Visual perception Numbers Worksheets for Ages 3-4 - Page 2
25 filtered results
-
From - To
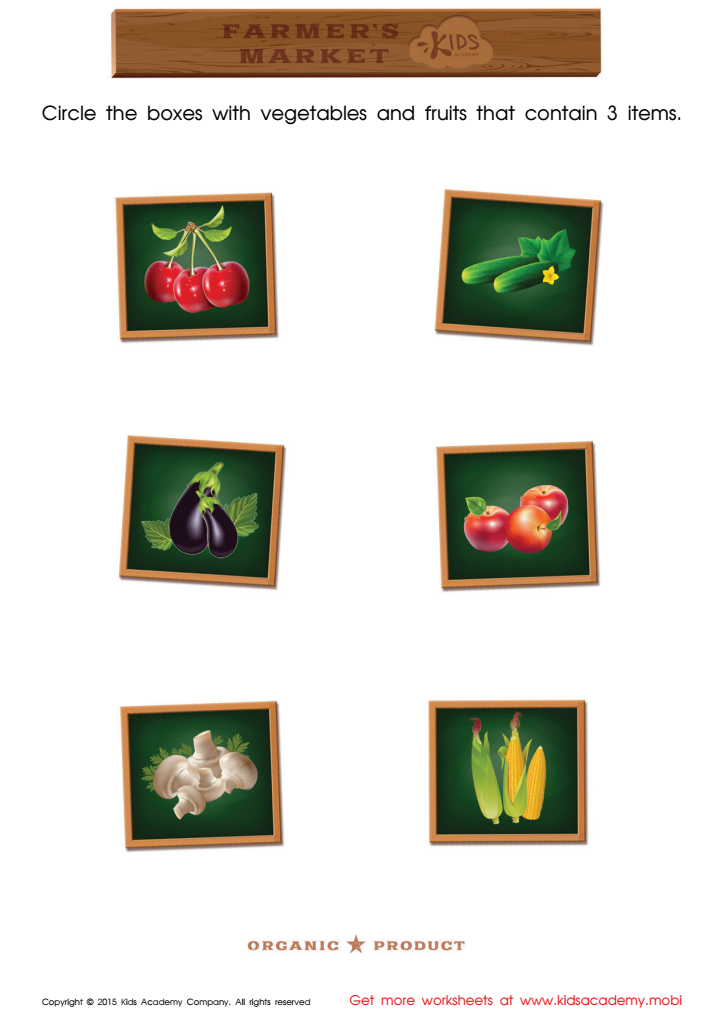


Count and Match Vegetables 1 – 5 Math Worksheet
Visual perception is crucial for young children, particularly in the context of numbers and early mathematical concepts. For children aged 3-4, developing these skills lays the groundwork for future academic success and everyday decision-making.
Visual perception refers to the brain's ability to make sense of what the eyes see. This skill helps children recognize patterns, compare quantities, and understand spatial relationships — all essential components of early math learning. When children can effectively interpret and process visual information, they better comprehend numbers, shapes, and arrangements.
At this age, children often learn through playful interactions and hands-on activities. By incorporating visually stimulating activities, parents and teachers can make learning about numbers enjoyable and engaging. Activities such as counting objects, matching number tiles, and sorting shapes help reinforce visual perception skills. These practices not only enhance their number recognition but also improve their fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination.
Strong visual perception skills contribute to a child’s ability to follow instructions, solve problems, and carry out daily tasks. Additionally, these skills are interconnected with literacy; for example, identifying numbers is similar to recognizing letters and words.
By focusing on these skills early, parents and teachers empower children with the foundational tools necessary for advanced learning, critical thinking, and cognitive development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students