Enhance fine motor skills Adding up to 100 Worksheets for Ages 6-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance fine motor skills with our engaging "Adding Up to 100" worksheets, specially designed for children aged 6-8. These printable activities provide a fun and interactive way to strengthen hand-eye coordination and improve dexterity while practicing essential math skills. Each worksheet features colorful illustrations and varied exercises that invite children to use scissors, crayons, and manipulatives, making learning enjoyable and effective. As kids add numbers together to reach 100, they will also refine their grip and control, laying a strong foundation for future writing and crafting. Explore our collection today and watch your child's fine motor skills flourish alongside their math abilities!
Enhancing fine motor skills in children aged 6-8 is crucial for their overall development and academic success. Fine motor skills refer to the ability to perform small movements with the hands and fingers, which are essential for everyday tasks such as writing, buttoning shirts, and using utensils. As children in this age group grow, they are often exposed to more complex academic activities that require precision and control.
Moreover, improving fine motor skills can foster independence and confidence in children. Mastering tasks like drawing and crafting encourages creativity and self-expression, while also preparing them for future learning in areas like mathematics and science. For instance, fine motor skills play a vital role in activities such as counting and manipulating small objects, thus laying the groundwork for a solid understanding of numeracy and literacy.
Moreover, developing these skills needed for physical tasks is also linked to increased brain development. Engaging in activities that refine fine motor skills can contribute to cognitive growth and enhance focus, which are vital traits for success in school. Therefore, parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skill development to support children’s essential life skills, academic achievement, and overall confidence.

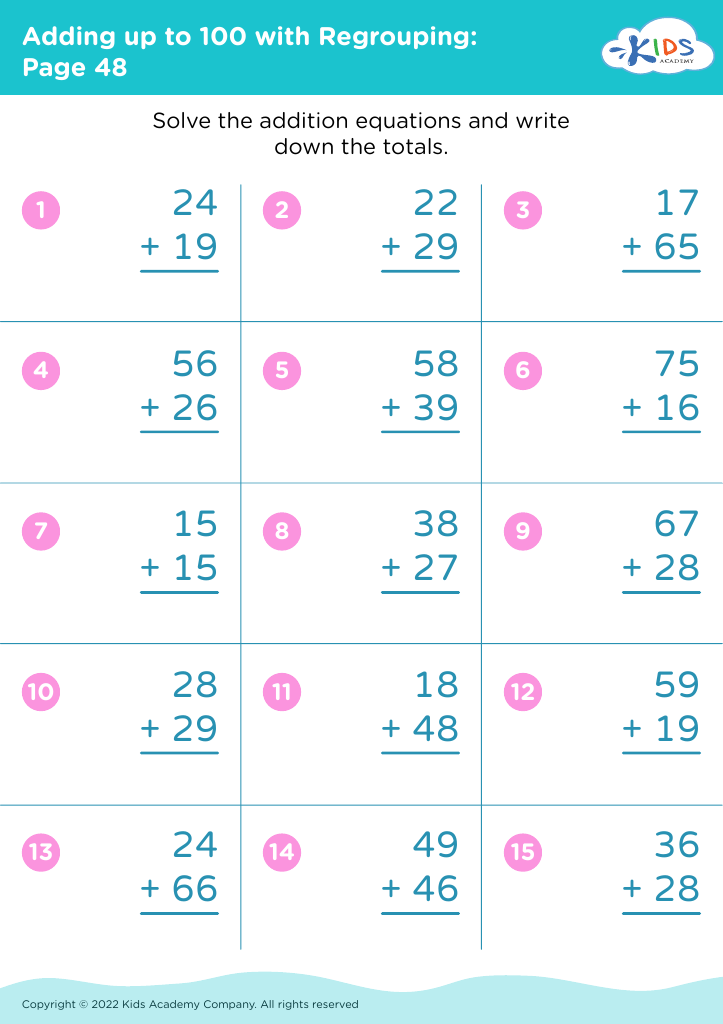
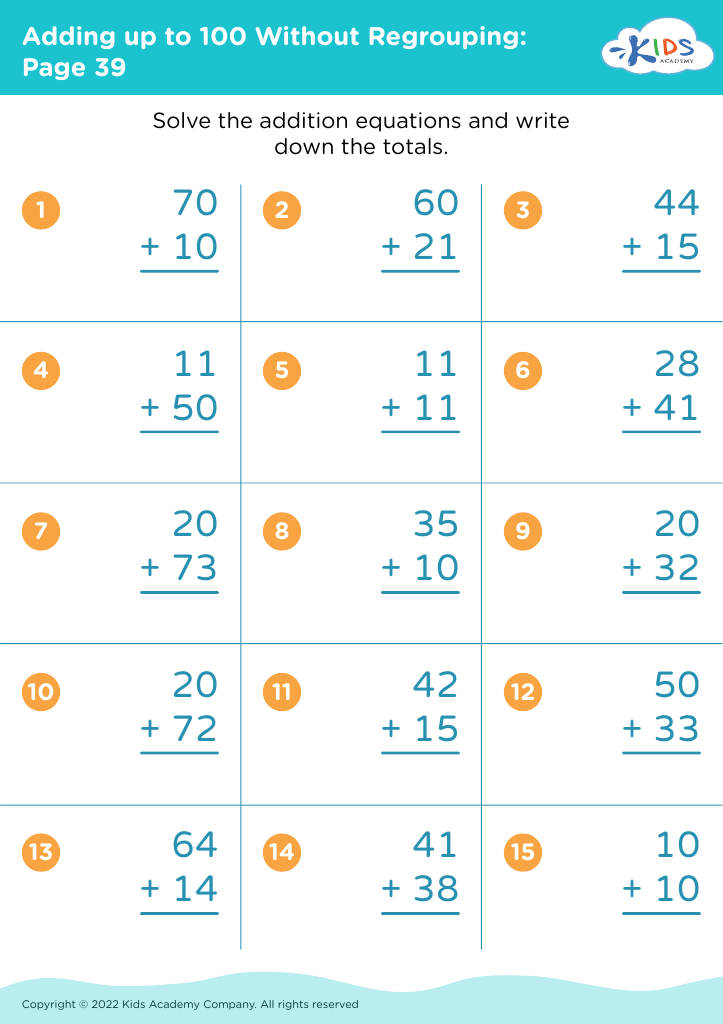
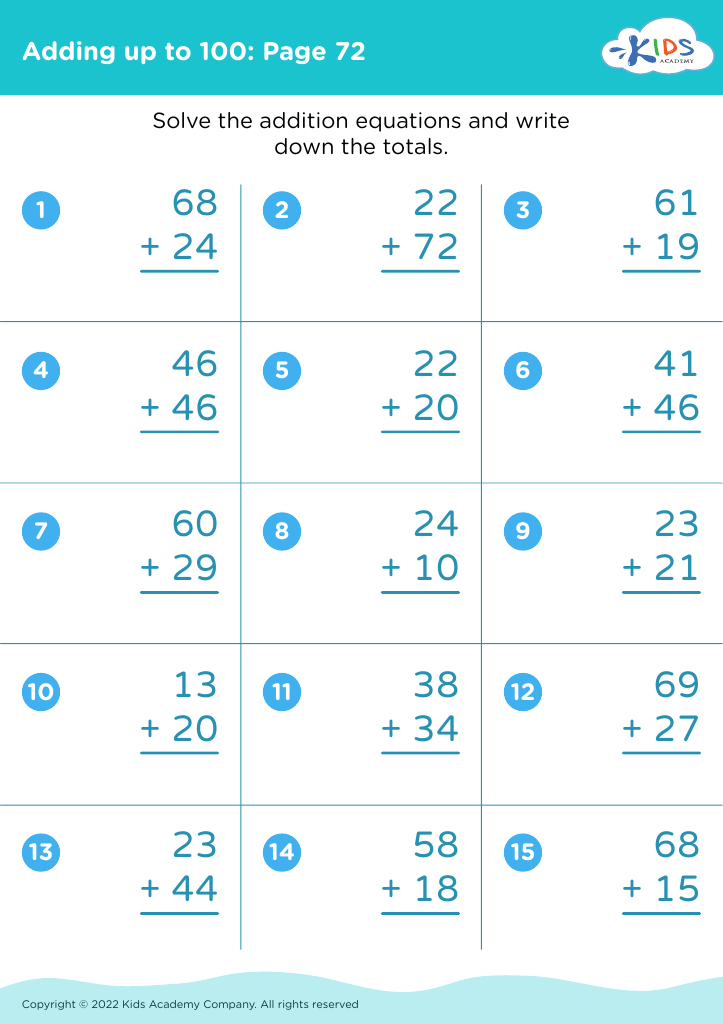





%20(1).jpg)









