Fine Motor Skills Geometry Worksheets for Ages 5-9 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To


Patchwork Math Worksheet
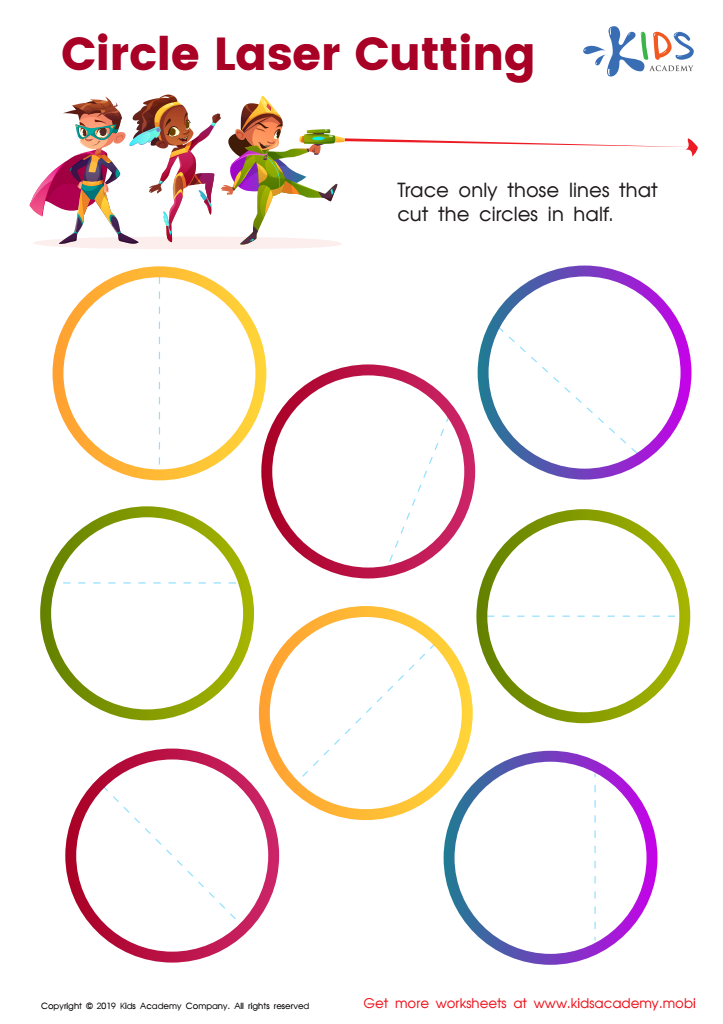

Circle Laser Cutting Worksheet

Build and Match Worksheet
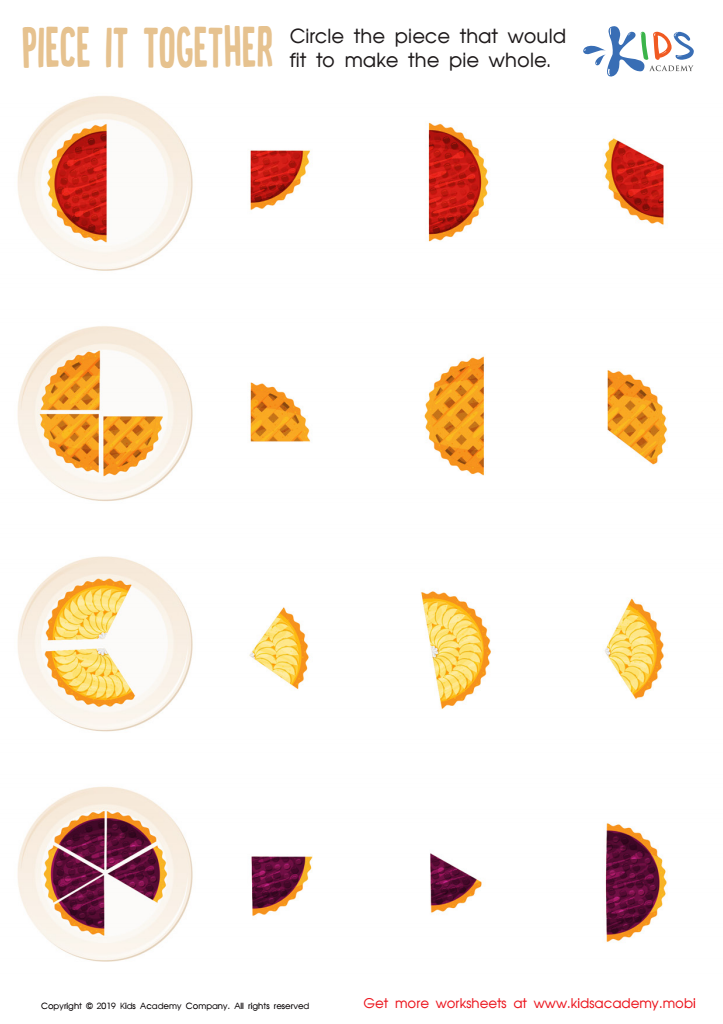


Piece it together Worksheet

Construction Shapes Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for children aged 5-9, particularly in their exploration of geometry. These skills involve the coordinated use of small muscles in the hands and fingers, essential for tasks such as drawing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. As children engage with geometric concepts, such as shapes, angles, and spatial relationships, fine motor skills enable them to create, visualize, and understand these shapes through hands-on activities.
Encouraging fine motor development through geometry not only supports children's cognitive growth but also enhances their problem-solving abilities. When children construct shapes using tools like scissors, rulers, and building blocks, they strengthen their understanding of geometric principles while refining their dexterity. This tactile experience is foundational for future academic learning in mathematics and art.
Additionally, fine motor skills are linked to self-regulation and concentration, allowing children to focus longer on tasks. Parents and teachers who emphasize fine motor skill development within the context of geometry can contribute to a more well-rounded education. This not only prepares children academically but also fosters creativity and critical thinking, equipping them with essential skills for their future. In essence, investing in both fine motor skills and geometry lays the groundwork for holistic development and lifelong learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students