Mathematical reasoning Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 5-8
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging Mathematical Reasoning Subtraction Worksheets designed specifically for children aged 5-8! These worksheets promote critical thinking and enhance problem-solving skills while making subtraction fun. Your child will encounter a variety of exercises that challenge them to apply their knowledge in practical scenarios, fostering a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts. From simple equations to word problems, each worksheet aims to boost confidence and competence in subtraction. Perfect for classroom use or home study, our resources enjoy vibrant illustrations that captivate young learners, making math enjoyable. Equip your child with essential skills today and watch them flourish in their mathematical journey!
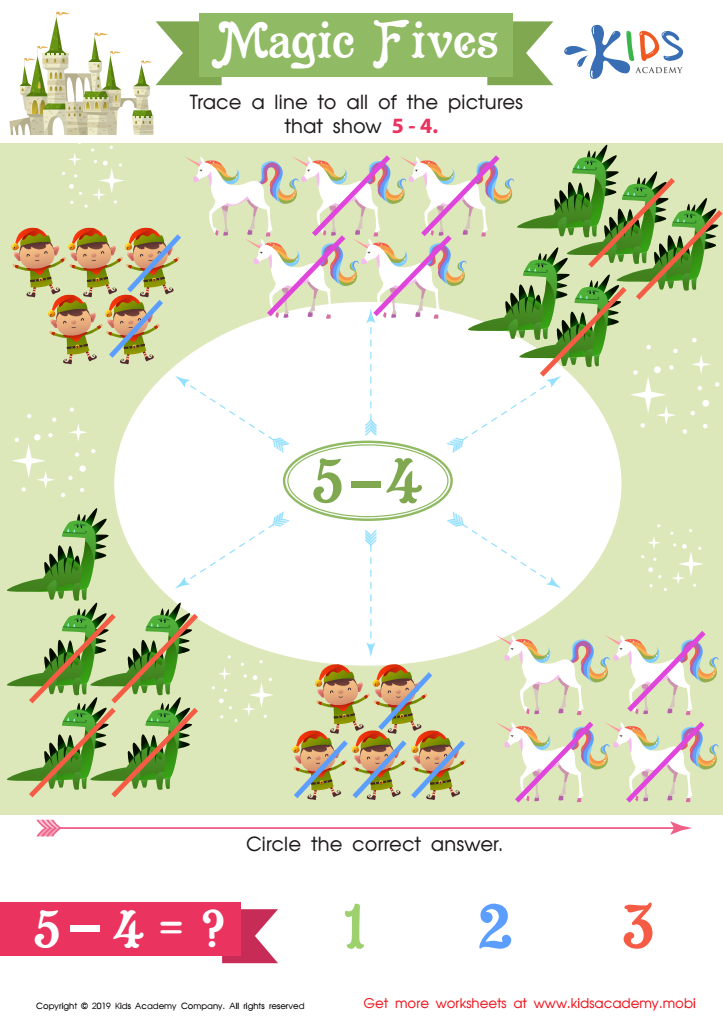

Magic Fives Worksheet
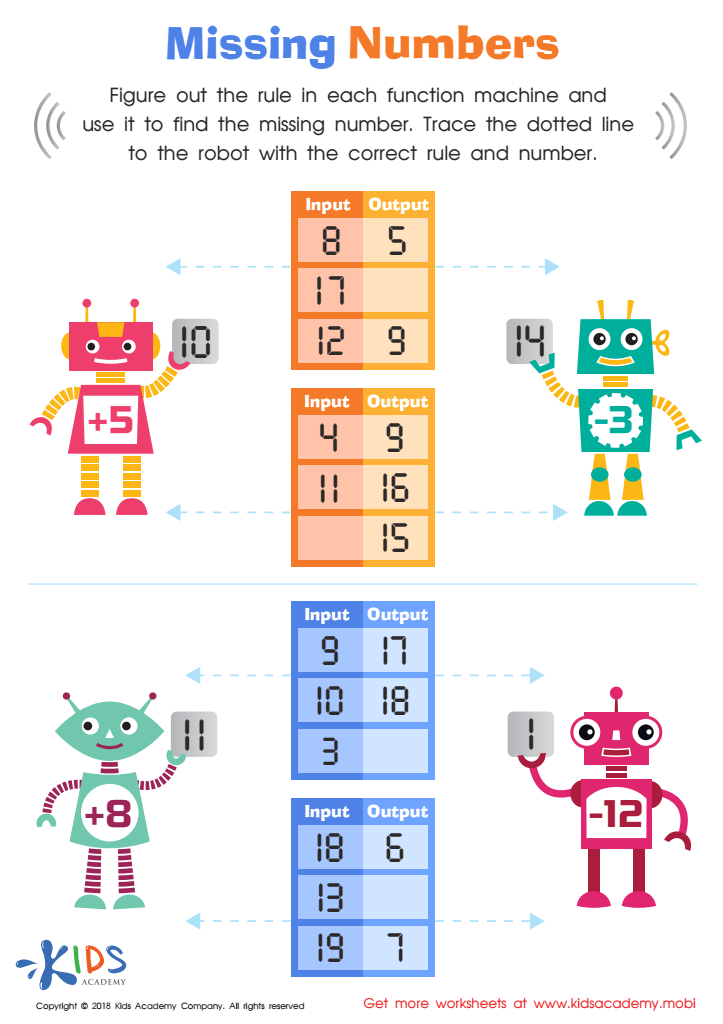

Missing Numbers Worksheet
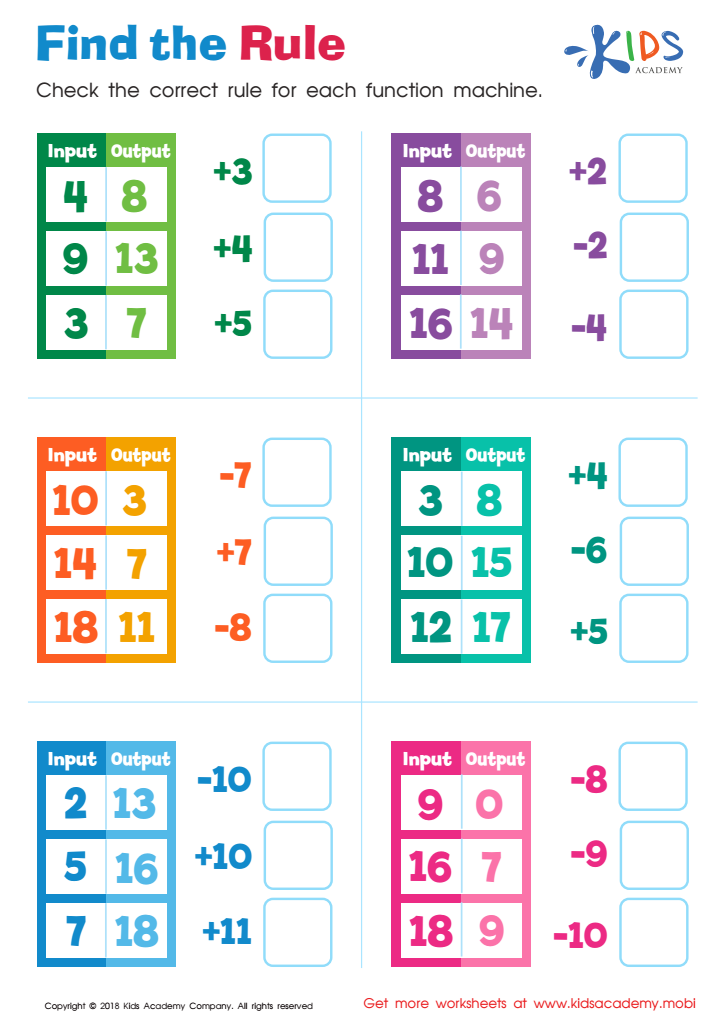

Find the Rule Worksheet
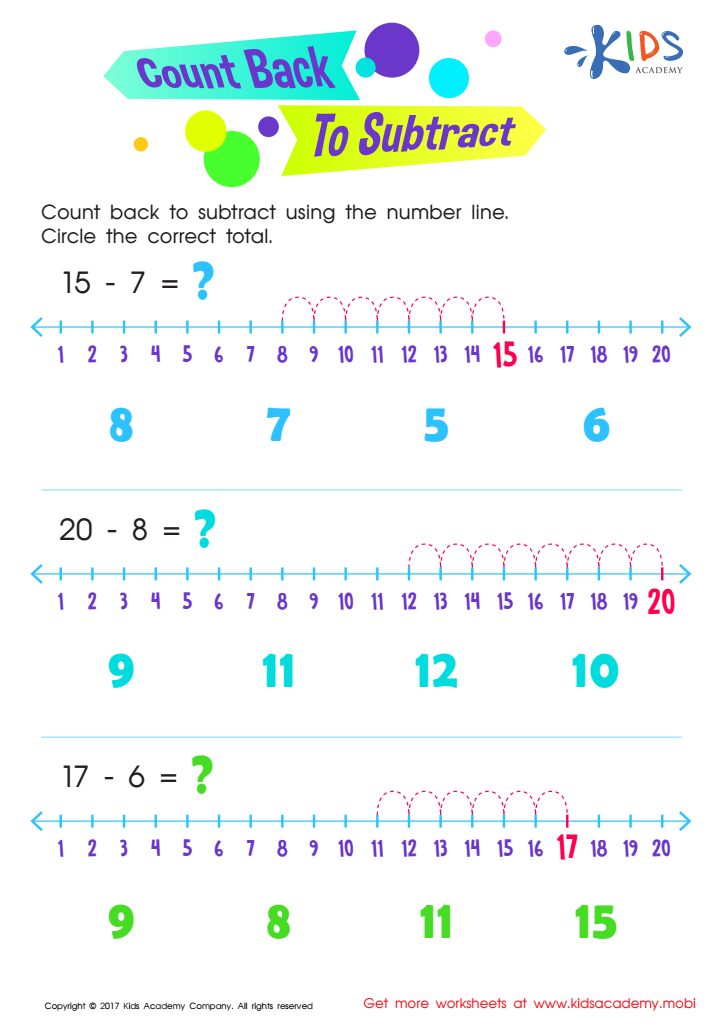

Count Back to Subtract Substraction Worksheet

Addition or Subtraction? Worksheet


Jungle Subtraction Word Problems Substraction Worksheet
Parents and teachers should care about mathematical reasoning in subtraction for children aged 5-8 because it lays the foundation for future mathematical understanding and problem-solving skills. At this developmental stage, children are not just learning to subtract but are also grasping the concept of quantity, relationships between numbers, and the idea of 'how many are left.' This stage of learning encourages them to think critically and develop reasoning abilities that are crucial for more advanced mathematics.
Recognizing the significance of subtraction helps children interpret real-world situations. When they learn to subtract by relating it to everyday scenarios—like sharing snacks or counting toys—they get a practical understanding of how math operates in daily life.
Moreover, fostering mathematical reasoning enhances their confidence in learning; as students learn various strategies for subtraction—such as counting back or using visual aids—they become more resilient in tackling numbers and engaging in discussions about their thought process.
In essence, nurturing mathematical reasoning in subtraction not only enriches a child's academic repertoire but also cultivates a love for learning, equips them with life skills, and prepares them for future challenges in mathematics and beyond. By prioritizing this aspect of math education, adults can support children in becoming proficient and confident learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















