Fine Motor Skills Easy Math Worksheets for Ages 4-6 - Page 2
38 filtered results
-
From - To


Planting Seeds for 11 Worksheet


Let's Pick Fruit Worksheet


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet
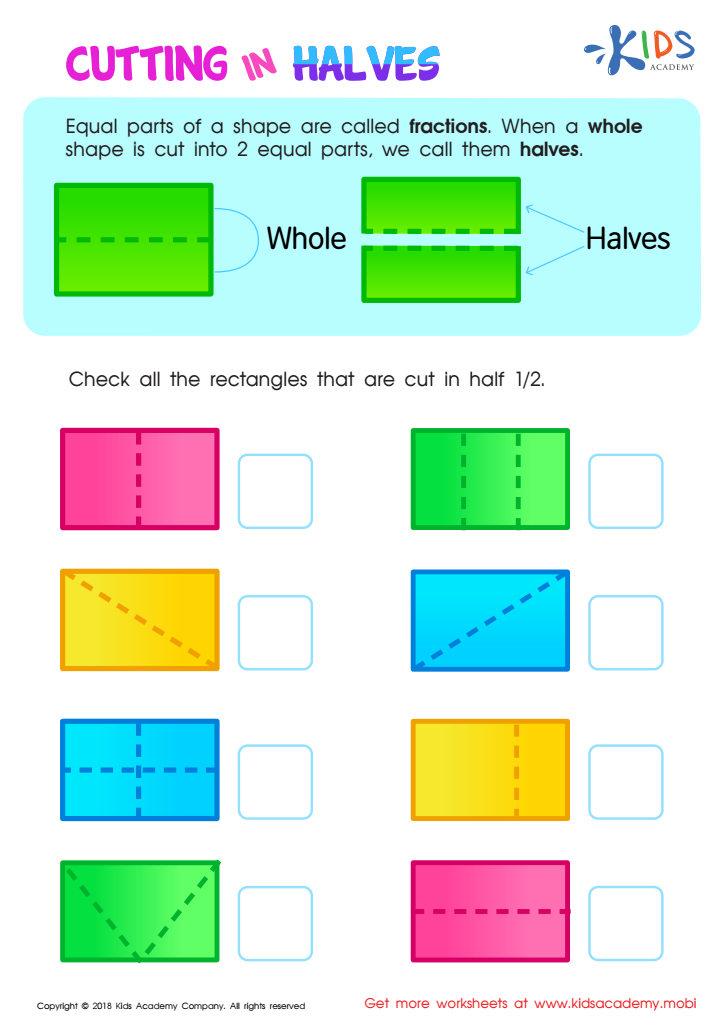

Cutting in Halves Worksheet


Build with 9 Worksheet

Drawing Ovals And Triangles with Fun Printable


Adding in the Arctic Worksheet

Build and Match Worksheet


Ordering 11–20: Dot–to–dot Seashell Printable


Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet


Counting on the City Skyline: Dot-to-Dot Worksheet


Counting Big City Buildings Worksheet

Construction Shapes Worksheet


Night Sky Numbers Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for the development of young children, particularly in the context of early math learning. For children ages 4-6, these skills involve the ability to control small hand movements, which are essential for tasks like writing, drawing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. Engaging in activities that enhance fine motor skills can significantly impact a child's mathematical understanding.
When children develop fine motor skills, they are better equipped to grasp tools they need for mathematical tasks—like markers, scissors, and manipulatives (e.g., counting bears or blocks). These tools help children visualize and physically interact with numbers and shapes, deepening their comprehension. For example, stringing beads can introduce addition or patterns, while tracing numbers reinforces counting skills.
Furthermore, fine motor activities improve hand-eye coordination, concentration, and cognitive abilities—all of which are fundamental in early math learning. By prioritizing fine motor skill development, parents and teachers set children up for success in math and other academic areas. Therefore, fostering these skills not only helps students excel in initial math concepts but also builds a strong foundation for future learning and problem-solving abilities, enhancing their confidence and readiness for more complex math.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students