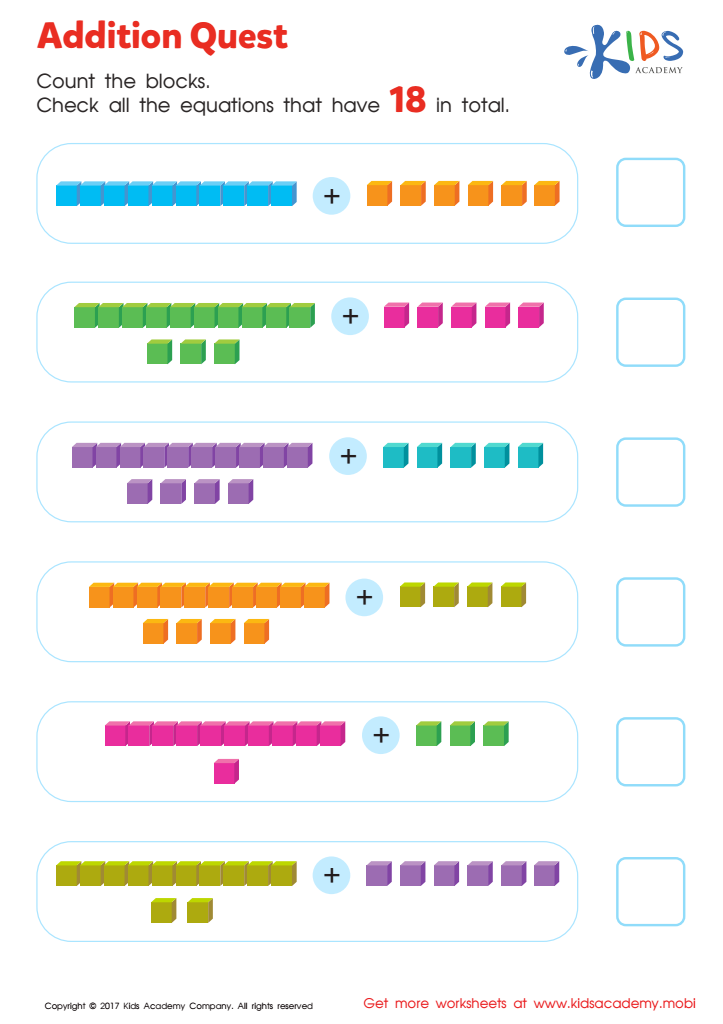

Addition Quest Worksheet: Part 2
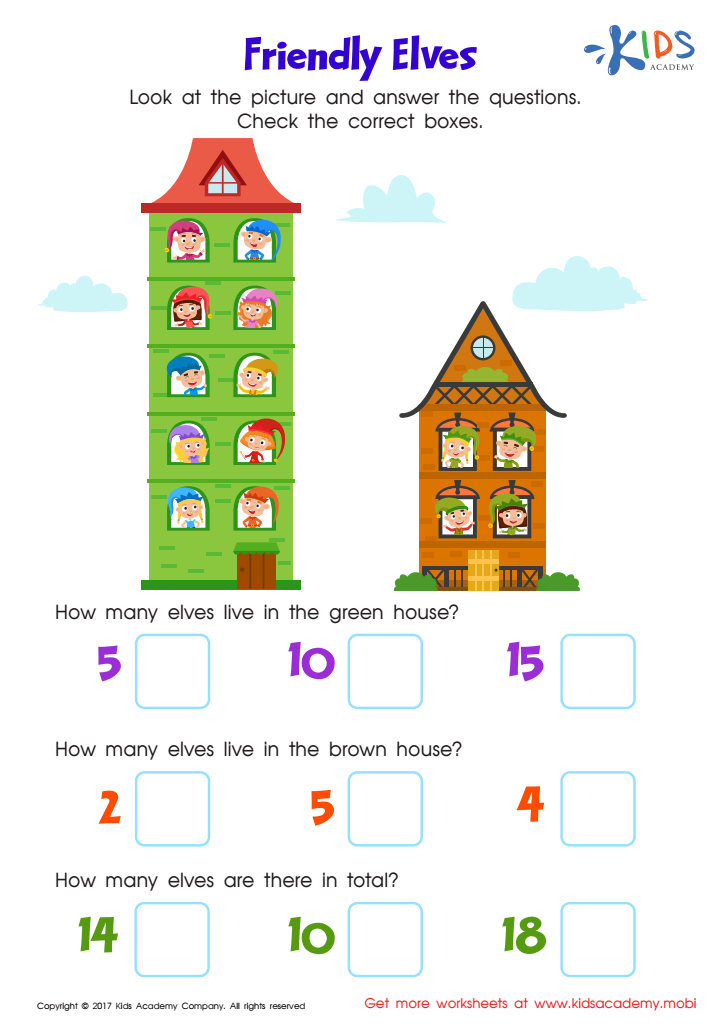

Place Value: Friendly Elves Worksheet


Building with 10 Worksheet


Clothes Math: Bar Graph Word Problems Worksheet
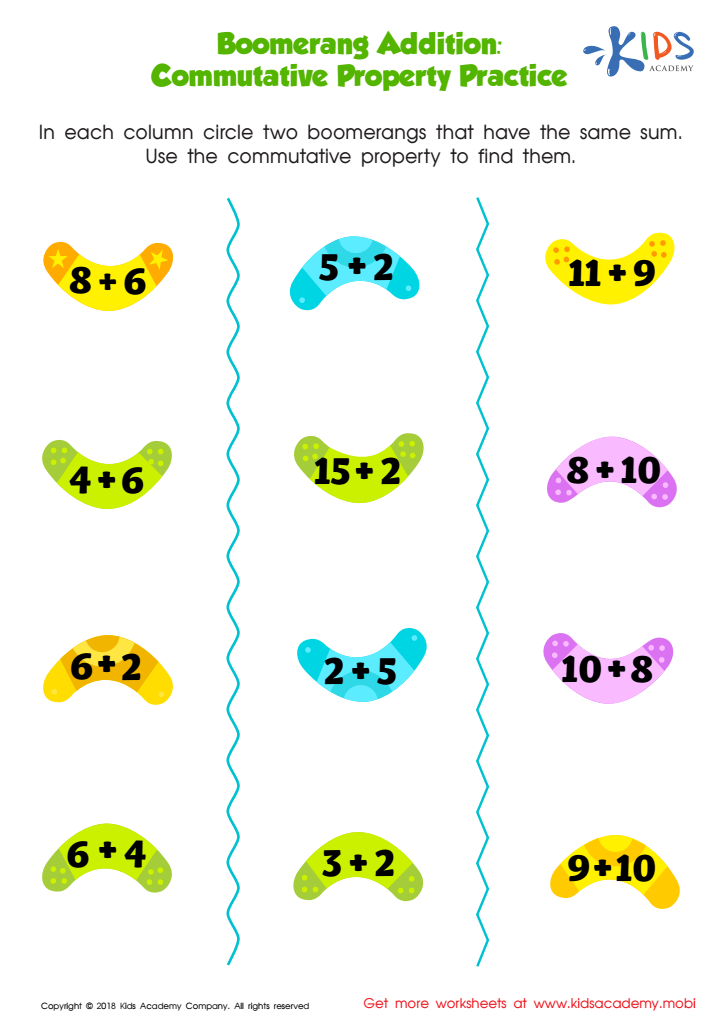

Boomerang Addition Worksheet
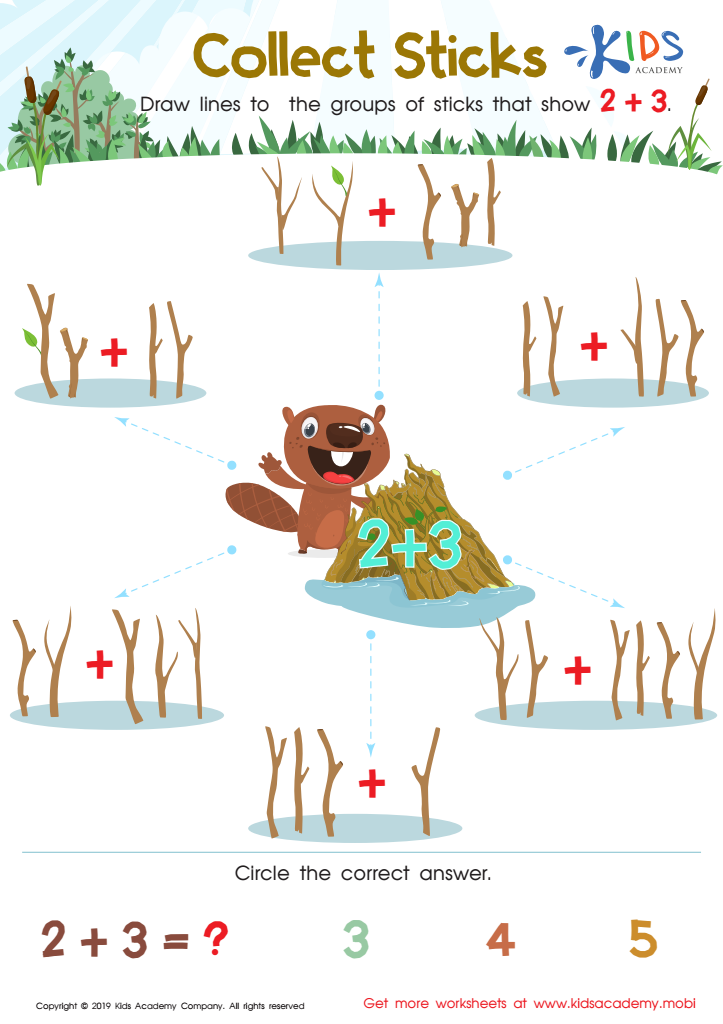


Collect Sticks Worksheet


Undersea Math Worksheet
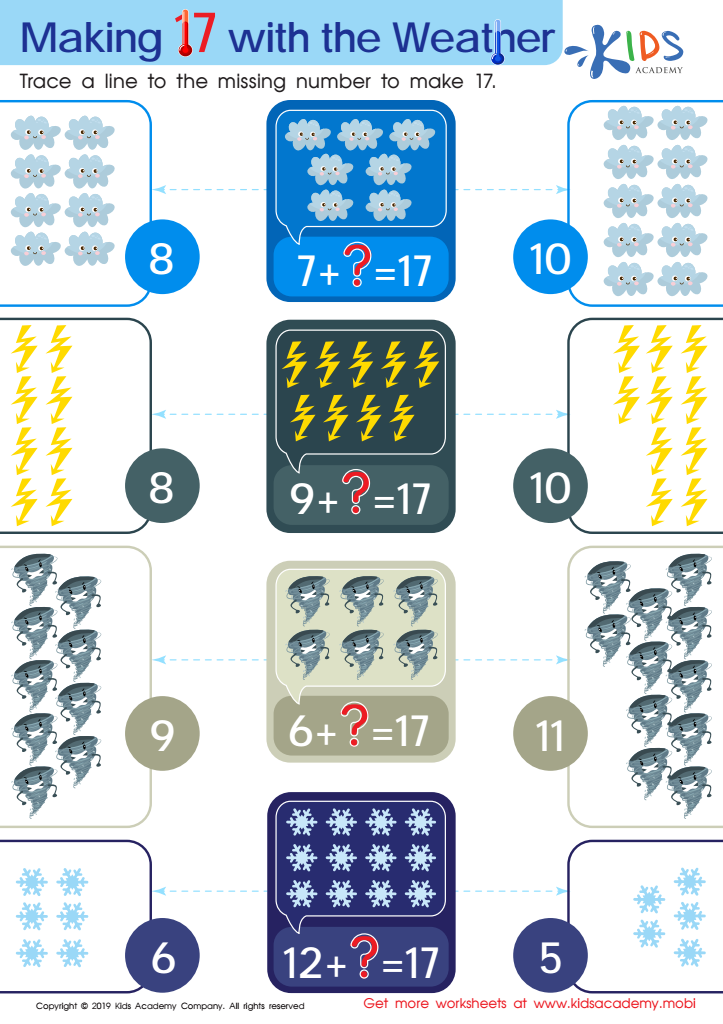

Making 17 with the Weather Worksheet


Pirate Ship Addition Worksheet

Airship Math Addition Printable

Adding Instruments with Addison Worksheet

Practice Addition: Part 2 Worksheet

Falling Leaves Worksheet

Pyramid Math to Make 11 Worksheet

Number Line Fun Worksheet
Addition practice is a cornerstone of early childhood education, setting the foundation for future mathematical comprehension and cognitive development. For children ages 3-8, addition practice helps in developing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. At this formative age, engaging in addition facilitates an understanding of basic mathematical concepts like counting, numerical order, and the relationship between numbers.
Parents and teachers should care about addition practice because it not only supports academic achievement but also builds confidence and reduces anxiety toward math as children progress in their education. Early practice solidifies foundational skills, which are essential for tackling more complex mathematical operations later on.
Addition activities can also be tailored to fit playful and interactive learning, enhancing the child’s engagement. Using manipulatives, games, and real-life scenarios makes addition more relatable and fun, fostering a positive attitude toward math.
Moreover, understanding addition boosts cognitive functions such as memory and attention span. It encourages children to approach challenges systematically and helps in developing patience and persistence.
For these reasons, structured and consistent addition practice is vital. It equips young learners with essential life skills, promotes positive attitudes towards learning, and lays the groundwork for academic success, ensuring that they are better prepared for future educational challenges.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















