Spelling Skills Reading Worksheets for Ages 5-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child’s spelling skills with our engaging Spelling Skills Reading Worksheets designed for ages 5-9. These worksheets provide a fun and interactive way for young learners to master spelling through a variety of activities, including fill-in-the-blank exercises, word matching, and puzzles. Each worksheet is crafted to support critical reading and writing skills in an enjoyable manner, making learning both effective and enjoyable. Our resources cater to different learning styles, ensuring personalized progression. Perfect for use at home or in the classroom, these worksheets will help build your child's confidence in spelling, laying a solid foundation for future literacy success!
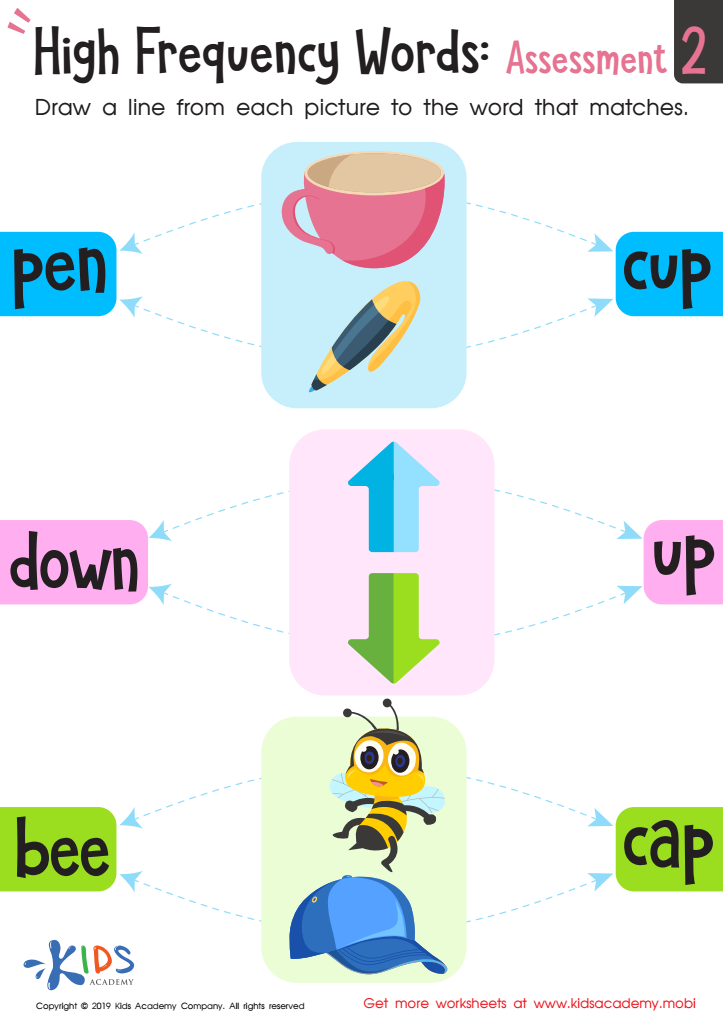

High Frequency Words: Assessment 2 Worksheet


First Words Worksheet


Upon, Around, Off Sight Words Worksheet
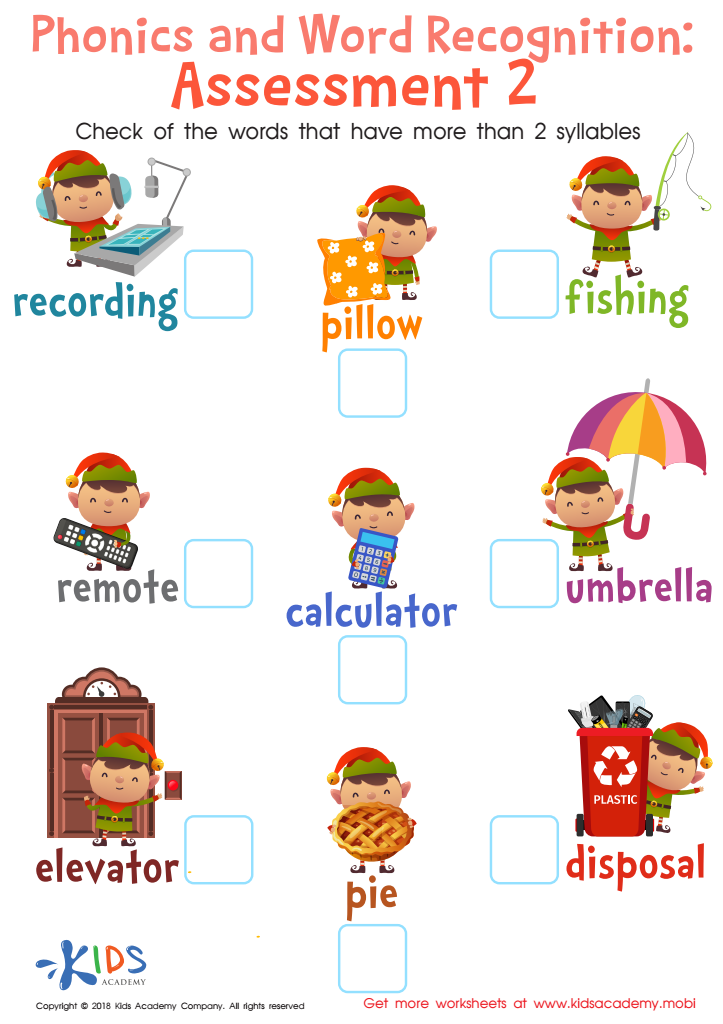

Phonics and Word Recognition: Assessment 2 Worksheet
Spelling skills are foundational for children's literacy development, especially for those aged 5 to 9. This stage is crucial, as children are transitioning from learning to read to reading to learn. Mastering spelling supports reading fluency and comprehension. When children are familiar with letter-sound relationships, they become better readers, enabling them to decode new words easily.
Moreover, spelling skills promote writing confidence. Children who can spell words accurately can focus on their ideas, leading to clearer communication rather than getting bogged down by the mechanics of writing. Strong spelling enhances vocabulary acquisition, as students are more likely to encounter and remember words they can spell.
Parents and teachers play a vital role in fostering these skills through engaging activities like word games, reading aloud, and encouraging daily writing practices. Good spelling fosters a sense of achievement in children, building their self-esteem and enthusiasm for learning. By emphasizing spelling alongside reading, parents and teachers give children essential tools that not only aid their current educational journey but also prepare them for future academic success. Therefore, cultivating spelling skills should be a priority for every educator and caregiver who aims to support literacy development in young learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students