Fine Motor Skills Numbers 0–10 Worksheets for Ages 4-8 - Page 2
48 filtered results
-
From - To
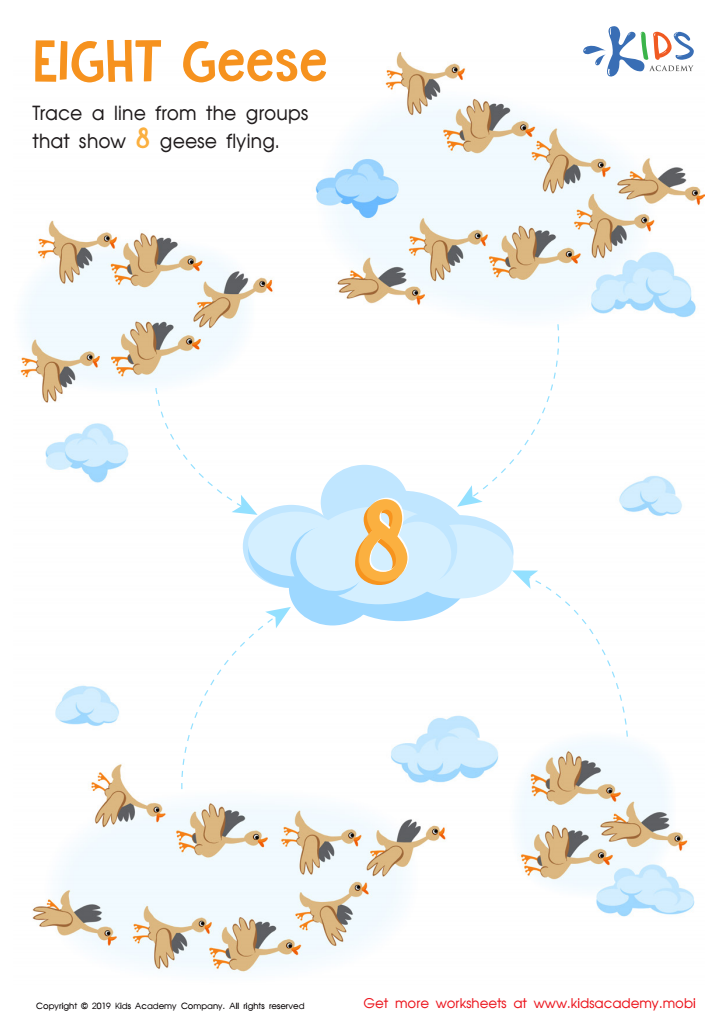

Eight Geese Worksheet


Number 8 Printable


Let's Pick Fruit Worksheet


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet
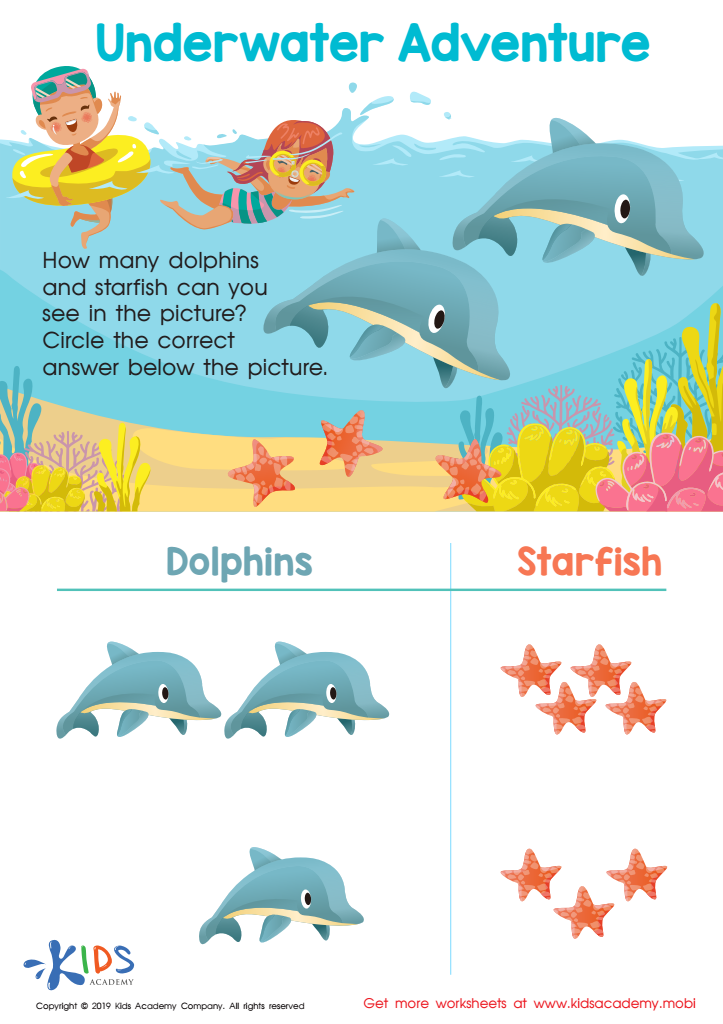

Underwater Adventure Worksheet

Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 2 Worksheet


Build with 9 Worksheet
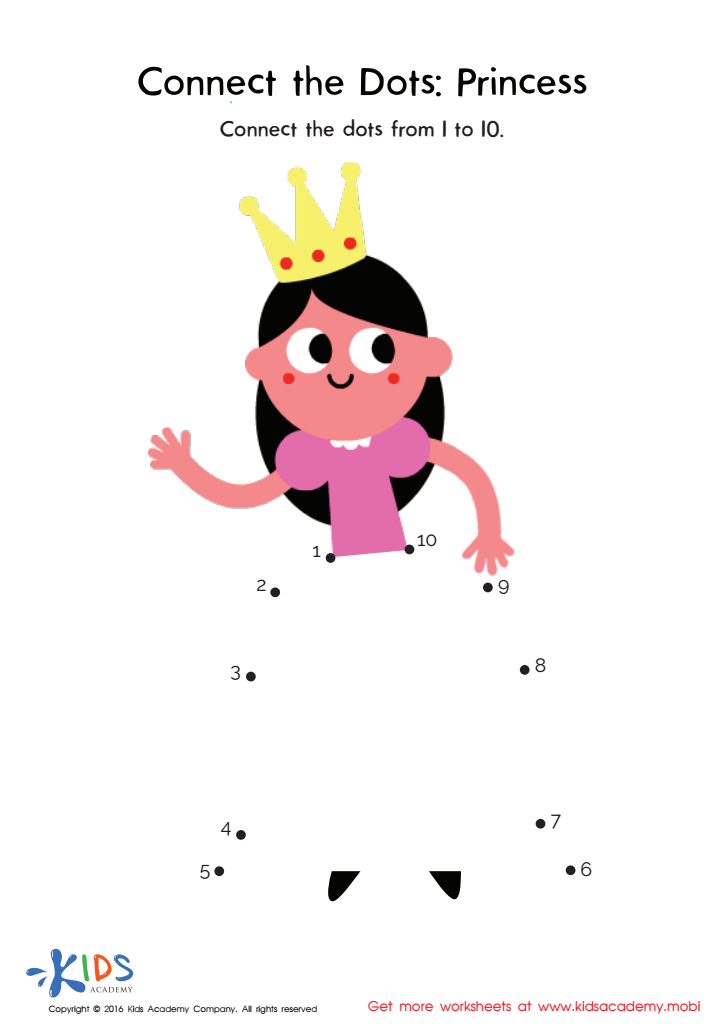


Princess Connect Dots Worksheet


Sloth – Coloring by Numbers
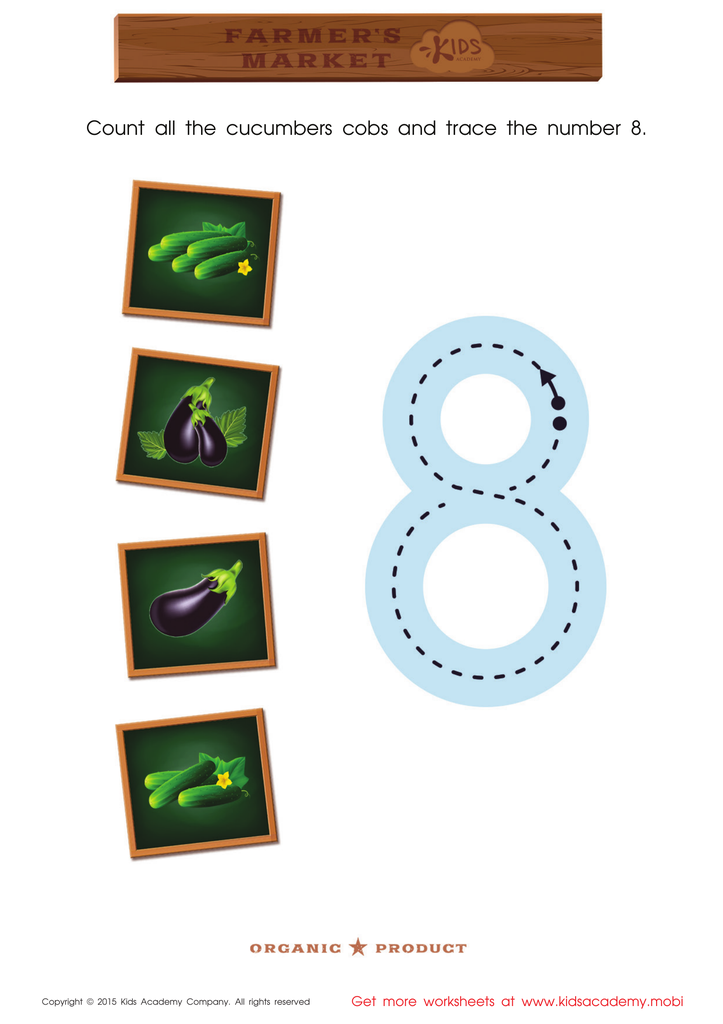


Count the Cucumbers and Trace the Number 8 Printable


Sea Adventure – Coloring by Numbers


Count and Match: Feed the Animals Worksheet


Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet


Great Hornbill – Coloring by Numbers


In the Treetops – Coloring Page


Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star – Coloring by Numbers


Hickory Dickory Dock – Coloring by Numbers


Wheels on the Bus – Coloring by Numbers


Night Sky Numbers Worksheet


Little Chef – Coloring by Numbers


A Fox and a Bird – Coloring by Numbers


Little Pilot – Coloring by Numbers


Little Red Riding Hood – Coloring by Numbers


In the Garden – Coloring by Numbers
Parents and teachers should prioritize the development of fine motor skills in children aged 4–8 when learning numbers 0–10 because these skills are foundational for academic success and daily activities. Fine motor skills, which involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, are crucial for tasks such as writing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. By focusing on numbers 0–10, children practice grasping pencils or crayons correctly, which enhances their control and precision in forming numbers. This early practice sets the stage for more complex handwriting and mathematical skills later on.
Moreover, engaging in activities like tracing, counting objects, or using manipulatives related to numbers helps reinforce number recognition and understanding, key components of early math literacy. Such activities also improve hand-eye coordination, cognitive development, and spatial awareness. For instance, threading beads while counting or stacking blocks by numbers can enhance both mathematical concepts and fine motor proficiency simultaneously.
Ultimately, honing fine motor skills through number-related activities equips children with the physical dexterity and intellectual foundation needed for academic tasks and everyday functions. Encouraging such development ensures children can comfortably and confidently engage with educational material, fostering a positive attitude towards learning and boosting their overall academic trajectory.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students