Number comparison Normal Math Worksheets for Ages 7-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Delight young learners with our engaging "Number Comparison" math worksheets, specifically crafted for ages 7-9. These printable resources from Kids Academy help children develop crucial skills in understanding greater-than, less-than, and equal-to relationships. Colorful and fun, each worksheet challenges kids to compare numbers, fostering confidence in their arithmetic abilities. Perfect for both classroom and home practice, our activities offer progressive difficulty to match your child's growing proficiency. Encourage your child to explore math joyfully and strengthen their foundational numeracy skills with our expertly designed number comparison worksheets!
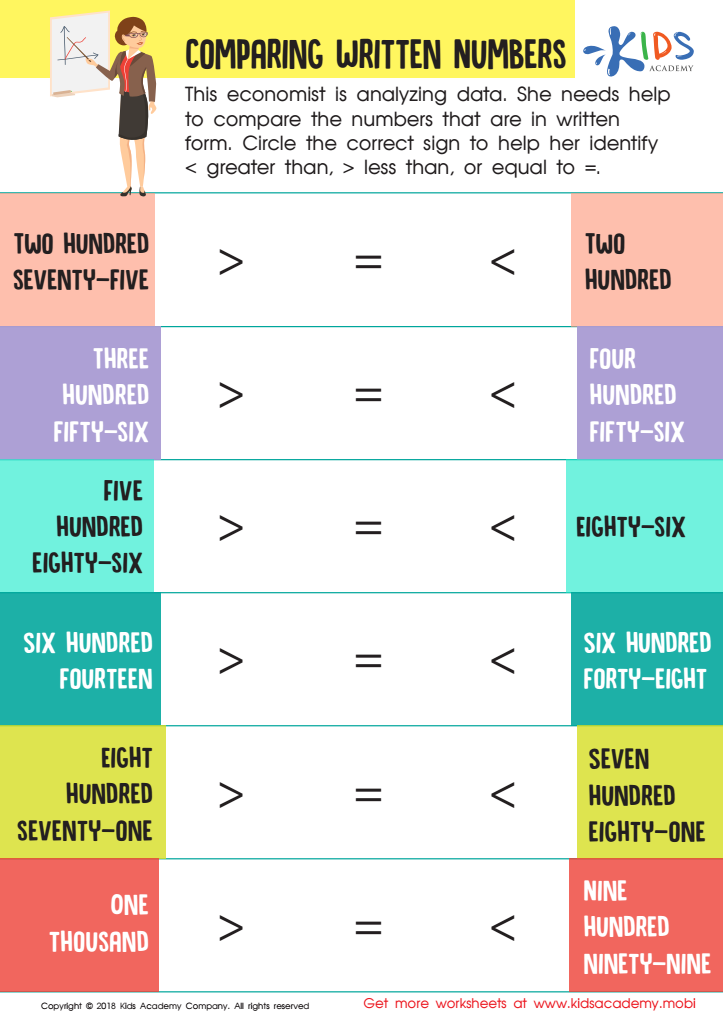

Comparing Written Numbers Worksheet
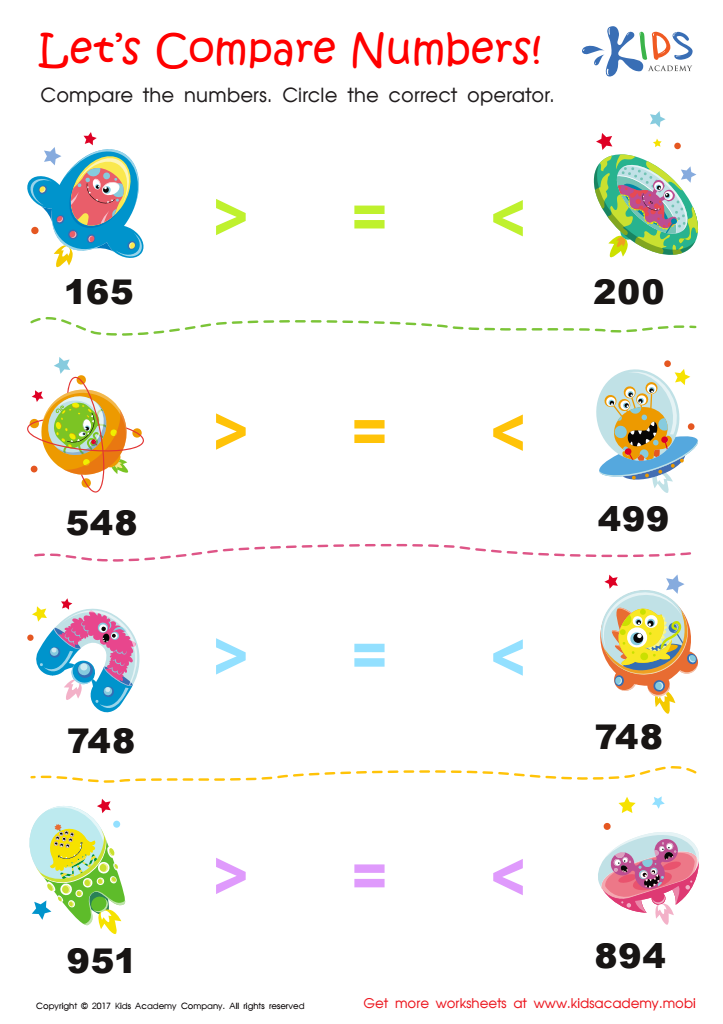

Comparing Numbers Worksheet for 2nd Grade
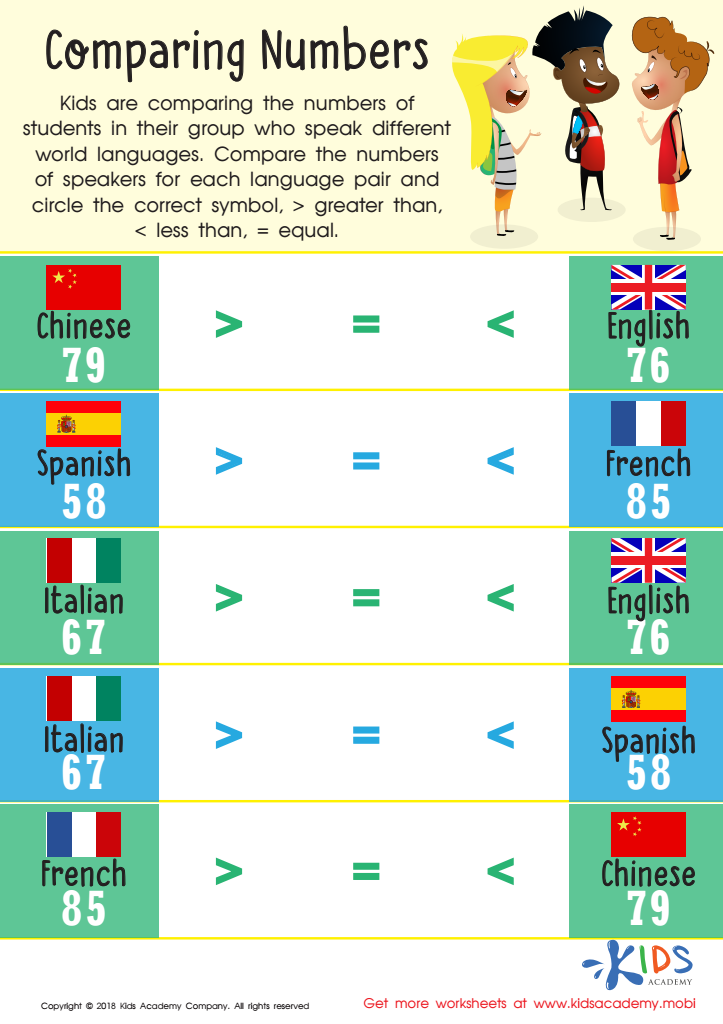

Comparing Numbers Worksheet for 1st Grade
Number comparison in normal math for ages 7-9 is a foundational skill that significantly impacts a child's overall mathematical development. This skill involves understanding the relative values of numbers, which is crucial for various mathematical concepts such as addition, subtraction, and recognizing patterns. Parents and teachers should care about fostering this ability because it lays the groundwork for more advanced mathematical reasoning and problem-solving abilities.
At this age, children transition from concrete to more abstract thinking. Learning how to compare numbers helps them grasp concepts of greater than, less than, and equal to. These basic comparisons also aid in real-world applications, such as telling time, managing money, and measuring quantities. Additionally, number comparison activities can boost logical thinking and decision-making skills. For example, deciding which of two quantities is greater helps children think critically and make informed choices.
Moreover, developing number sense through comparison can prevent math anxiety. Early familiarity and competence in basic math skills build a child's confidence and foster a positive attitude towards the subject. Hence, focusing on number comparison is essential for creating a solid mathematical foundation, fostering cognitive development, and instilling a love for learning in young children.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students