Writing practice Worksheets for Ages 4-5 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To
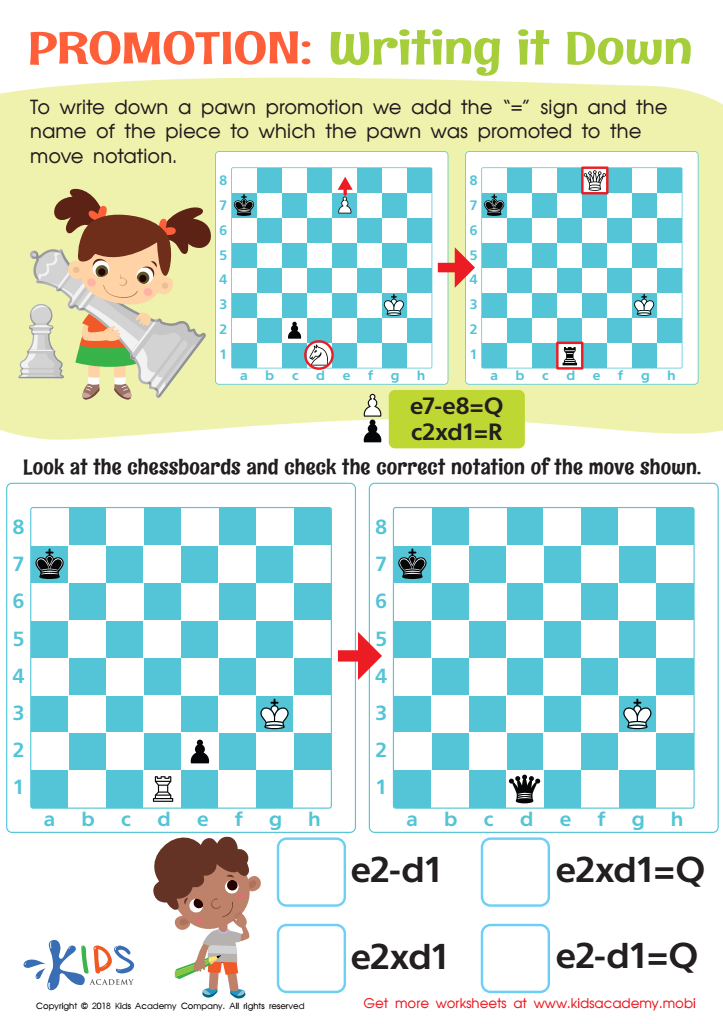

Writing it Down Worksheet
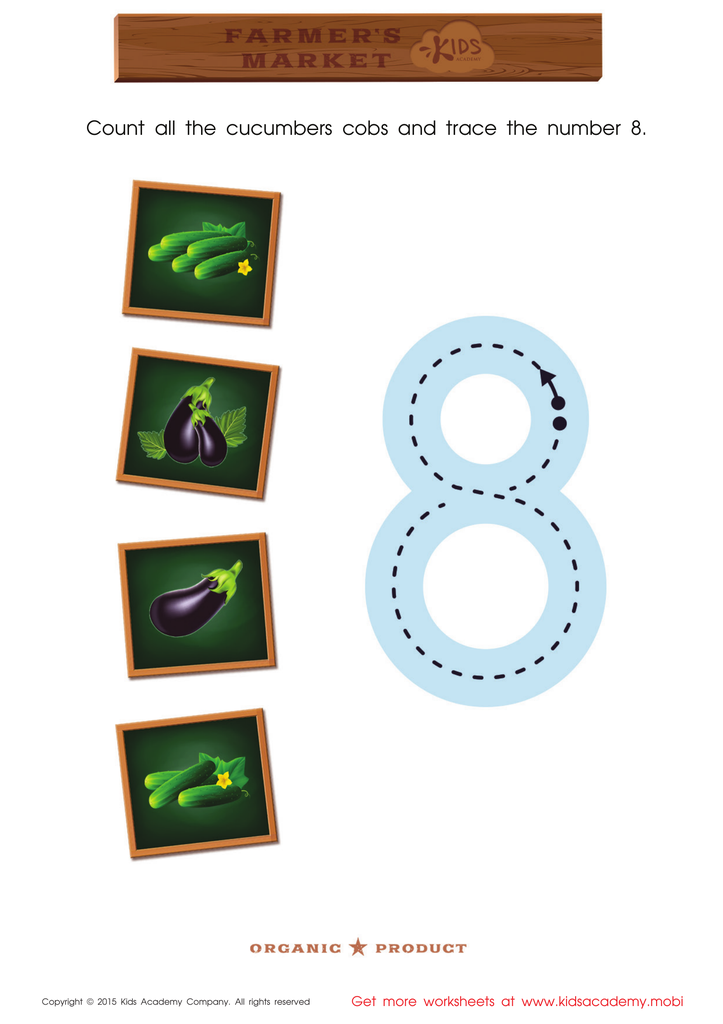


Count the Cucumbers and Trace the Number 8 Printable
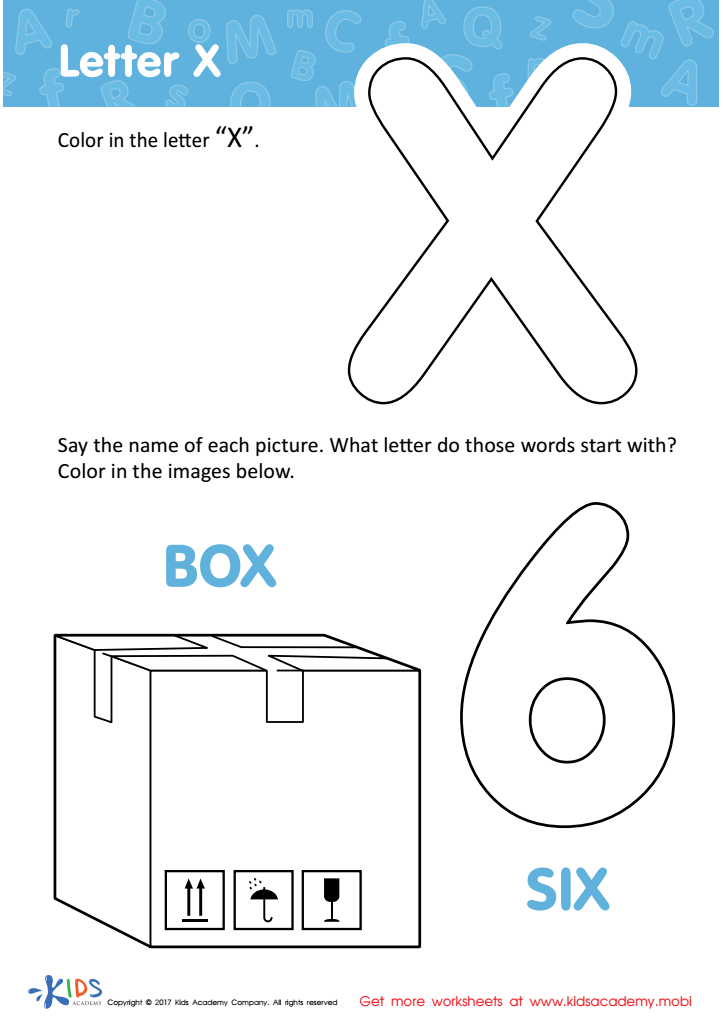

Letter X Coloring Sheet
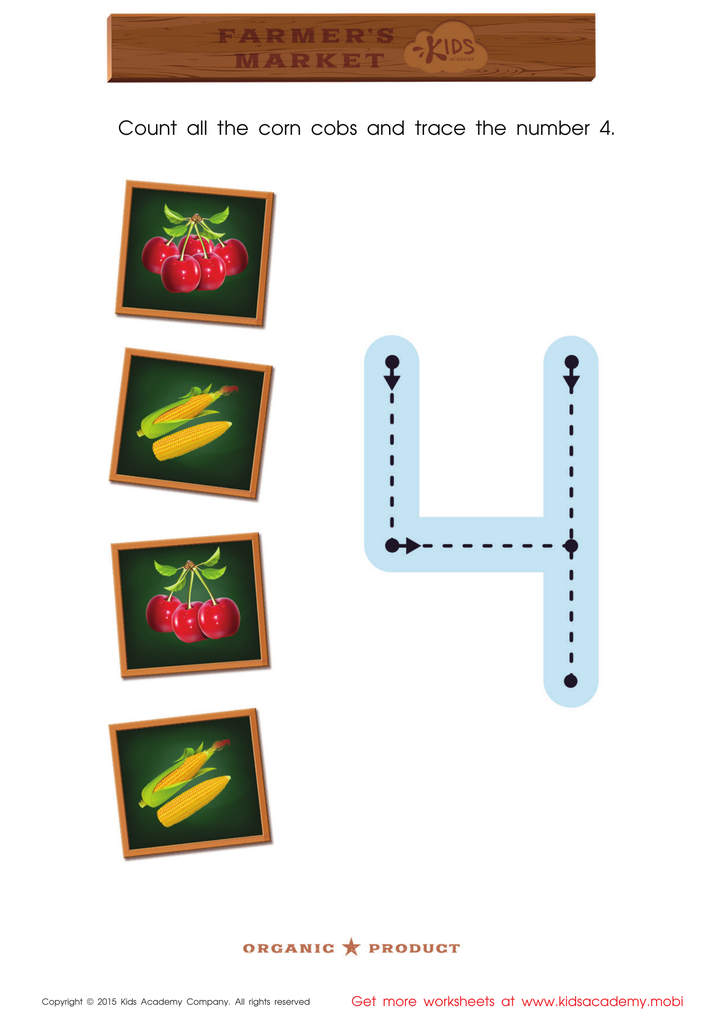

Count the Corncobs and Trace the Number 4 Worksheet
Writing practice for ages 4-5 is essential because it lays the foundation for literacy and communication skills that are critical throughout a child's life. At this developmental stage, children are highly receptive and absorb information like sponges. Engaging in early writing practice helps them understand the connection between spoken and written language, thereby enhancing their vocabulary and comprehension skills.
The physical act of writing also supports fine motor development. When young children manipulate a pencil or crayon, they're refining essential hand-eye coordination and motor skills, which are crucial not only for writing but for other everyday tasks such as buttoning clothes or using utensils.
Moreover, writing practice fosters cognitive development. It encourages young minds to organize their thoughts and express ideas logically. Through activities like drawing shapes, copying letters, or even attempting to write their names, children start to recognize patterns and sequences, which are fundamental skills in mathematics and logical reasoning.
Socially and emotionally, early writing endeavors can build confidence and a sense of achievement. As children successfully communicate through writing, they feel a sense of accomplishment that boosts their self-esteem.
Therefore, by prioritizing writing practice for ages 4-5, parents and teachers give children a head start that influences academic performance, fine motor skills, cognitive growth, and emotional well-being.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students