Fine Motor Skills ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-6 - Page 2
38 filtered results
-
From - To
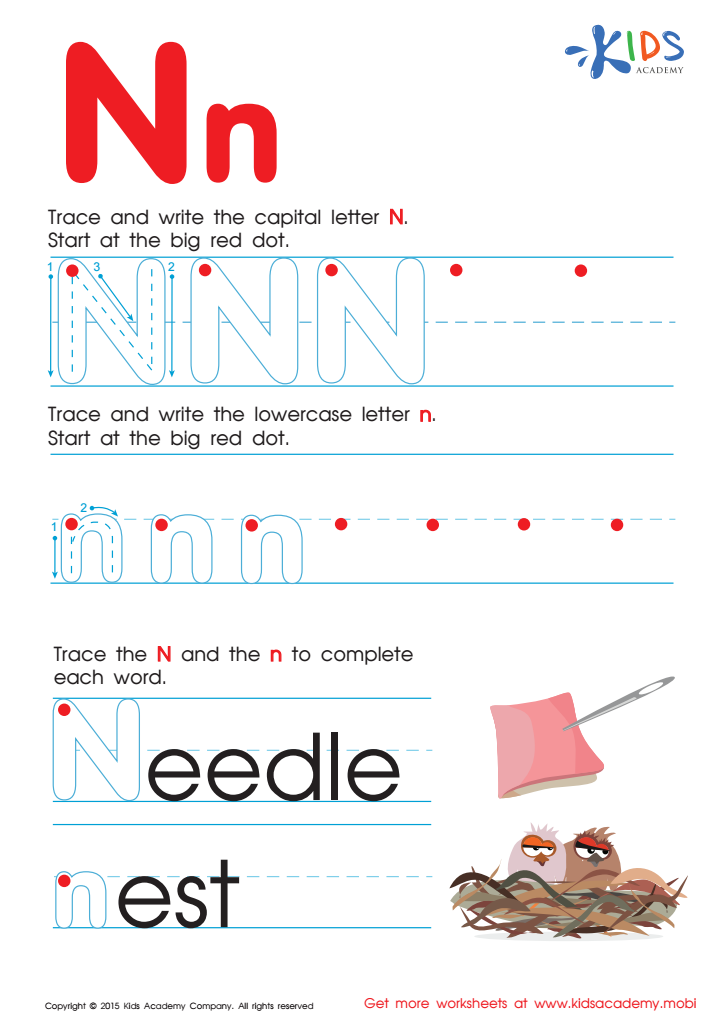

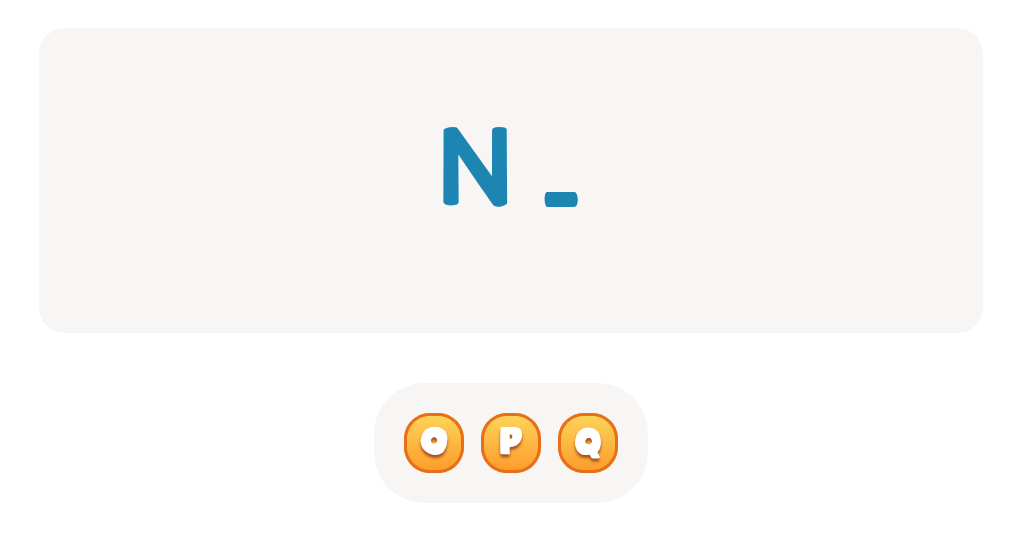
Letter N Tracing Page


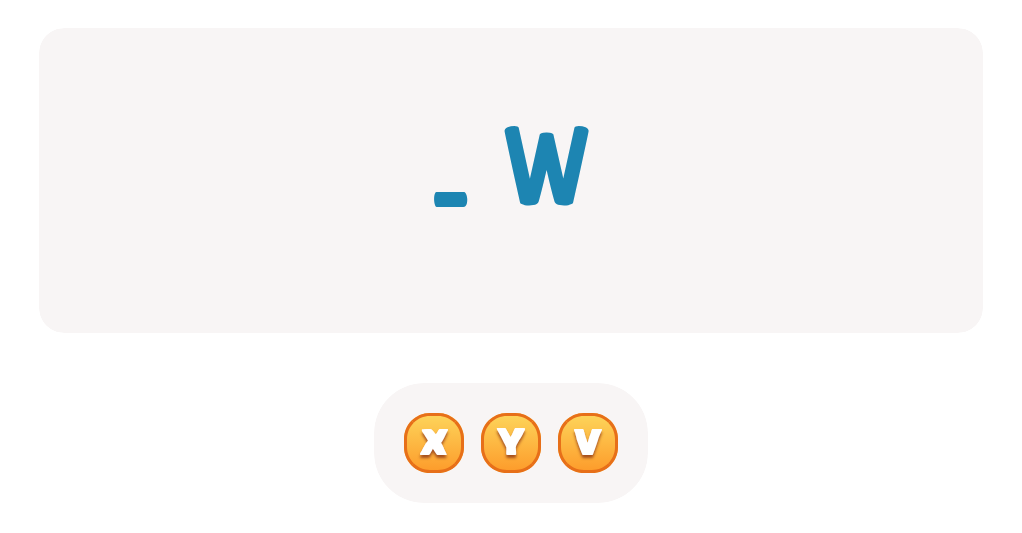
Letter V Tracing Page

Letter P Coloring Sheet

Letter E Tracing Page


Letter G Coloring Sheet


Letter Z Coloring Sheet


Letter J Coloring Sheet

Letter Y Coloring Sheet


Letter F Tracing Page


Uppercase Letters Y Z Worksheet

Letter F Coloring Sheet

Letter T Tracing Page


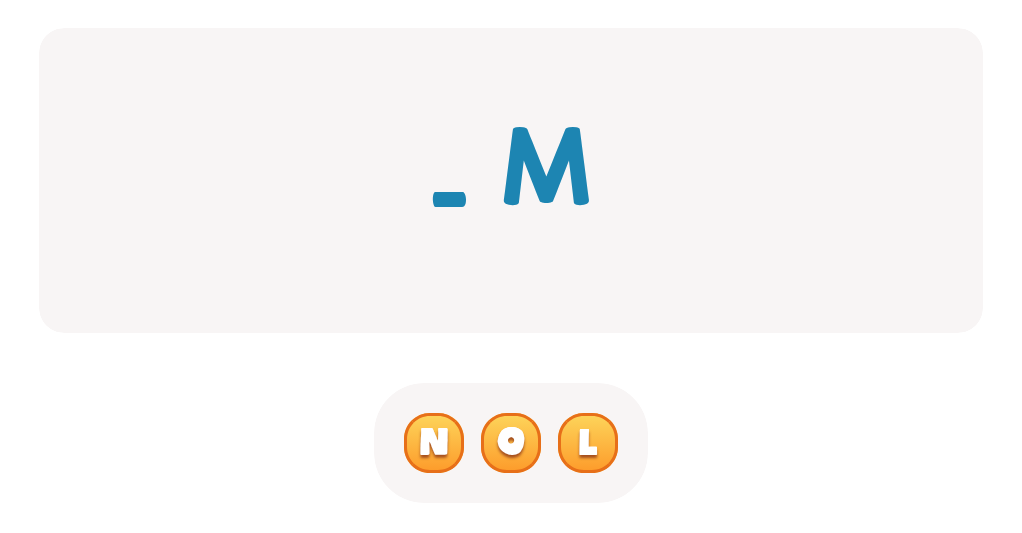
Letter N Coloring Sheet


Letter D Tracing Page
Fine motor skills are crucial for children aged 3-6 as they form the foundation for various essential tasks, including writing, drawing, and self-care activities like buttoning shirts and tying shoelaces. Developing fine motor skills, particularly in letter formation, aids in a child's literacy and cognitive development. Engaging with the alphabet through activities that strengthen grip, hand-eye coordination, and dexterity helps children become more confident and competent in their early writing abilities.
Parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skills for multiple reasons. Firstly, these skills support academic success, allowing children to express their thoughts clearly through writing as they progress in school. Secondly, fine motor development is linked to future learning capabilities, social interactions, and self-esteem. Roughly 10% of a child’s potential learning stems from early fine motor skill practices, making early intervention vital.
Furthermore, fun, engaging activities like playdough, tracing, or lacing can reinforce these skills while keeping children motivated. Prioritizing fine motor development not only establishes a solid educational groundwork but also allows children to enjoy the learning process. By supporting their exploration of letters and sounds, parents and teachers foster curiosity and a lifelong love for learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students