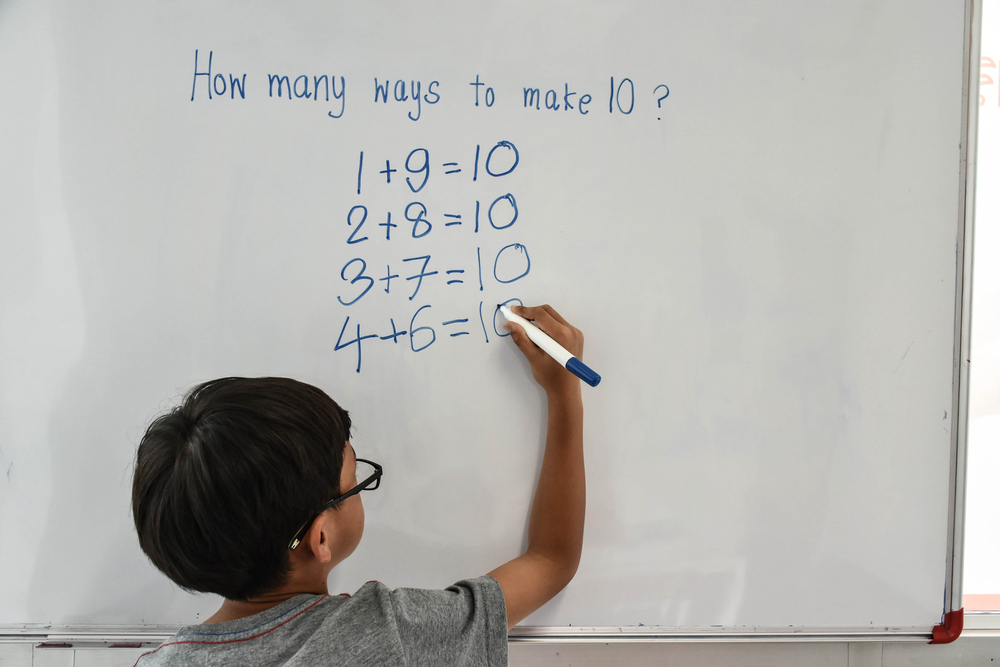Hand-eye Coordination Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To
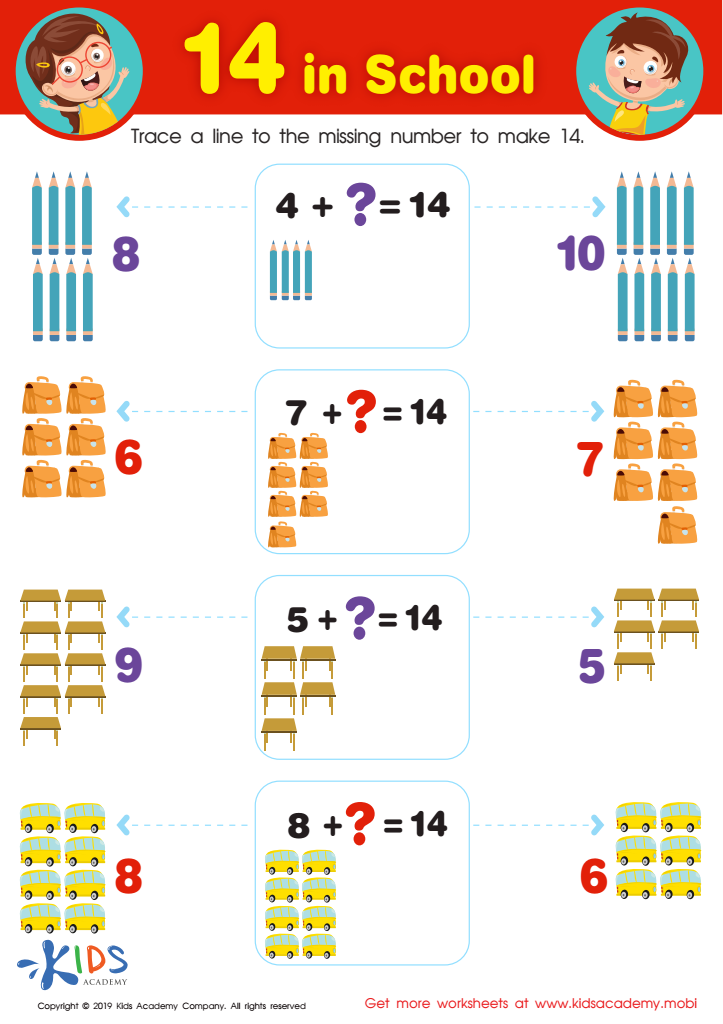

14 in School Worksheet
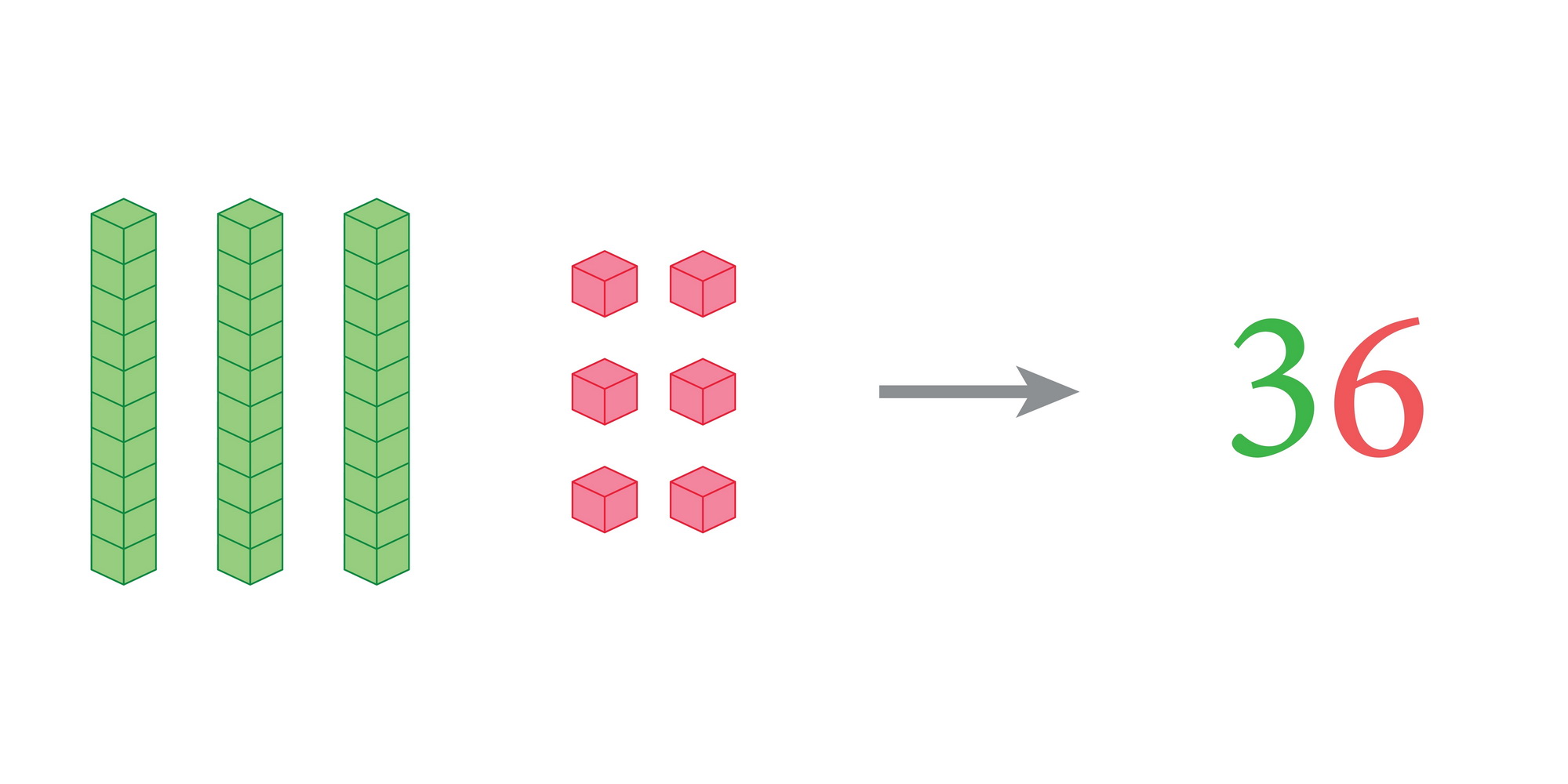
Hand-eye coordination is a crucial skill that combines visual input with physical actions, enabling children to interact effectively with their environment. For children aged 3-8, this skill is particularly important as it lays the foundation for many developmental milestones, including writing, reading, and various motor skills. When teaching addition and subtraction, incorporating hand-eye coordination activities helps children not only understand mathematical concepts but also enhances their physical dexterity and focus.
Engaging children in activities such as counting with physical objects, using finger math, or playing interactive games that require them to match numbers to quantities can significantly improve their cognitive and physical abilities. These methods encourage kinesthetic learning, where children learn best by doing, leading to improved retention and understanding of addition and subtraction.
Moreover, developing hand-eye coordination fosters confidence and self-esteem in young learners. Successful engagement in these activities helps them feel accomplished and motivated, making them more likely to enjoy learning. Both parents and teachers can benefit from prioritizing these skills, as they not only promote academic success but also contribute positively to a child's overall physical and cognitive development. Consistent practice in this area ensures that children are well-prepared for future learning challenges and everyday tasks.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students