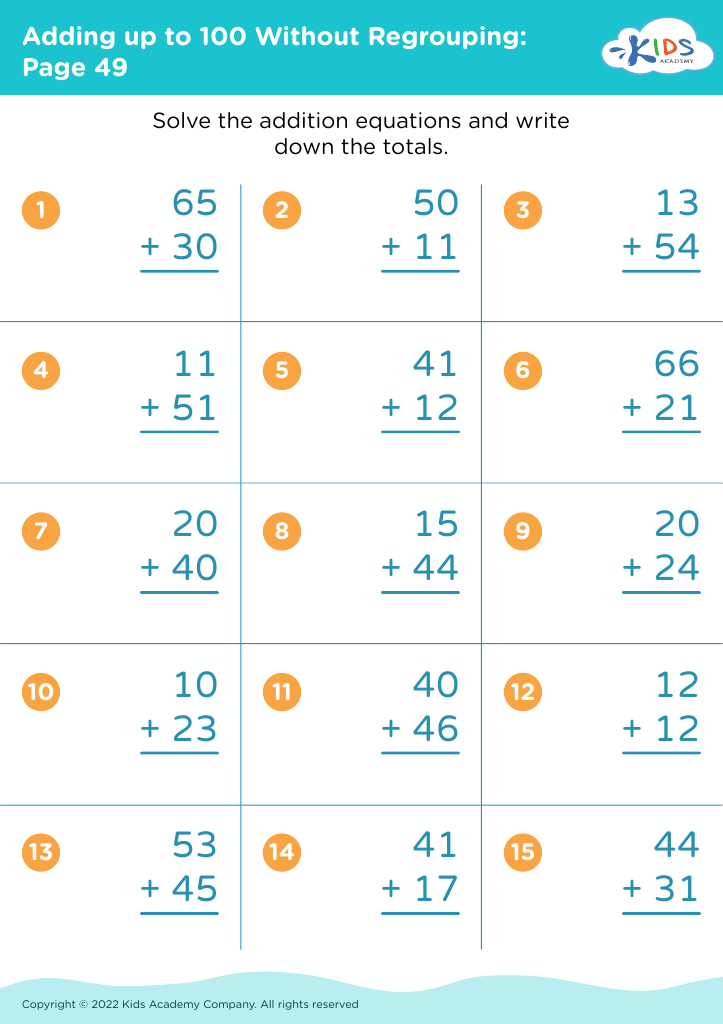
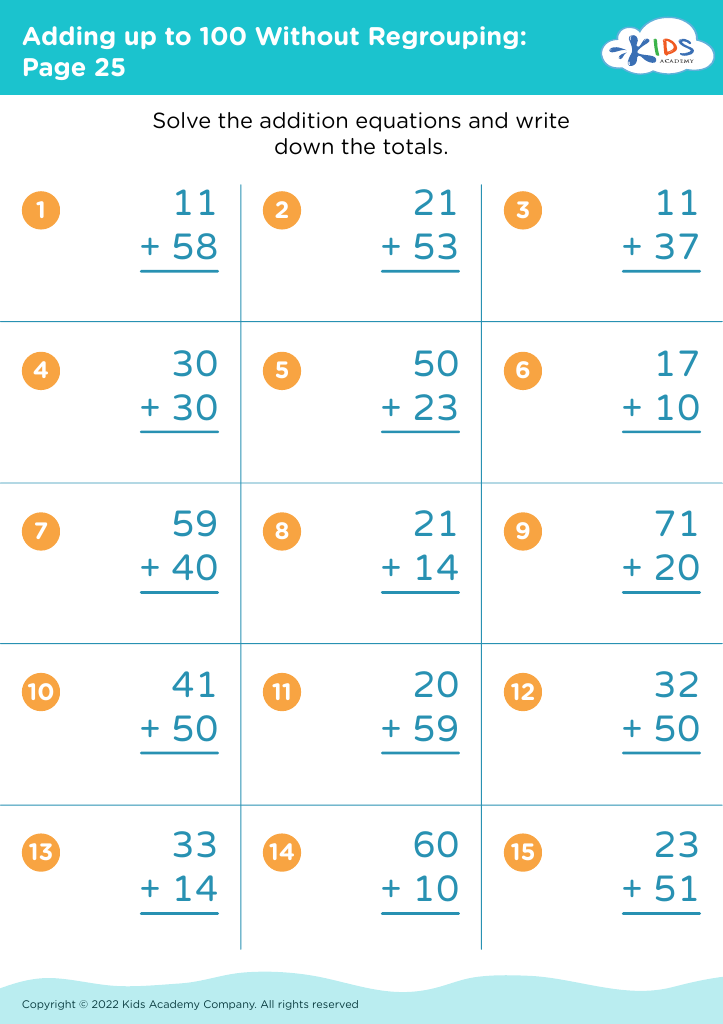
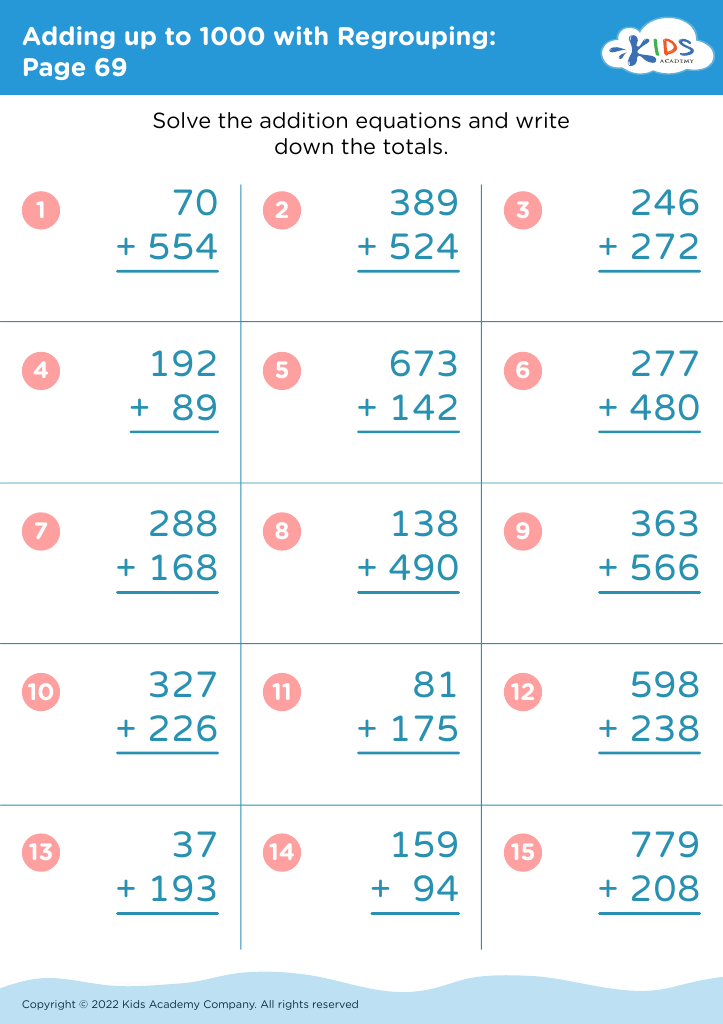
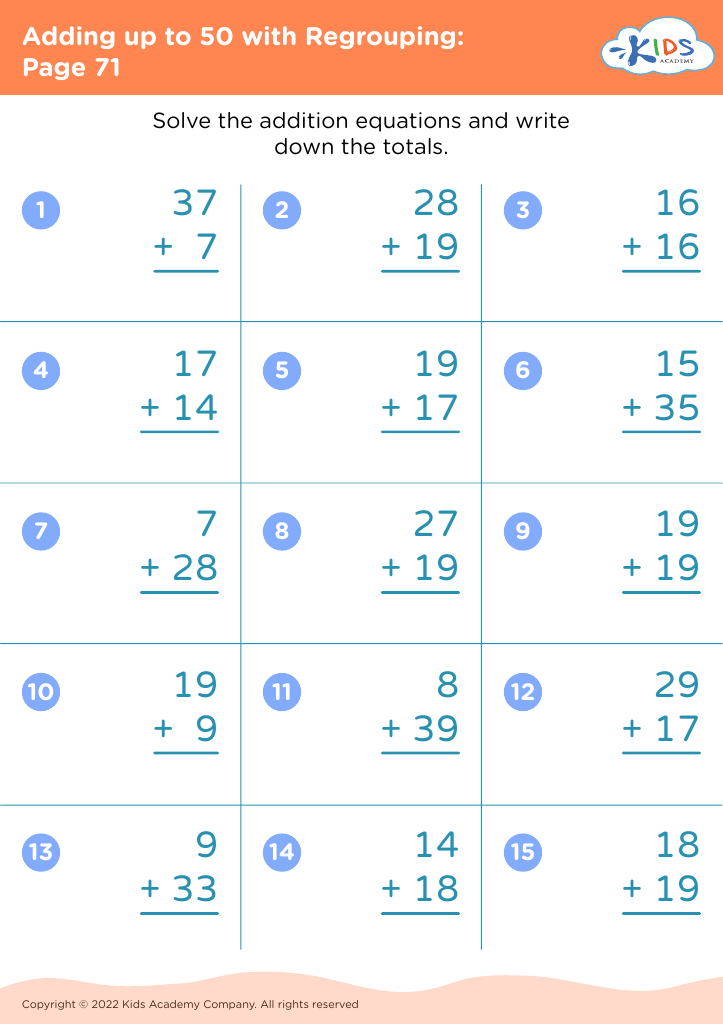
Visual discrimination Addition Worksheets for Ages 6-8
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your child's math skills with our Visual Discrimination Addition Worksheets designed for ages 6-8. Perfect for developing sharp eye-hand coordination, these engaging activities challenge young learners to distinguish and solve addition problems through vibrant and fun visuals. By combining important math concepts with visual puzzles, our worksheets enhance cognitive development and improve focus. Tailored to captivate young minds, these educational tools make learning math both enjoyable and effective. Transform math practice time into an exciting adventure and witness your child’s arithmetic confidence grow. Ideal for classroom use or at-home learning. Download now at Kids Academy!
Visual discrimination is a crucial skill for children aged 6-8 because it underpins many aspects of learning, particularly in reading, writing, and mathematics. In the context of addition, visual discrimination enables children to accurately interpret symbols (like numbers and operational signs), recognize patterns, and identify salient features of addition problems. This foundational ability helps them distinguish between similar-looking numbers, such as 6, 9, and 0, thereby reducing the likelihood of errors.
For young children, being able to visually differentiate can lead to a more precise understanding of mathematical concepts, facilitating smoother progression to more complex arithmetic operations. Additionally, strengthening visual discrimination enhances overall cognitive skills, including attention to detail, memory retention, and problem-solving abilities.
Parents and teachers who focus on activities that bolster this skill help children become more adept at decoding visual information quickly and accurately. This translates into a more confident and capable learner, ready to tackle higher-order math with greater ease. Early intervention and consistent practice through engaging exercises and interactive games are key strategies to promote strong visual discrimination skills, ultimately setting children up for long-term success in all academic areas.