Fine Motor Skills Geometry Worksheets for Ages 6-8 - Page 2
27 filtered results
-
From - To
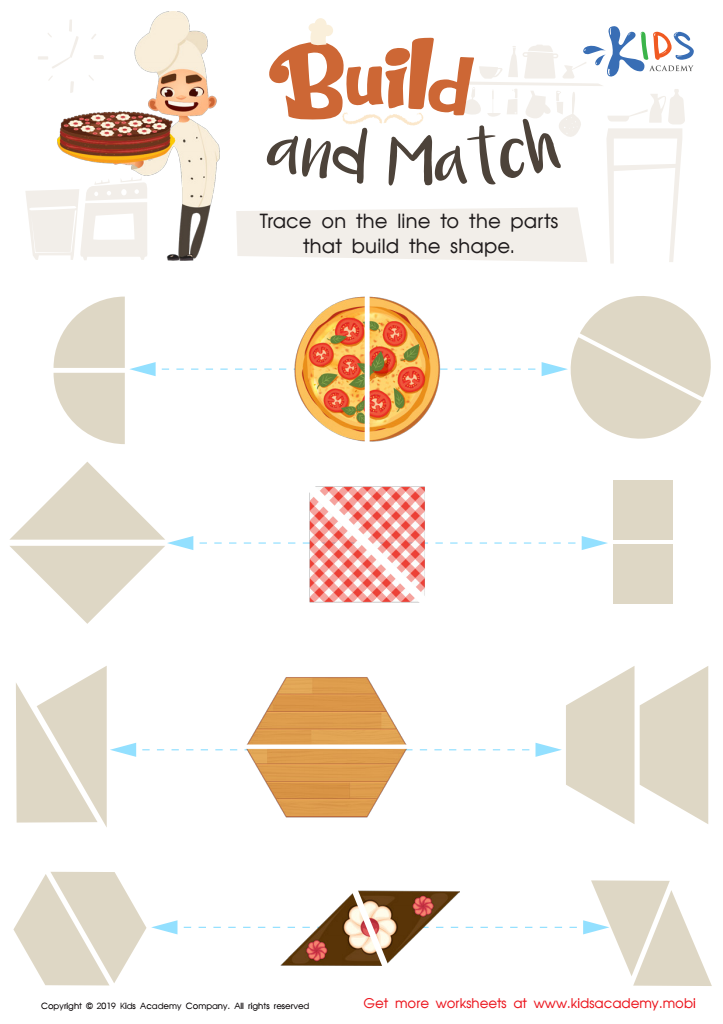

Build and Match Worksheet
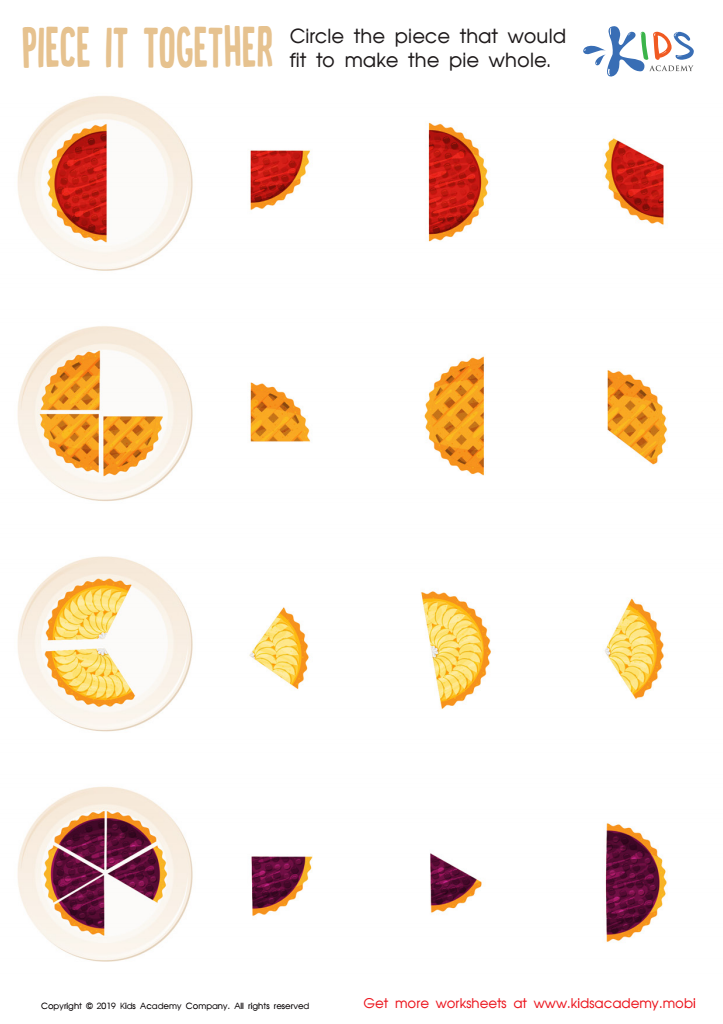


Piece it together Worksheet
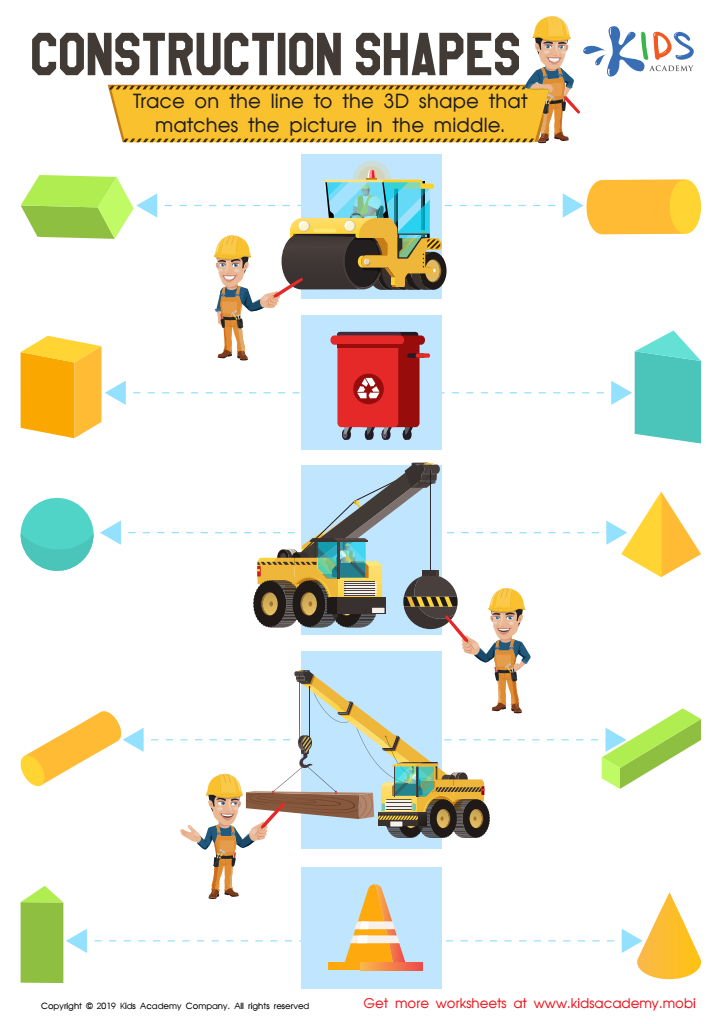

Construction Shapes Worksheet
Fine Motor Skills Geometry for ages 6-8 is crucial for young children’s overall development, and hence, parents and teachers should pay careful attention to it. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in movements—primarily in the hands and fingers—while geometry introduces children to fundamental concepts of shape, size, symmetry, and spatial reasoning. Combining these two areas provides a dual benefit.
Firstly, activities that integrate fine motor skills with geometric concepts inherently improve hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Tasks such as tracing shapes, cutting along lines, and constructing basic geometric figures with building blocks or drawing enhance physical control and precision. These advances are essential for everyday tasks like writing, dressing, and self-feeding.
Secondly, engaging young learners in geometric exercises fosters cognitive development. Children begin to understand spatial relationships and geometric properties, building a foundation for mathematical reasoning, problem-solving, and logical thinking. Such skills are pivotal as they progress in school and face more complex STEM subjects.
Teachers and parents should thus incorporate activities that blend fine motor skill development with geometry, such as puzzle-solving, drawing geometric designs, and using manipulatives like tangrams or pattern blocks. This holistic approach ensures that children develop the necessary physical and cognitive tools, underpinning both academic success and practical life skills.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students