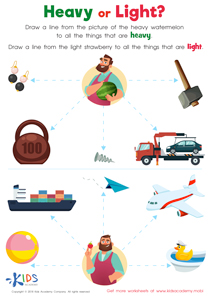
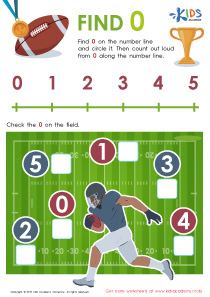
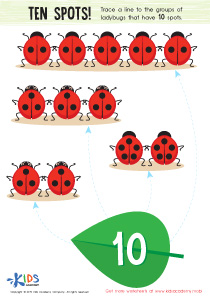
Fine Motor Skills Normal Math Worksheets for Ages 4-5 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To
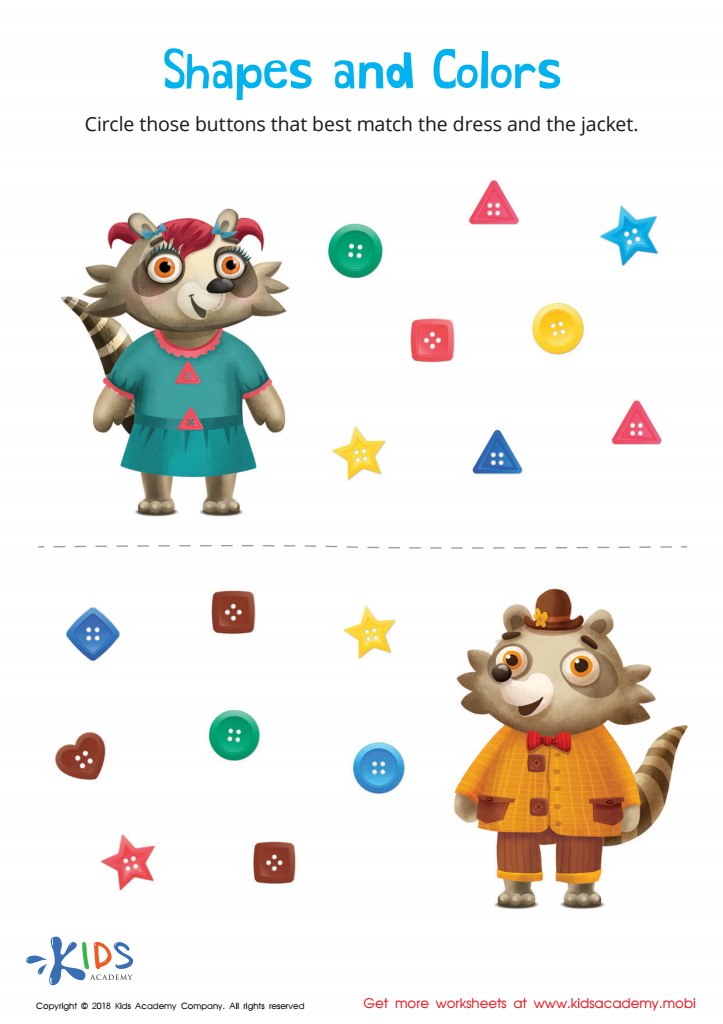


Shapes and Colors Worksheet


Frog Countdown Worksheet


Easy Drawing of Ovals And Rectangles Worksheet


Help the Bee Find 16 Flowers Worksheet


Learn to Write the Number 2 Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for children aged 4-5 as they lay the foundation for a wide range of activities, including academic tasks and daily living skills. At this age, children are developing the small muscle control needed for tasks such as holding a pencil, cutting with scissors, and manipulating small objects. Strong fine motor skills facilitate more effective problem-solving and logical thinking in math. For instance, when children can properly grip writing utensils and tools, they can execute math tasks like drawing shapes, counting, and writing numbers with greater ease and confidence.
Furthermore, engaging in fine motor activities enhances cognitive development. Activities that incorporate fine motor skills, like threading beads or using playdough, not only improve dexterity but also encourage spatial awareness and number recognition—essential components of mathematical understanding. Parents and teachers who prioritize fine motor skills create supportive environments for young learners, fostering confidence and interest in math from an early age.
By recognizing the link between fine motor skills and mathematics, educators and parents can implement targeted activities that cultivate these abilities, ensuring a smoother transition into more complex mathematical concepts as children grow.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students


.jpg)