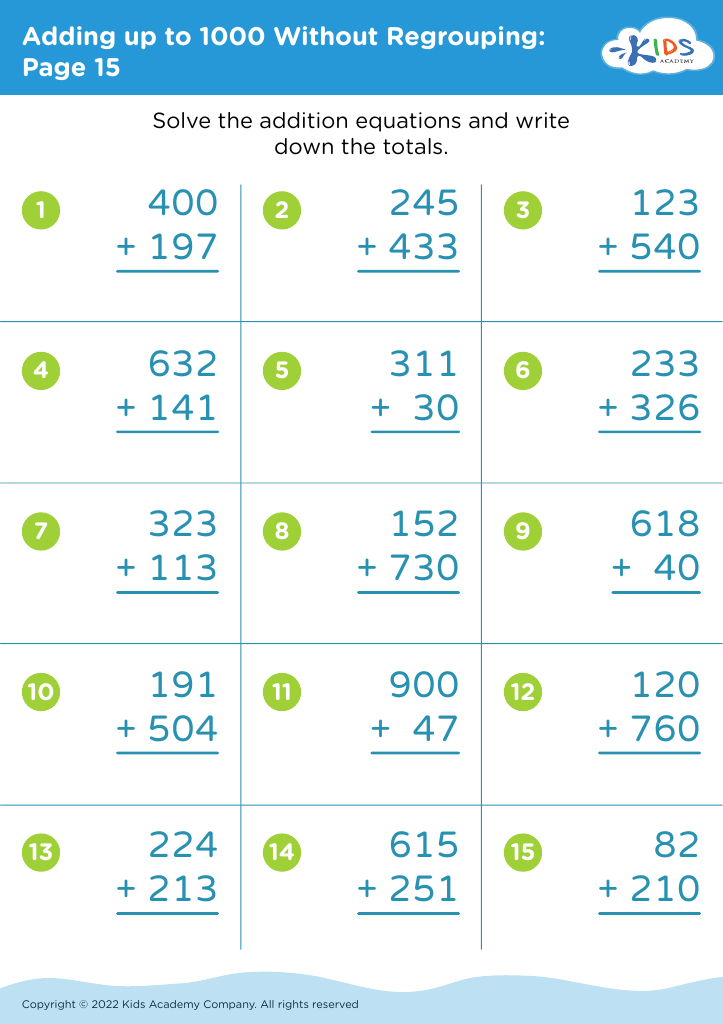
Problem-Solving Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-9 - Page 7
149 filtered results
-
From - To
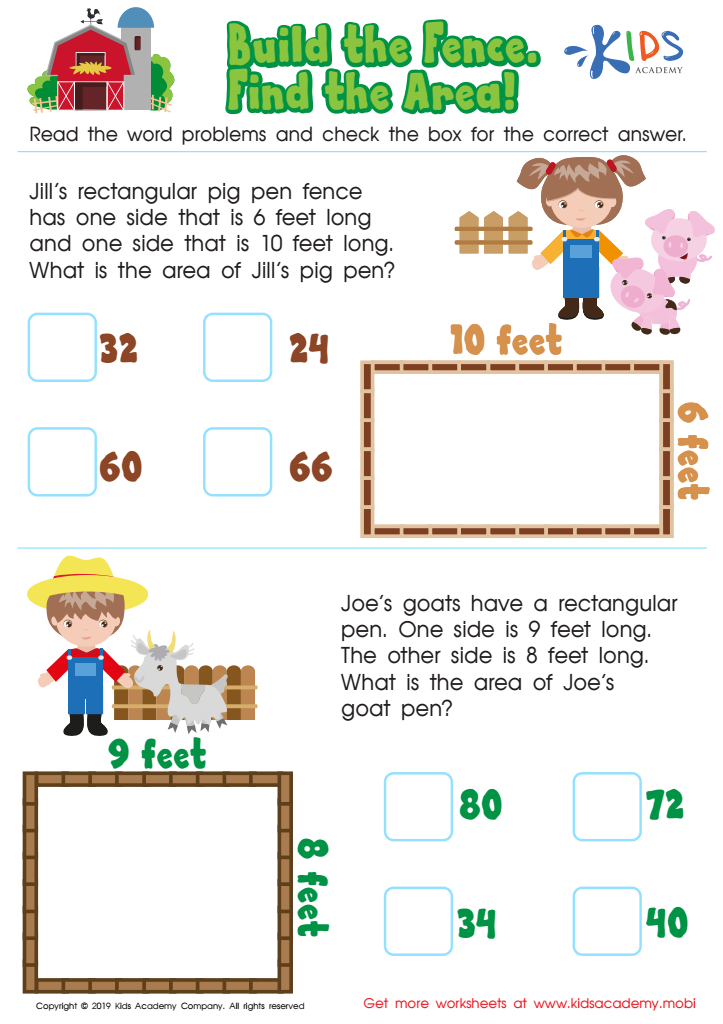

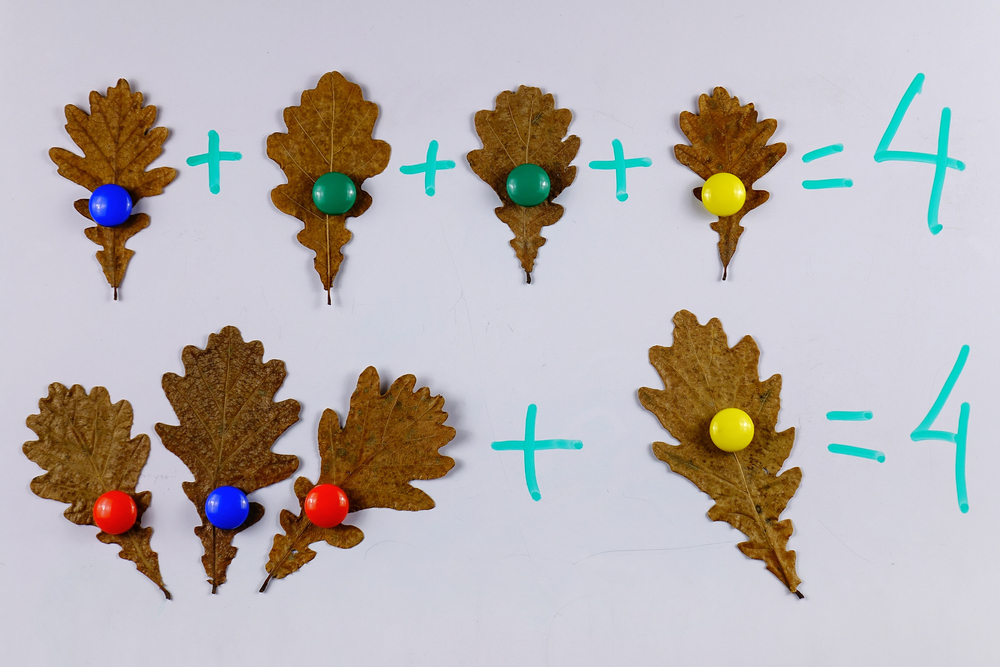
Build the Fence, Find the Area Worksheet
Developing problem-solving skills in children aged 4-9 is crucial for their cognitive, social, and emotional development. First, fostering these skills strengthens a child's ability to think critically and independently. As kids navigate basic addition problems, they learn to analyze, strategize, and derive solutions, laying a strong foundation for mathematical and logical thinking essential in later academic years.
Second, mastering problem-solving in the context of addition enhances self-confidence and persistence. When children successfully tackle a problem, they experience a sense of accomplishment, which encourages them to approach future challenges with optimistic determination. This positive attitude toward problem-solving transcends math, affecting other learning areas.
Lastly, problem-solving activities offer opportunities for collaborative learning and social interaction. Whether working in pairs or small groups, children learn to communicate, share ideas, and listen to others. This collaborative spirit not only makes learning enjoyable but also instills important social skills such as cooperation, patience, and empathy.
Therefore, parents and teachers should prioritize early problem-solving in addition. It not only builds crucial cognitive abilities but also fosters emotional resilience and social competence, preparing children to be well-rounded, resourceful individuals ready to face the complexities of the real world.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students