Fine Motor Skills English for Beginners Worksheets for Ages 6-7 - Page 3
62 filtered results
-
From - To


White Tracing Color Words Worksheet
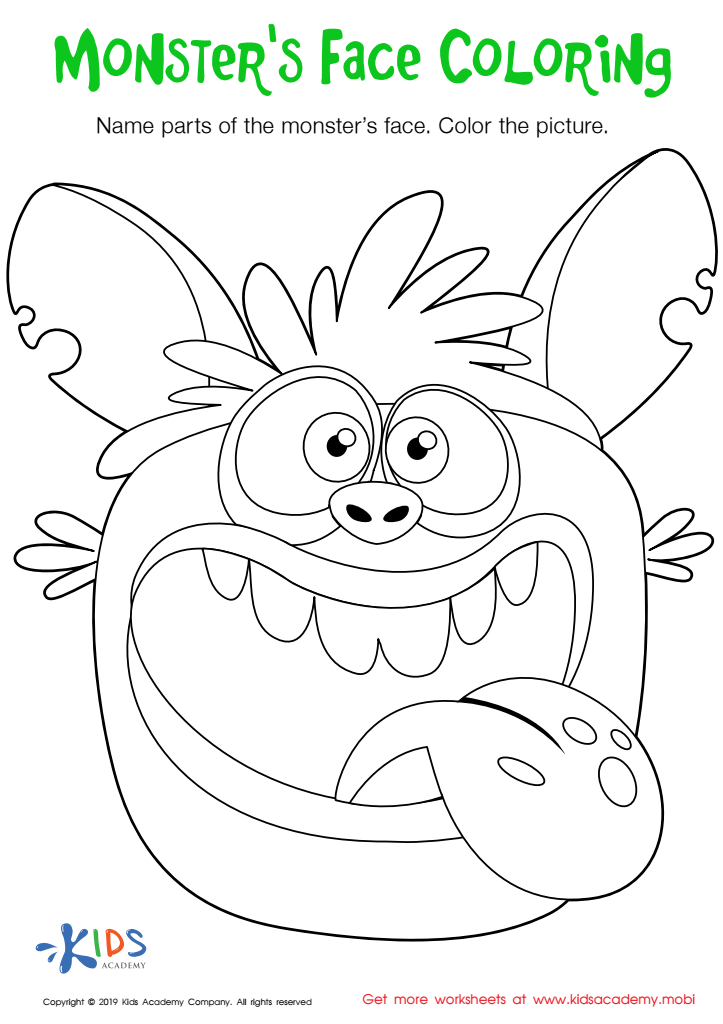


Monster's Face Coloring Worksheet


Letter G Coloring Sheet


Letter Z Coloring Sheet


Letter J Coloring Sheet
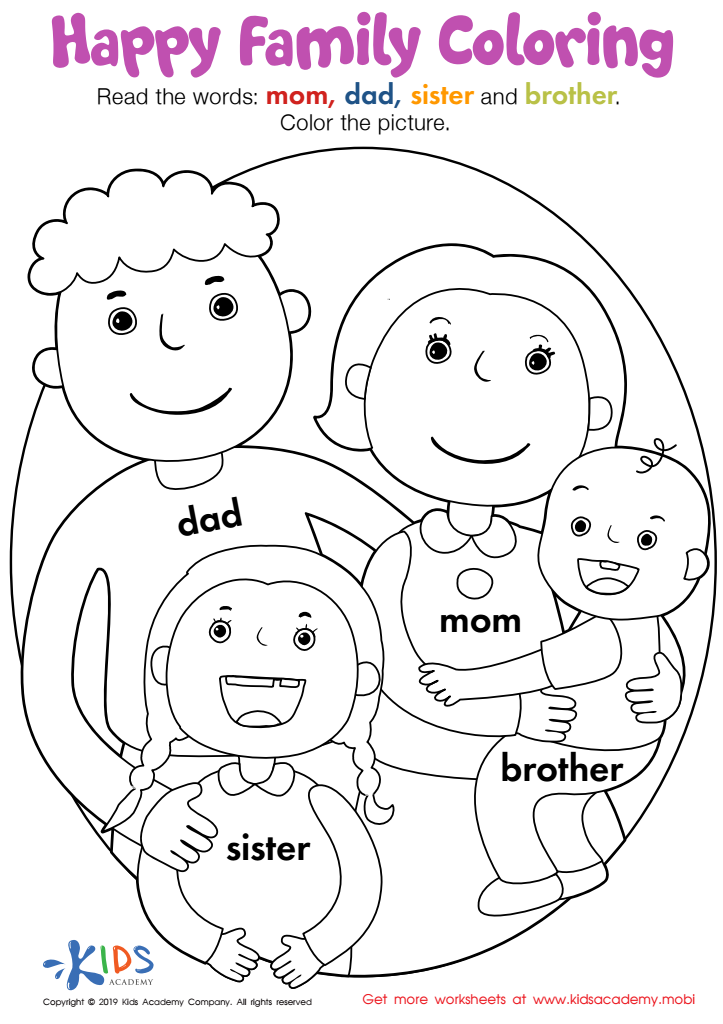


Happy Family Coloring Worksheet

Letter Y Coloring Sheet


Learn to Write the Number 2 Worksheet


Letter F Tracing Page


White and Pink Coloring Fun Worksheet

Letter F Coloring Sheet

Letter T Tracing Page


Letter N Coloring Sheet


Letter D Tracing Page
Fine motor skills are crucial in early childhood development, specifically for children aged 6-7, as they build the foundation for everyday tasks and academic success. These skills involve the small muscles in the hands and fingers, and their development directly impacts a child's ability to perform essential tasks such as writing, cutting, buttoning clothes, and tying shoelaces. Proficiency in fine motor skills supports more precise and controlled hand movements, which is critical in learning to write legibly and efficiently.
For ages 6-7, when children's formal schooling typically begins, embedding fine motor skills in English learning can significantly enhance their educational journey. Writing letters, forming words, and expressing thoughts clearly are integral parts of English learning. When children engage in activities like tracing letters, cutting shapes, or holding a pencil correctly, they are simultaneously improving their hand-eye coordination and dexterity.
Developing fine motor skills early on also boosts a child's self-esteem and independence, as they can manage self-care tasks without constant adult assistance. This progression supports their emotional and social growth and sets a vital precedent for a positive attitude towards learning. Therefore, prioritizing fine motor skills development helps pave the way for academic success and self-sufficiency, making it a key area of focus for parents and teachers.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students












