Fine motor skills (writing) Math Worksheets for Ages 3-5 - Page 2
35 filtered results
-
From - To


Counting Flowers Worksheet
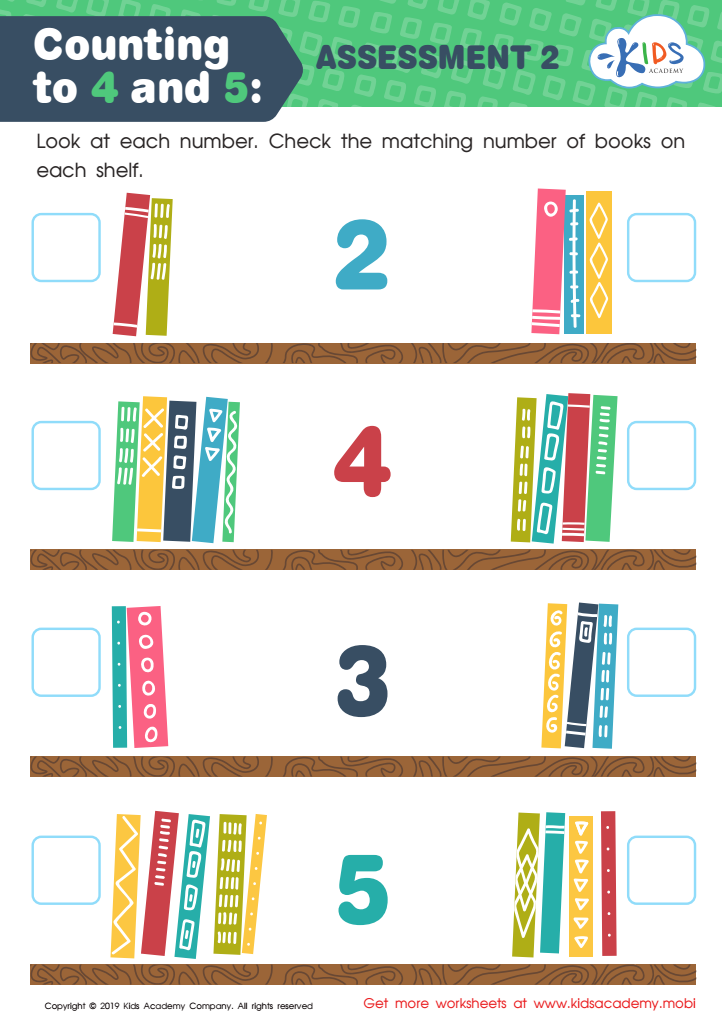

Counting to 4 and 5: Assessment 2 Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for young children aged 3-5 as they play a significant role in foundational academic abilities, particularly in writing and math. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands, allowing children to perform tasks that require precision, such as holding a pencil, cutting with scissors, or manipulating small objects.
For writing, effective fine motor skills enable children to form letters and numbers correctly, facilitating better communication and expression of ideas. As children develop their writing skills, they gain confidence in their ability to engage academically, setting a positive tone for their future learning experiences.
In math, fine motor skills contribute to a child’s ability to manipulate counting blocks, shape sorters, and other educational tools that introduce basic concepts of numeracy and spatial awareness. Children who excel in these areas are more likely to feel successful and motivated, further promoting their cognitive development.
Investing time in activities that strengthen fine motor skills not only supports a child’s ability to master early literacy and numeracy but also enhances their overall cognitive and social development, paving the way for lifelong learning and academic success. This foundational phase is essential for building confidence and competence in critical early childhood skills.


 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students










.jpg)










