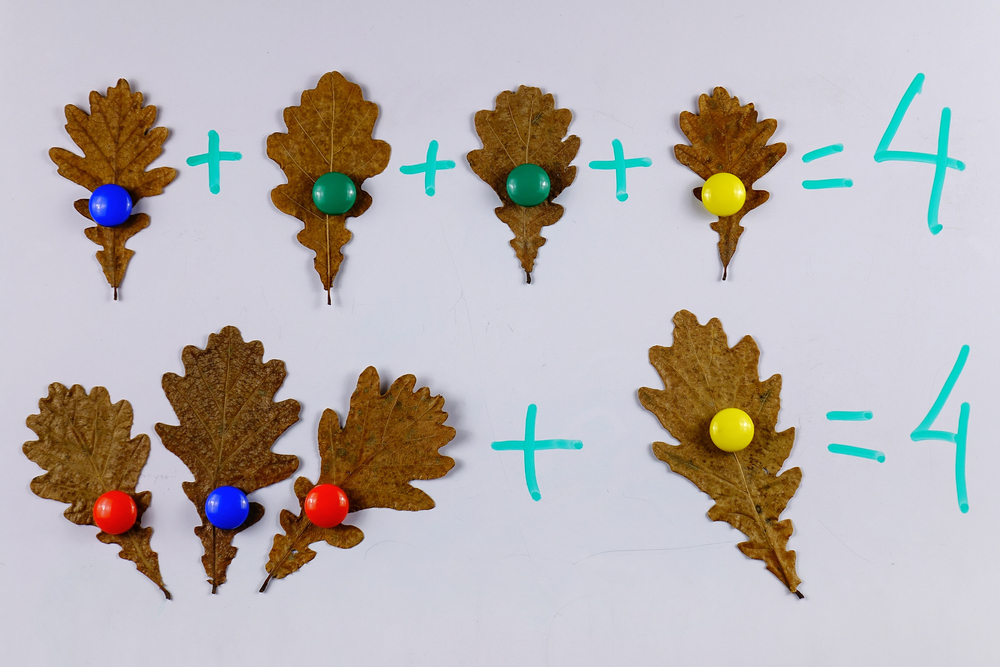
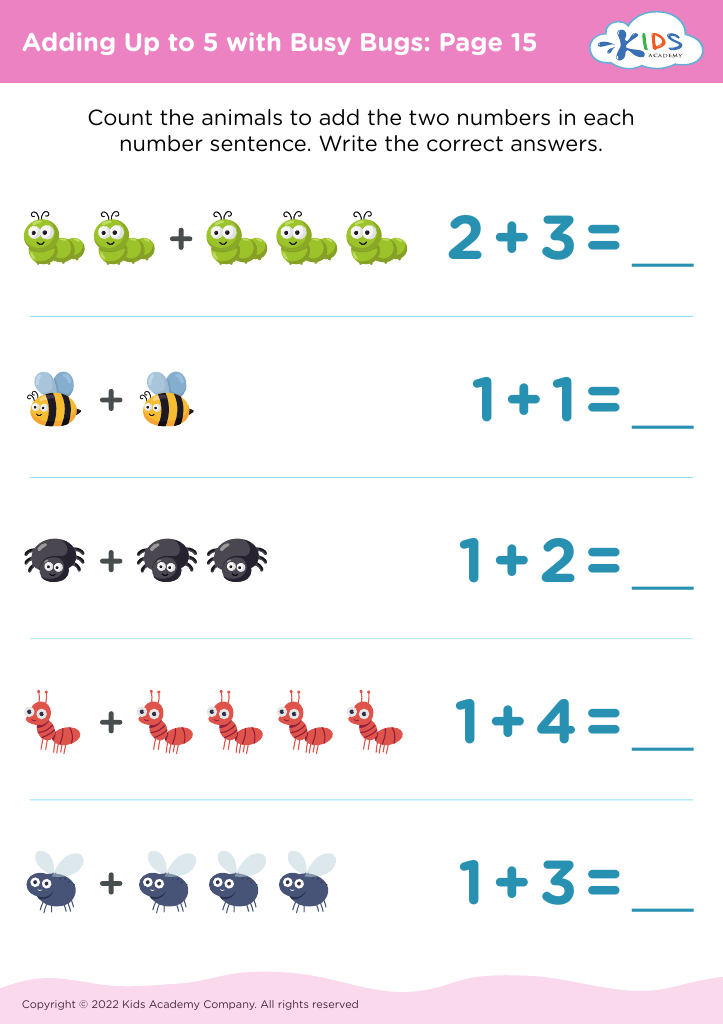
Understanding quantity and addition for children aged 5-8 is crucial for several reasons, both for parents and teachers. At this developmental stage, children are building foundational mathematical concepts that are essential for future learning. Grasping these early concepts sets a solid groundwork for more complex problem-solving and reasoning skills.
Firstly, understanding quantity helps children make sense of the world around them. It aids them in making everyday decisions, like determining how many apples they need to share equally with friends. These real-life applications make learning relevant and engaging.
Secondly, mastering addition and understanding quantity contribute to a child's confidence in math. Early success in arithmetic helps build a positive attitude toward math, reducing anxiety and fostering a mindset geared toward lifelong learning and curiosity.
Moreover, comprehension in these areas nurtures logical thinking and cognitive development. Tasks such as grouping objects, counting, and solving simple addition problems enhance critical thinking and analytical skills.
Lastly, early proficiency in math is closely linked to academic achievement in later years. Children who have a robust understanding of basic math skills often perform better in school overall. Therefore, parents and teachers should prioritize helping children aged 5-8 develop a strong grasp of quantity and addition, as it is integral to their educational and personal growth.