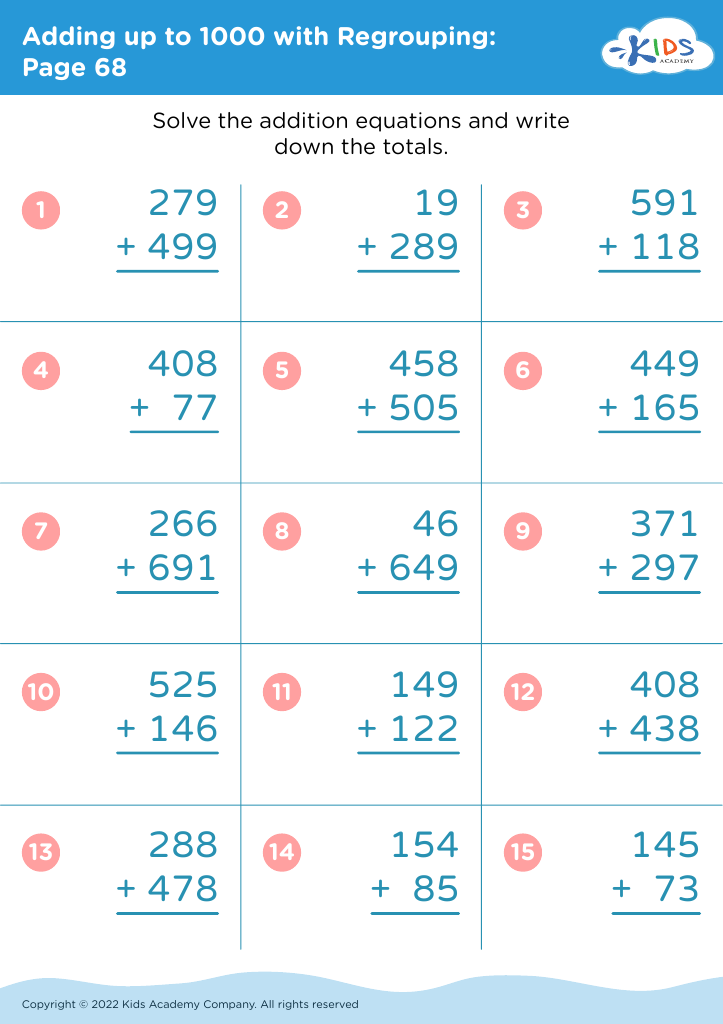
Handwriting practice Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-7
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's math skills and handwriting with our Handwriting Practice Addition & Subtraction Worksheets, designed for ages 3-7. These engaging, age-appropriate worksheets combine basic arithmetic with handwriting practice, helping young learners to reinforce their math knowledge while improving their fine motor skills. Easy-to-follow and thoughtfully crafted, each worksheet makes learning fun and effective, ensuring that your child builds a strong foundation in both math and writing. Ideal for interactive learning at home or in the classroom, our worksheets are the perfect tool to foster confidence and academic growth in your little ones.
Handwriting practice, coupled with learning addition and subtraction, is crucial for children aged 3-7, forming a cornerstone of early educational development. During these formative years, young brains are exceptionally malleable, optimizing the acquisition of foundational skills. Integrating handwriting practice with math activities not only promotes cognitive synergy but also enhances multifaceted learning.
Handwriting boosts fine motor skills, crucial for young learners. By gripping pencils and practicing letter formations or number writing, children enhance their dexterity and hand-eye coordination, building essential skills for future tasks, both academic and everyday.
Mathematical concepts such as addition and subtraction introduce structured thinking and problem-solving abilities. When intertwined with handwriting, it reinforces number recognition and pattern recognition. Visibly writing out problems helps solidify abstract concepts, making them more tangible to young minds.
Furthermore, tailored activities bolster confidence and academic interest. A solid grasp of early math and handwriting lays the groundwork for more advanced learning, fostering a smoother transition through various academic stages.
Thus, parents and teachers should recognize the value in these integrated practices, understanding that they nurture not only academic competencies but also holistic development, paving the way for future success in school and beyond.