Develop fine motor skills Adding up to 100 Worksheets for Ages 6-8
5 filtered results
-
From - To
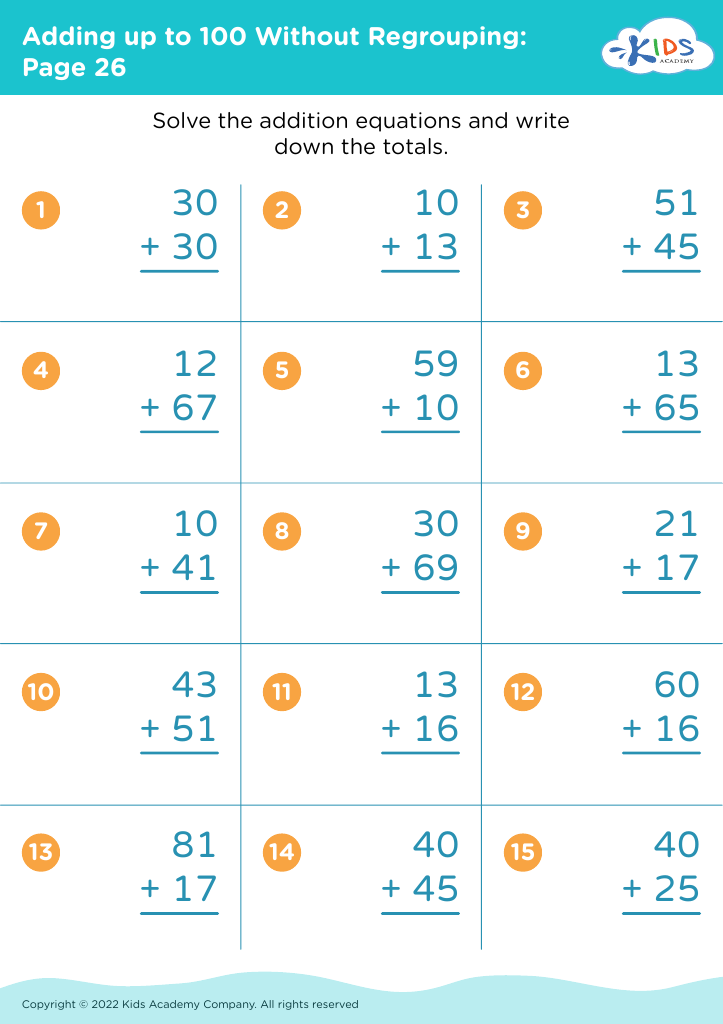
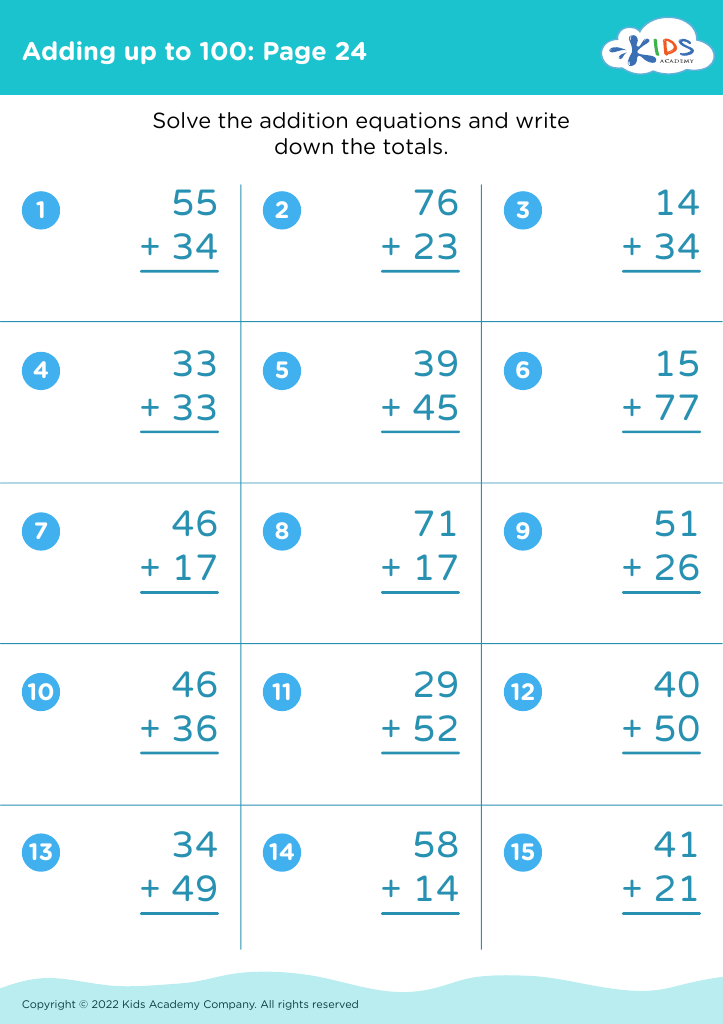
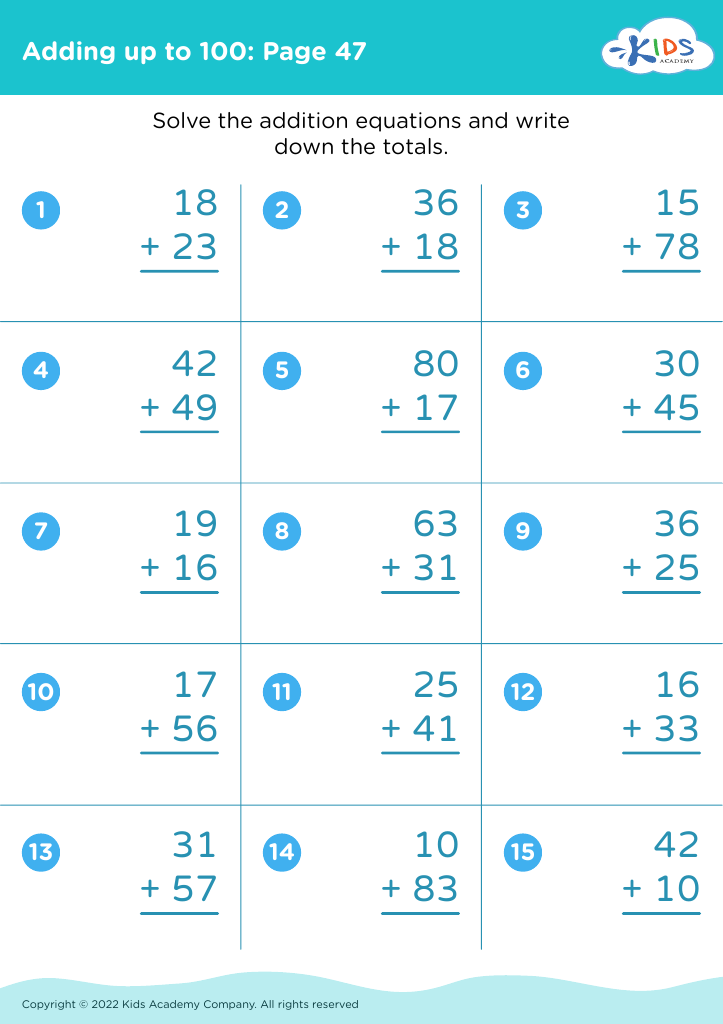
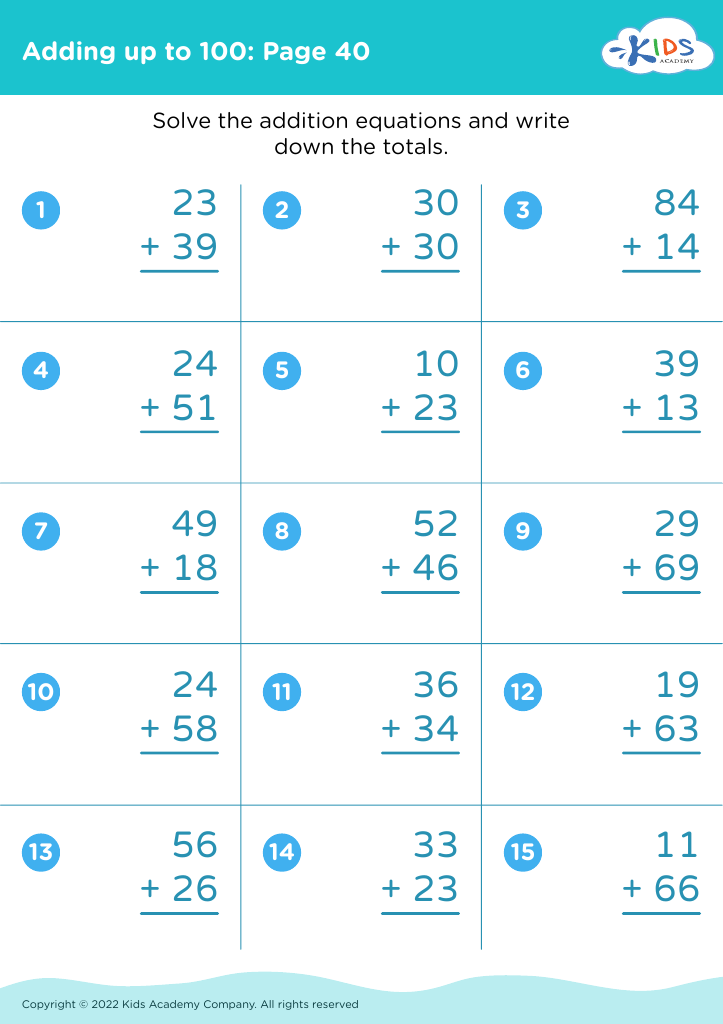
Discover the essential worksheets for developing fine motor skills in children ages 6-8 with our "Adding Up to 100" collection. These engaging activities are designed to enhance hand-eye coordination and dexterity while helping young learners master addition concepts. Through fun, interactive exercises, children will practice writing numbers, manipulating pencil grip, and tracing lines, all while reinforcing their understanding of addition up to 100. These thoughtfully created worksheets not only support academic growth but also promote confidence and independence in young learners. Download now to provide your child with the tools they need for success in math and fine motor skill development!
Developing fine motor skills is crucial for children aged 6 to 8, as it lays the groundwork for various academic and everyday tasks. Fine motor skills involve the use of small muscles in the hands and fingers, and mastering these skills enables children to perform vital activities, such as writing, drawing, cutting, and tying shoelaces. When children can manipulate objects with precision, their confidence in performing academic tasks, particularly in writing and art, significantly increases.
For parents and teachers, fostering fine motor skills is essential not only for academic success but also for enhancing children's cognitive and social development. Engaging activities like cutting with scissors, threading beads, and playing with clay promote focus, patience, and problem-solving abilities. These skills contribute to higher achievement in school settings, making children more adept at completing assignments and participating in hands-on learning experiences.
Moreover, strong fine motor skills may positively affect children's self-esteem and independence, allowing them to complete tasks independently, from dressing to personal hygiene. Investing in fine motor skill development creates a strong foundation for lifelong learning and daily living skills, ultimately equipping children with the tools they need to thrive in both academic and personal contexts.





%20(1).jpg)










