Number Recognition Adding up to 50 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 5-7
15 filtered results
-
From - To
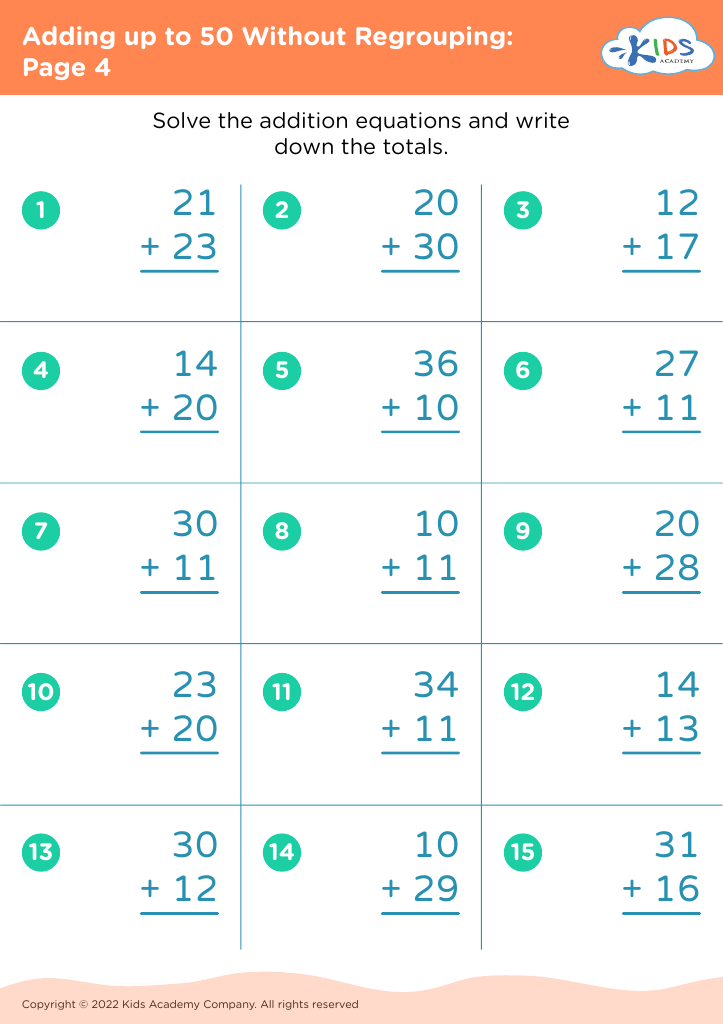
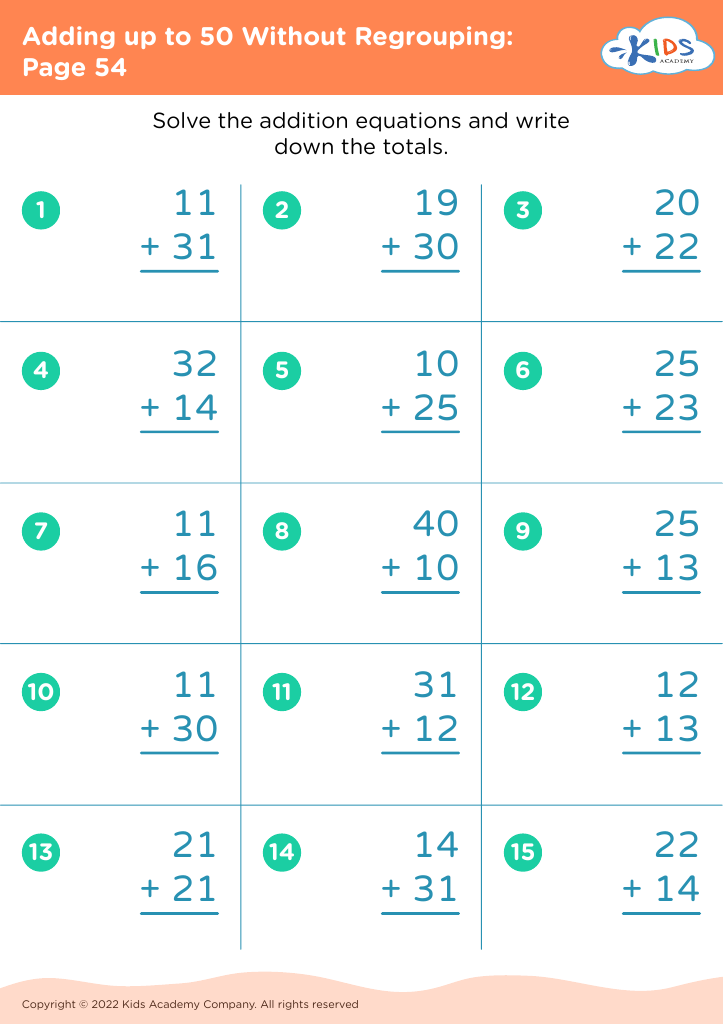
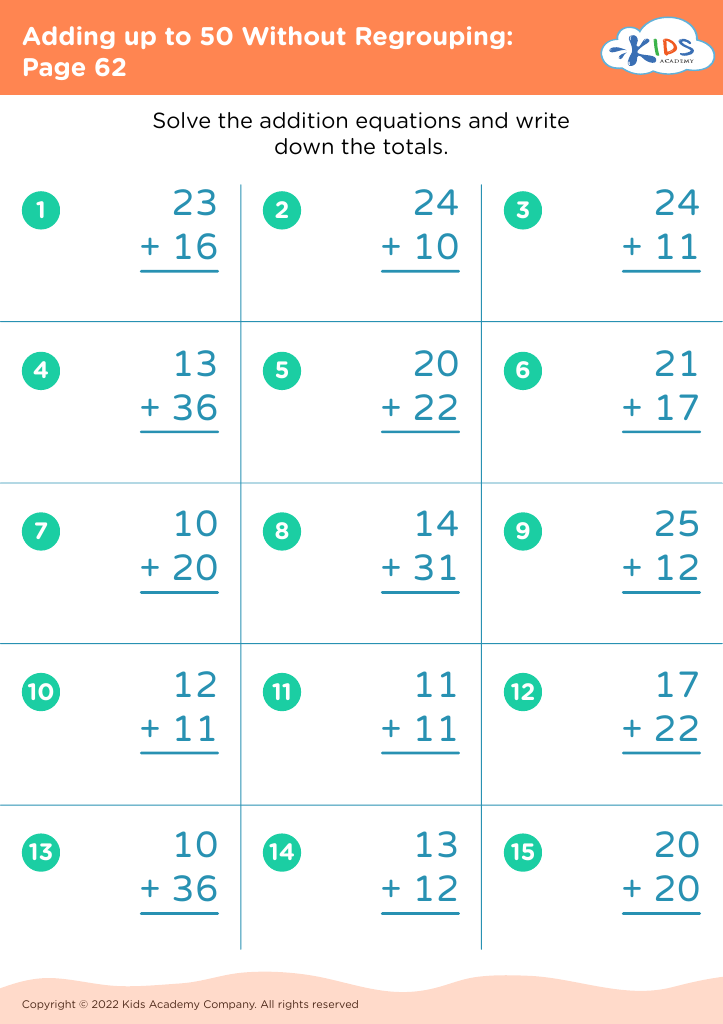
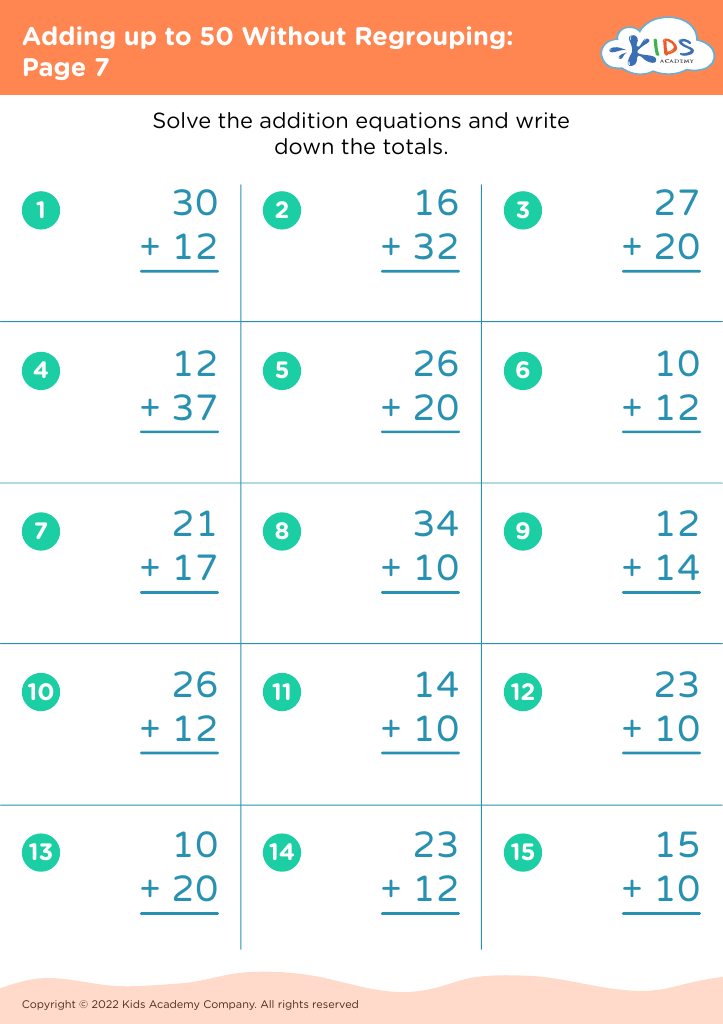
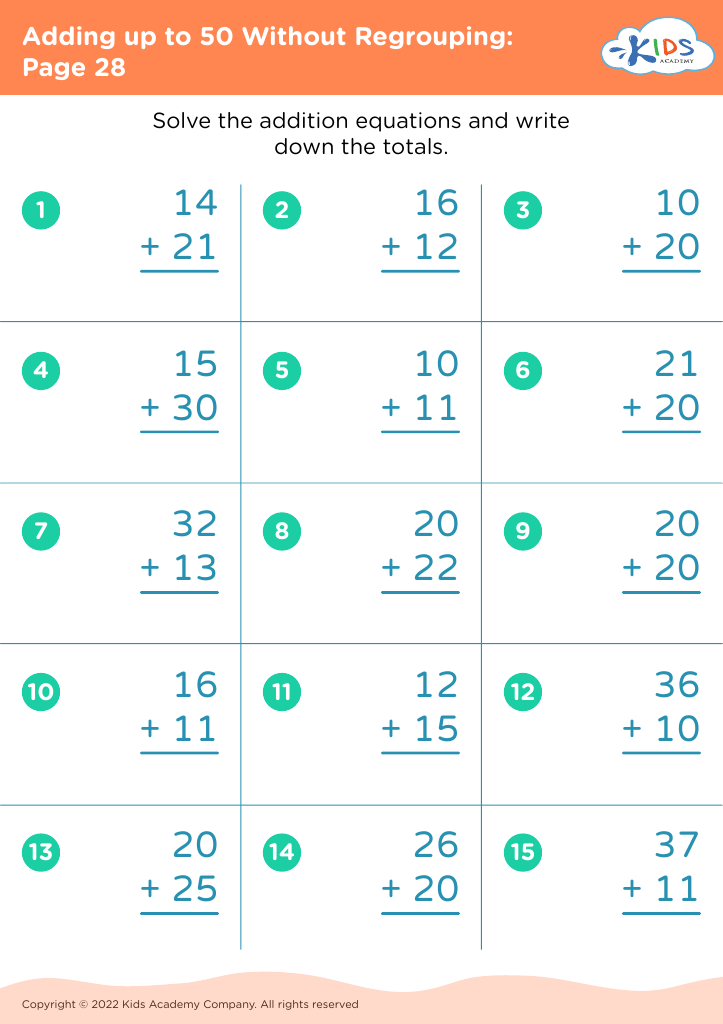
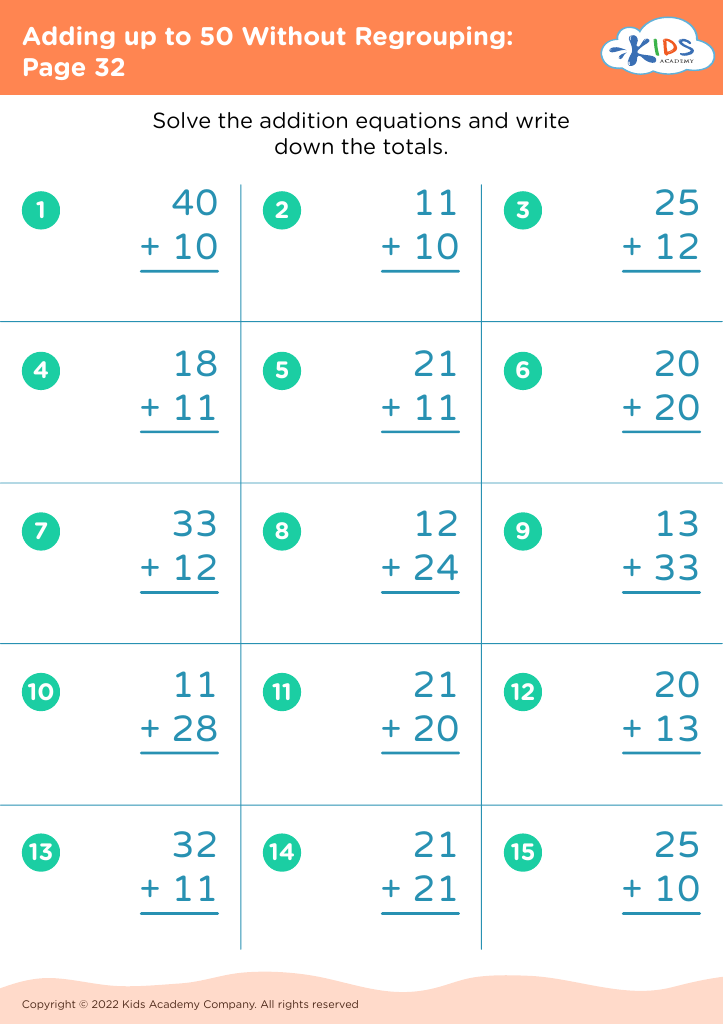
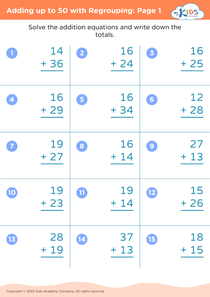
Discover the perfect learning resource for young learners aged 5-7 with our "Number Recognition Adding up to 50 Without Regrouping Worksheets". These engaging worksheets are designed to help children improve their number recognition skills while building confidence in addition. Each activity presents simple, no-regrouping addition problems that gradually increase in difficulty, thereby allowing children to practice at their own pace. By focusing on sums up to 50, these worksheets ensure foundational math skills are strengthened for future learning. Ideal for classroom or home use, these printable resources provide a fun and interactive way to support your child's math journey.
Number recognition and the ability to add numbers up to 50 without regrouping are fundamental skills that form the cornerstone of early mathematics education for children aged 5-7. This age-appropriate arithmetic promotes cognitive development and provides a foundation for more complex mathematical concepts.
Firstly, mastering number recognition enables students to understand numerical relationships and sequences. It enhances their ability to follow instructions involving numbers, such as games, activities, and practical tasks, thereby reinforcing everyday life skills.
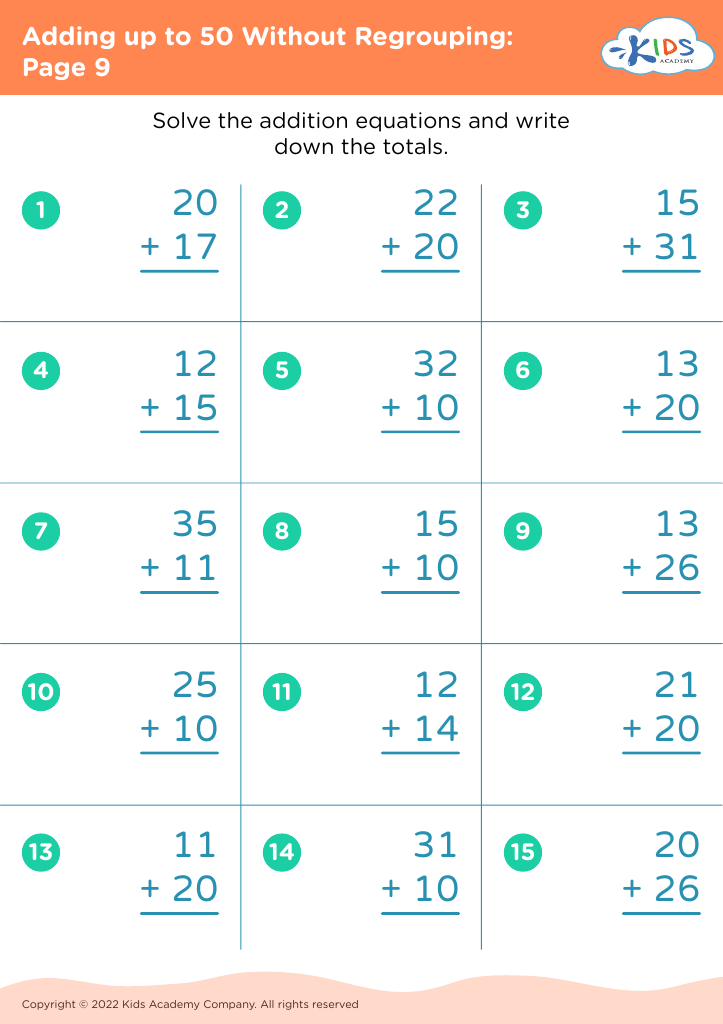
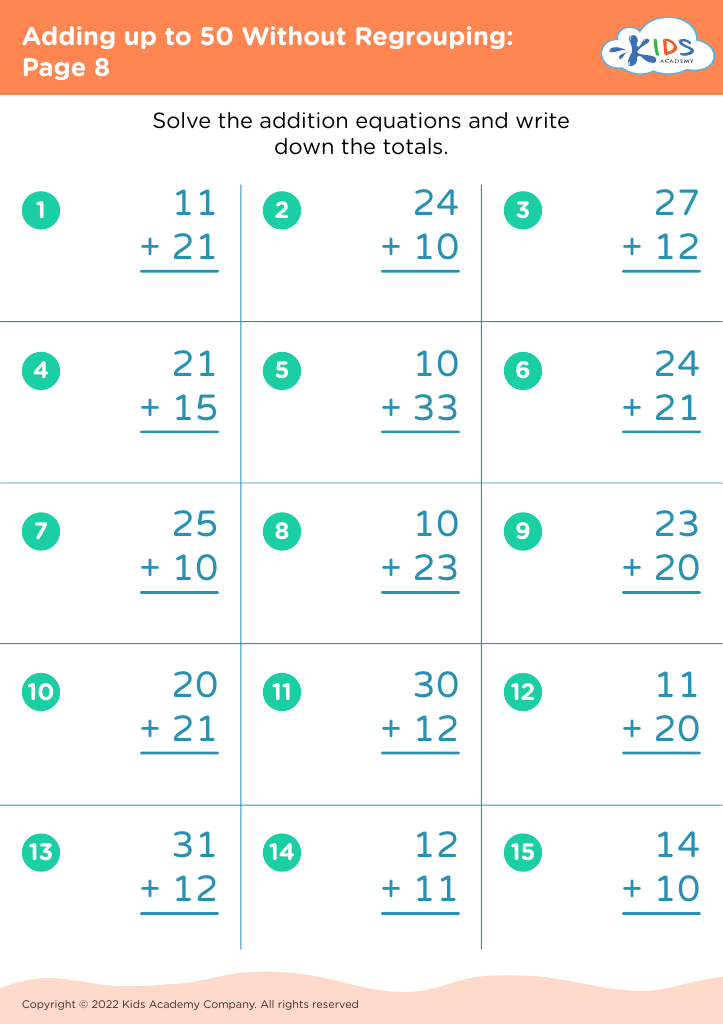
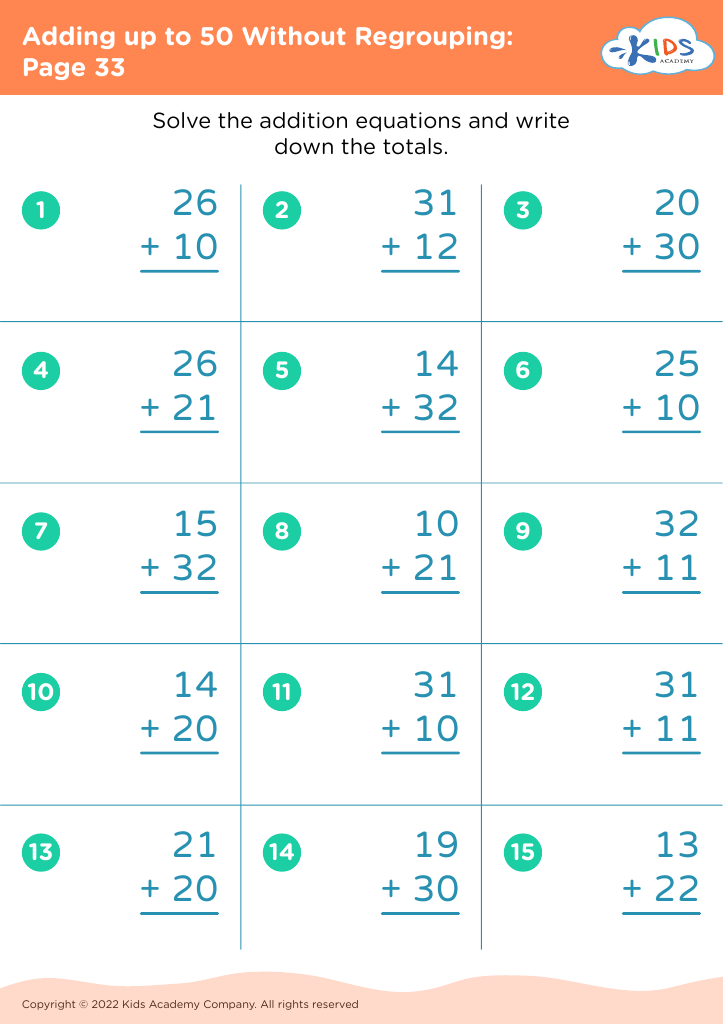
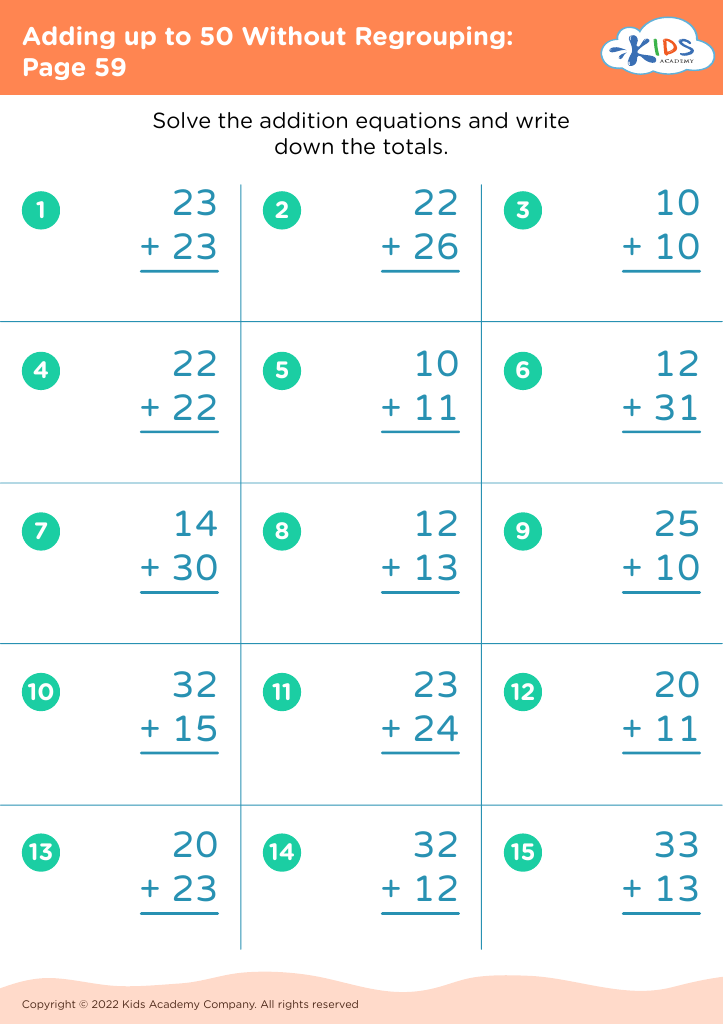
When children learn to add numbers up to 50 without regrouping (carrying), they're developing basic computation skills that boost their confidence and competency in handling math problems. This process aids mental math abilities, enabling kids to perform calculations in their heads, thus improving their overall academic performance and fostering independent problem-solving capabilities.
Moreover, engaging in these numeric exercises helps children hone their concentration, attention to detail, and systematic thinking. By presenting arithmetic challenges appropriate to their cognitive level, parents and teachers can nurture a positive attitude towards mathematics. This mitigates math anxiety, a common issue in later school years.
Investing in these fundamental skills establishes a groundwork upon which more sophisticated math skills can effectively build. Teachers and parents who prioritize such early numeracy education indirectly equip children with the tools needed for long-term academic success and daily practical use.