Develop fine motor skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-8
9 filtered results
-
From - To
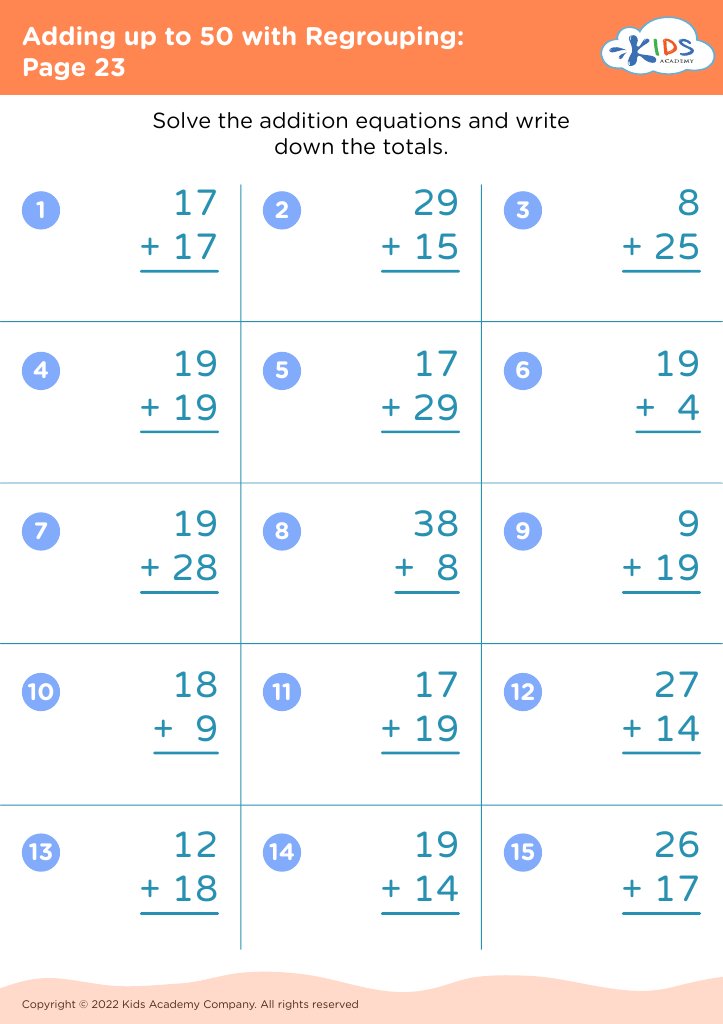
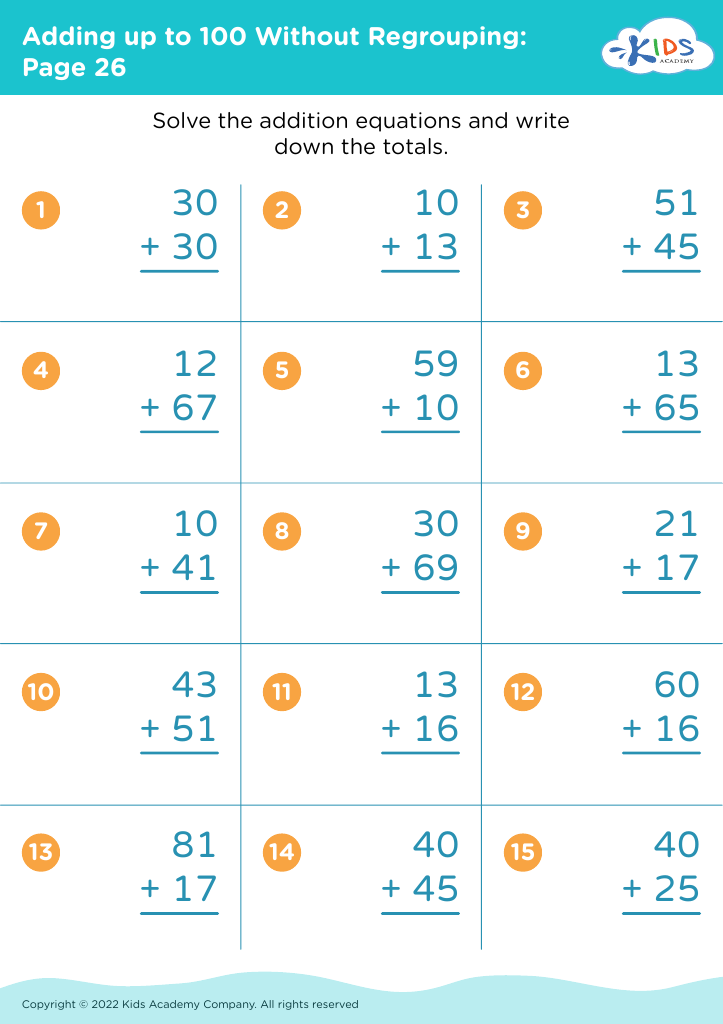
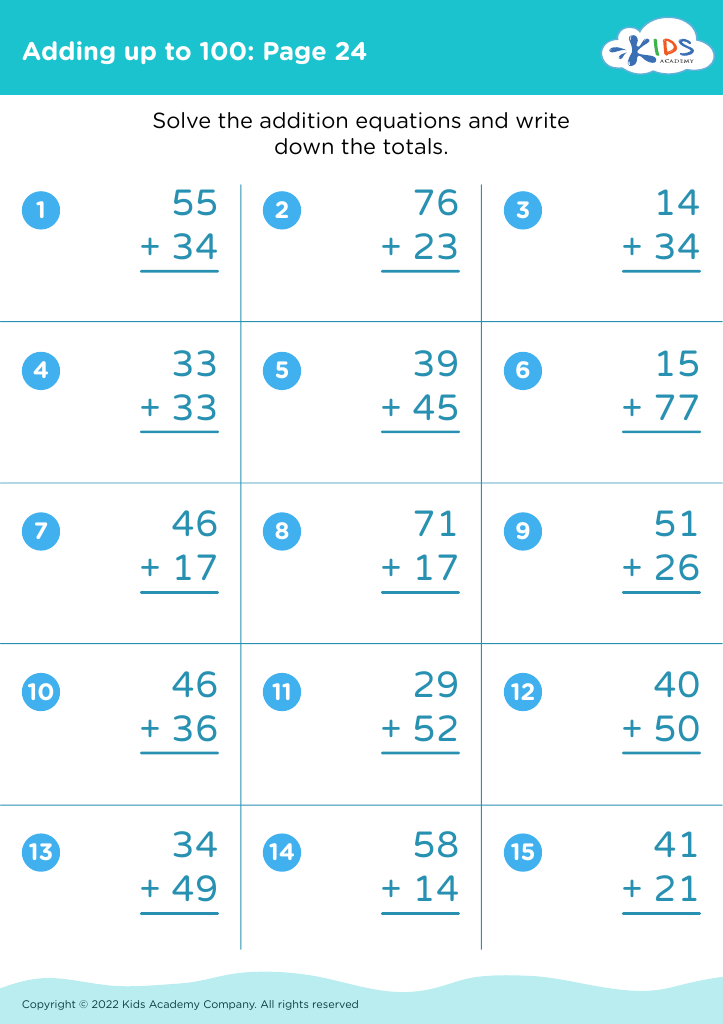
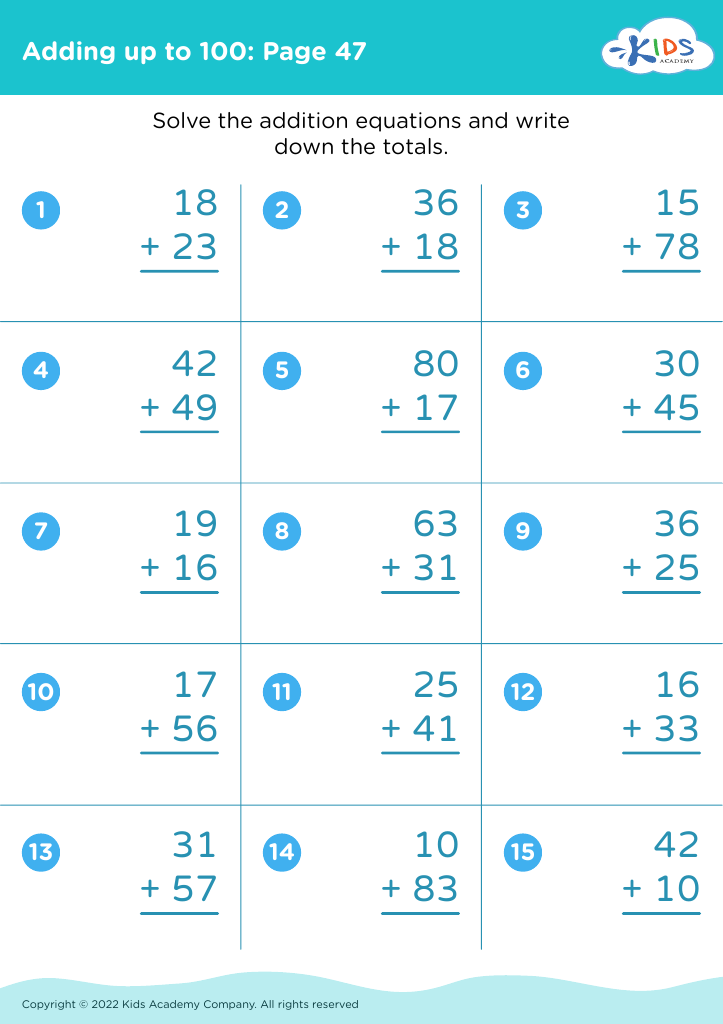
Our "Develop Fine Motor Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-8" are designed to enhance your child's math abilities while also strengthening their fine motor skills. These engaging worksheets provide a dual benefit, combining fun addition exercises with activities that promote hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Perfectly suited for young learners, each worksheet challenges students to solve addition problems through interactive tasks, such as tracing, drawing, and cutting. Our expertly crafted resources help children build crucial skills that are essential for success in both school and everyday life. Boost confidence and educational growth with these fantastic, multi-faceted worksheets!
Developing fine motor skills is crucial for children aged 4-8, and parents and teachers should pay attention to this area for multiple reasons. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscle movements, particularly in the hands and fingers, which are essential for performing everyday tasks and academic activities.
Firstly, fine motor skills are foundational for handwriting. Children who can control a pencil or crayon effectively are able to focus more on learning letters, numbers, and creative expression instead of struggling with holding and moving writing tools. Effective handwriting skills are closely linked to academic success, making it easier for children to complete tasks and communicate.
Secondly, these skills are essential for self-care activities. Children need them to button shirts, zip coats, tie shoelaces, and manipulate eating utensils. These activities foster independence, confidence, and a sense of responsibility in young learners.
Additionally, fine motor skills contribute to cognitive development. By working on tasks like cutting shapes or beading, children also enhance their spatial awareness, problem-solving abilities, and attention to detail.
Lastly, engaging in activities that build fine motor skills, such as puzzles and craft projects, can improve hand-eye coordination and encourage patience and concentration. Therefore, developing these skills forms a comprehensive part of a child's early education and overall development.
By supporting fine motor skills development, parents and teachers set the groundwork for long-term success in school and life.