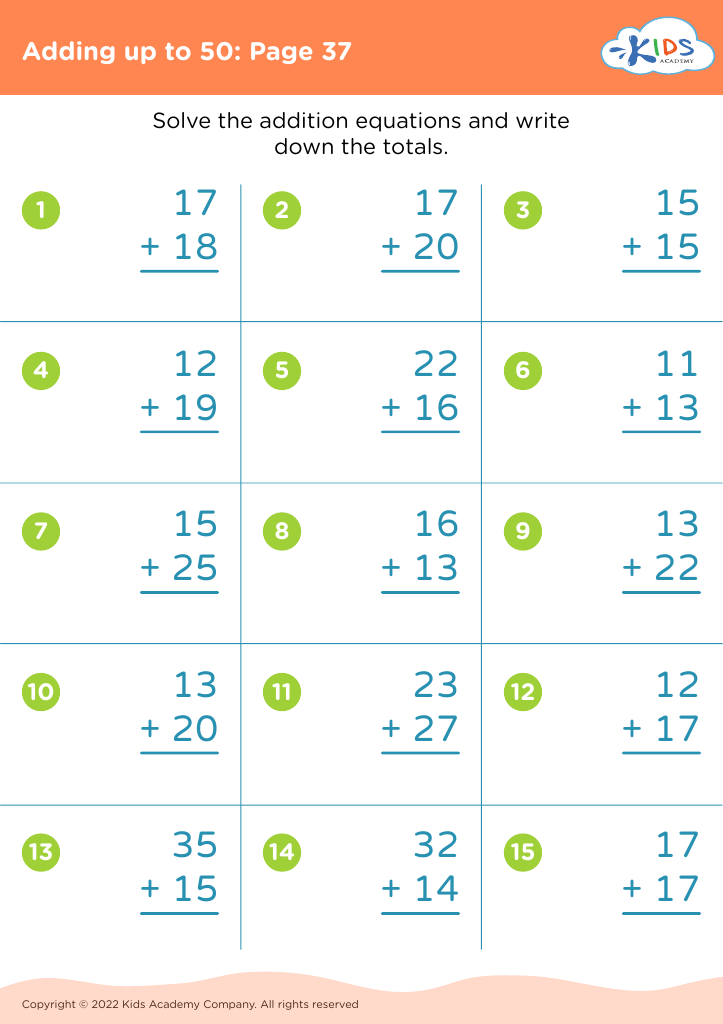
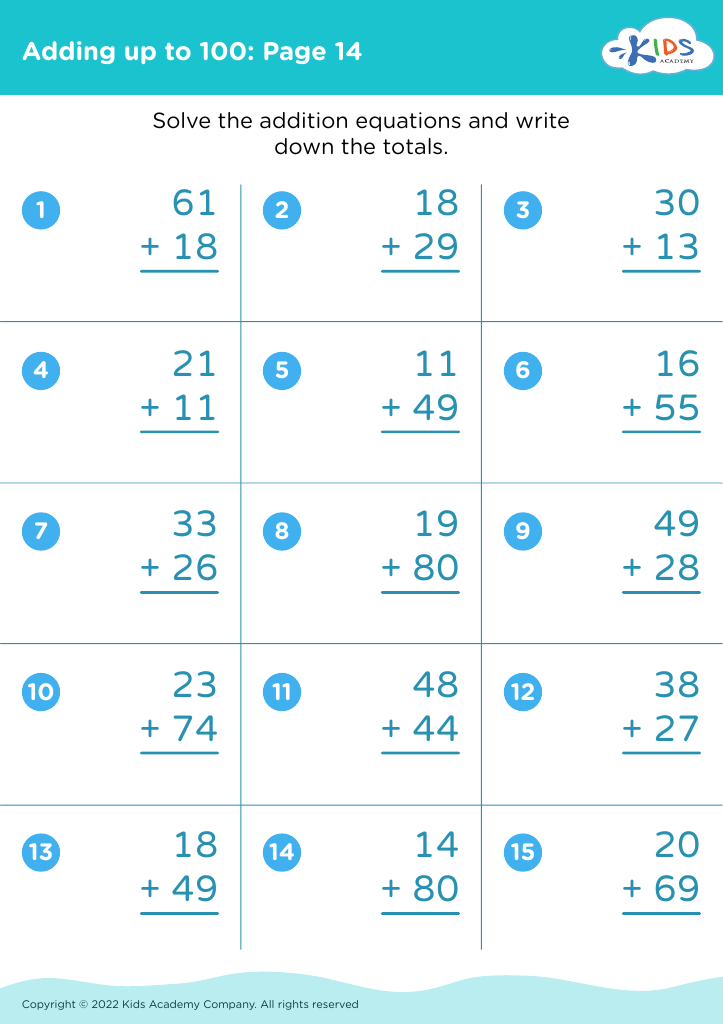
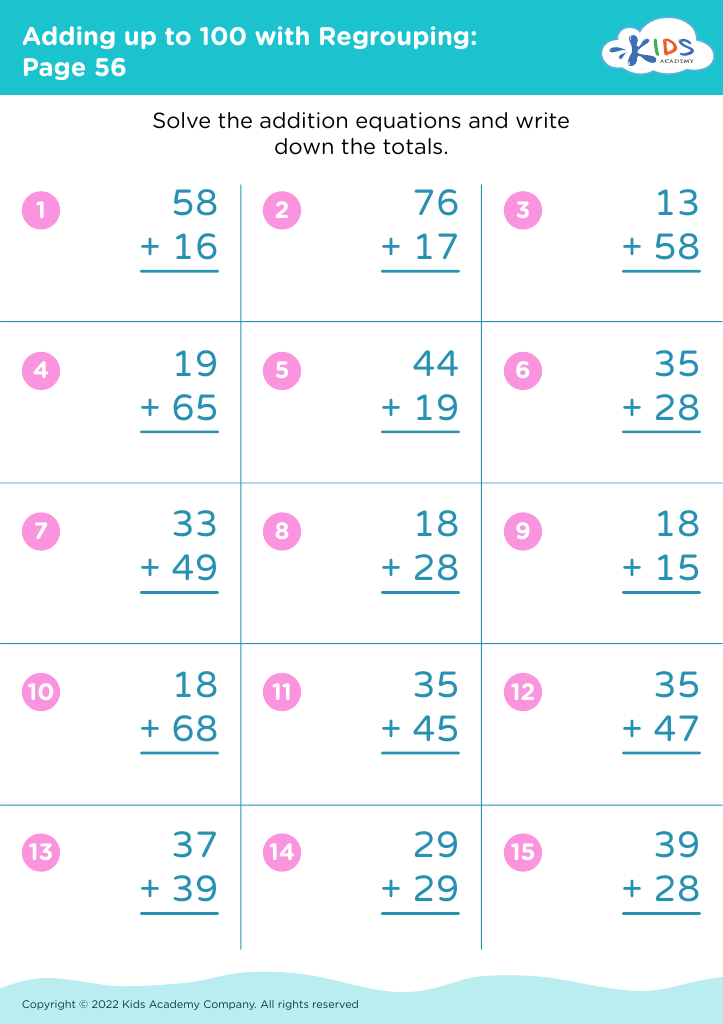
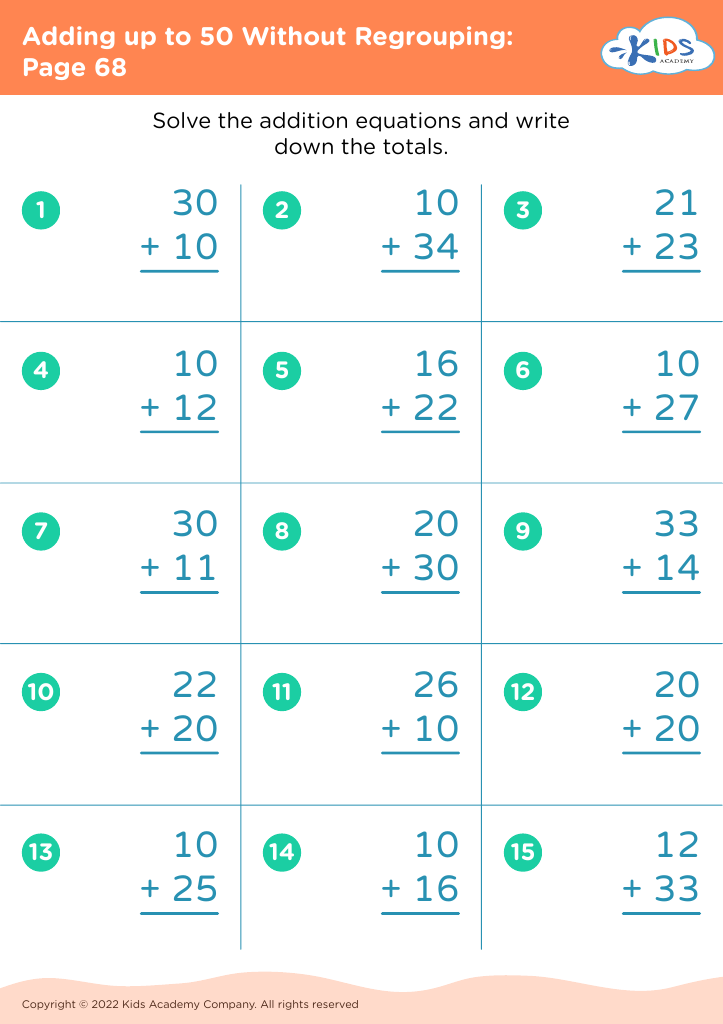
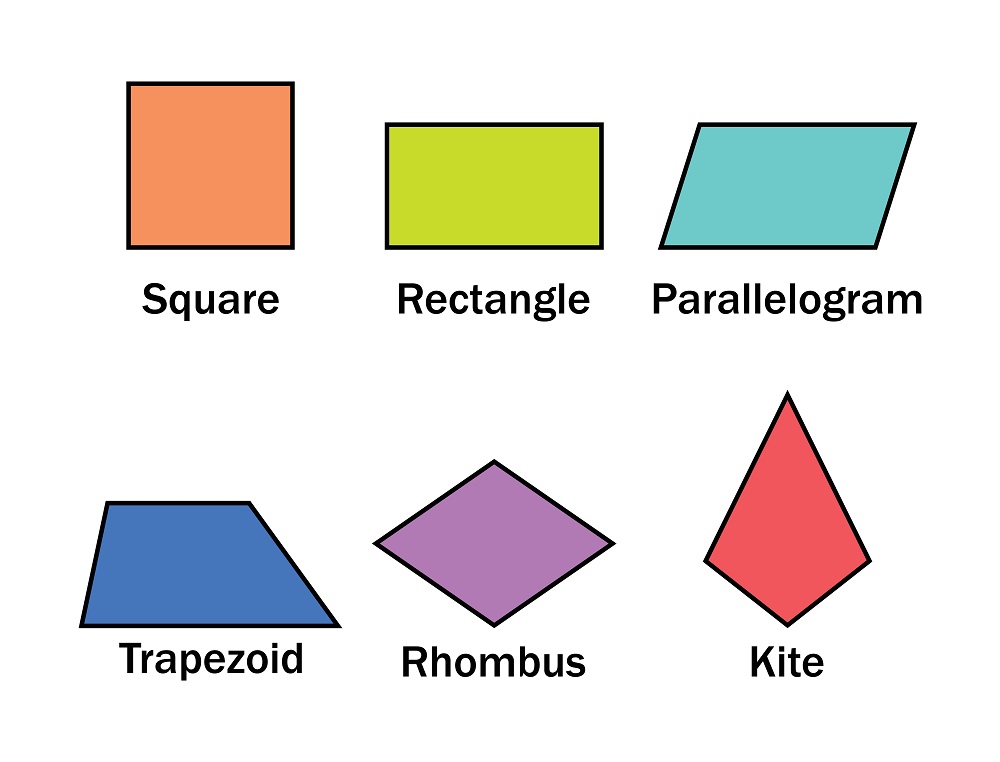
Recognizing shapes and understanding addition are foundational skills in early childhood education that significantly contribute to a child's overall cognitive development. For children aged 6-8, these skills form the basis of mathematics and problem-solving.
Firstly, shape recognition is essential as it helps children develop spatial awareness, an important cognitive skill used in various educational contexts, including geometry, art, and even reading. Understanding shapes provides children with the tools they need to identify and create patterns, build objects, and navigate their environments more effectively.
Secondly, addition is a fundamental mathematical operation that is used in everyday life. By learning addition early, children build number sense, an essential aspect of mathematics that allows them to understand quantities, make comparisons, and perform more complex operations later on. Early mastery fosters confidence in math, reducing math anxiety as they progress.
Combining these two areas—shapes and addition—creates opportunities for interactive learning through fun activities like shape-based addition games. When parents and teachers engage children with these concepts, they inspire curiosity and promote critical thinking skills, laying a strong educational foundation for future academic success. Thus, caregivers should actively encourage exploration and practice in both shapes and addition to facilitate well-rounded cognitive growth.