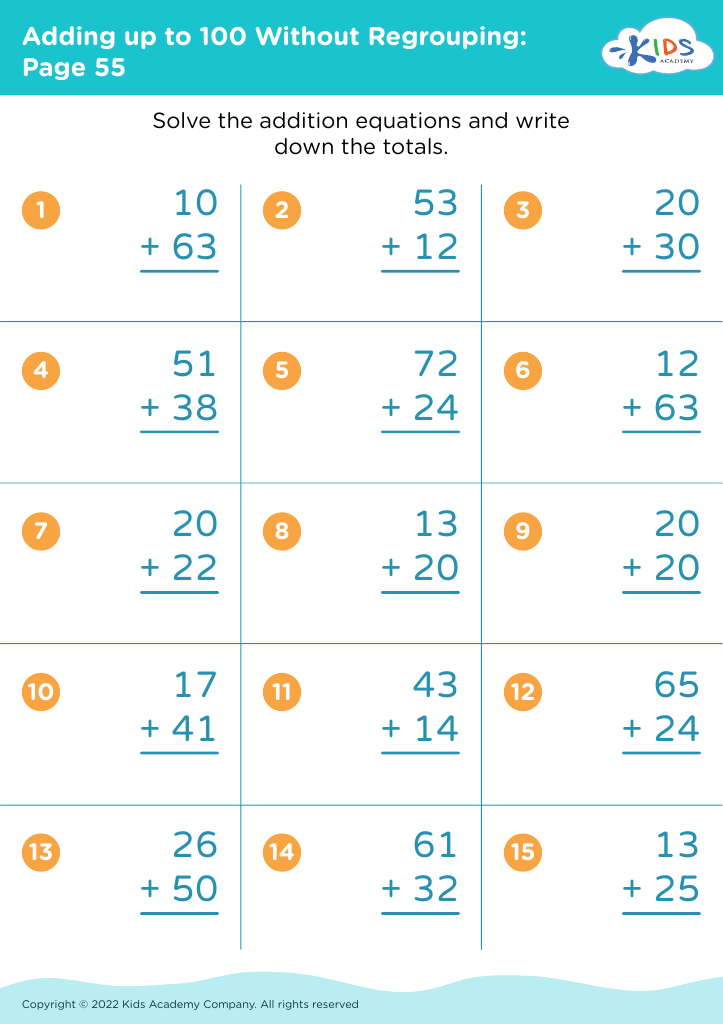
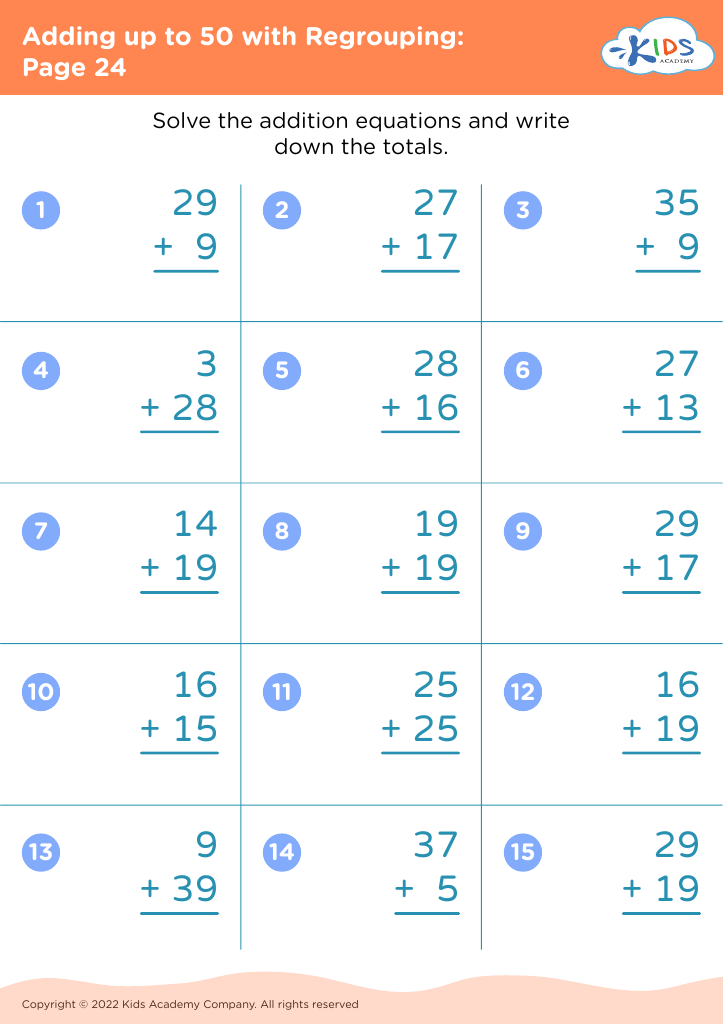
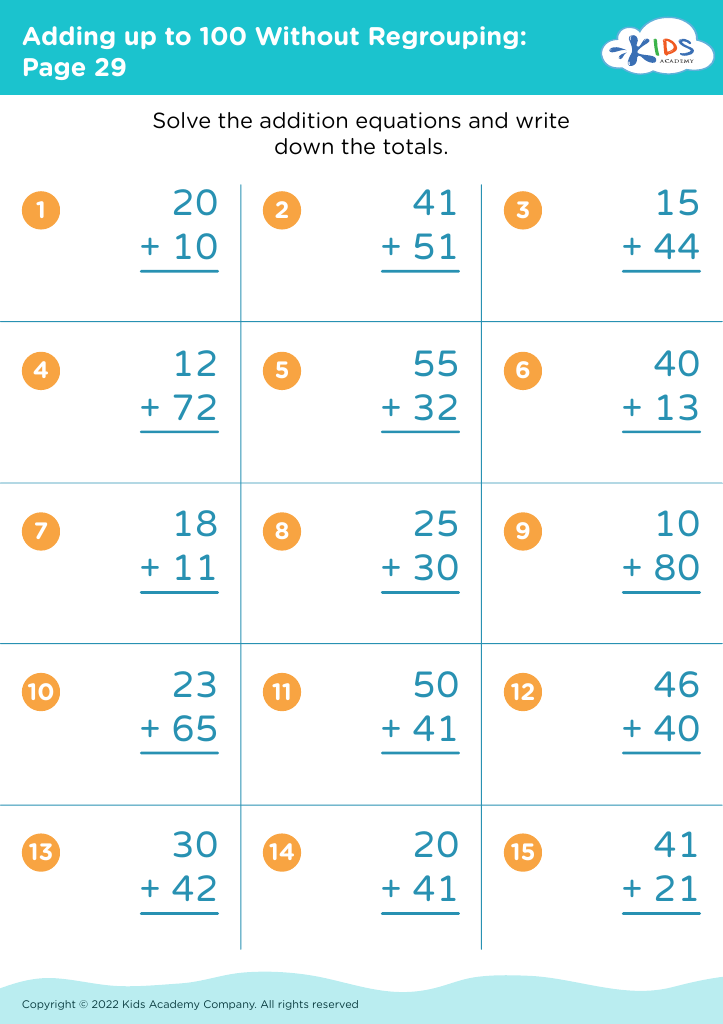
Basic subtraction Addition Worksheets for Ages 8-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Looking for engaging and effective Basic Subtraction and Addition Worksheets for children aged 8-9? Our collection provides a diverse range of activities designed to strengthen young learners' arithmetic skills. Each worksheet features a variety of problems targeting subtraction and addition concepts through fun and interactive designs. This helps to nurture a love for math while enhancing their problem-solving abilities. The worksheets are perfect for use in the classroom or at home, ensuring children can practice at their own pace. With clear instructions and colorful visuals, these worksheets make learning enjoyable and effective. Boost your child’s confidence in math today!
Basic addition and subtraction are foundational skills that significantly influence a child's academic success and overall cognitive development. For children aged 8-9, who are generally in the third or fourth grade, mastery of these concepts is crucial as they transition into more complex mathematics. Parents and teachers should care about these skills for several reasons.
Firstly, proficiency in addition and subtraction enhances a child's problem-solving abilities and critical thinking skills. These basic operations form the building blocks for more advanced math concepts such as multiplication, division, and even fractions. A strong grasp of these basics can boost a child's confidence in handling numerical challenges.
Secondly, understanding addition and subtraction ensures that students can effectively apply these skills in everyday situations, from budgeting allowances to understanding distances and time. This practical relevance reinforces their importance outside academic settings.
Lastly, early intervention is key; children who struggle with these concepts may experience frustration and a lack of motivation in math, potentially developing a long-term aversion to the subject. By prioritizing addition and subtraction, parents and teachers can create a strong mathematical foundation, helping foster a positive attitude towards learning and equipping students with the skills they'll need for future success.