Counting skills Extra Challenge Numbers Worksheets for Ages 3-4
22 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock your child's potential with our Counting Skills Extra Challenge Numbers Worksheets, tailored for ages 3-4! These engaging and interactive worksheets enhance your little one's understanding of numbers while introducing them to counting concepts. Designed to captivate young minds, each activity promotes essential skills in a fun, colorful format, ensuring effective learning. From hands-on counting games to tracing exercises, these worksheets foster creativity and critical thinking in early learners. Perfect for home or classroom use, our resources support foundational math skills and boost confidence in counting. Let the counting adventure begin and watch your child thrive! Explore our worksheets today!


Counting Floors Worksheet
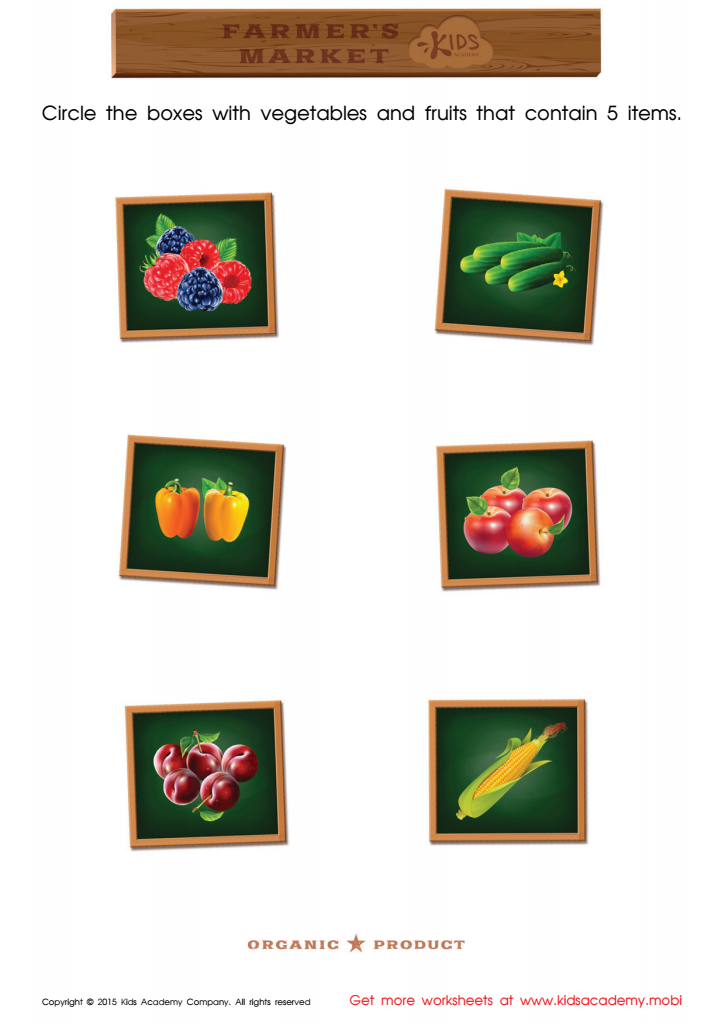


Count and Match Vegetables 1 – 7 Math Worksheet


Ducks in a Row Worksheet


Counting With Pirates Worksheet
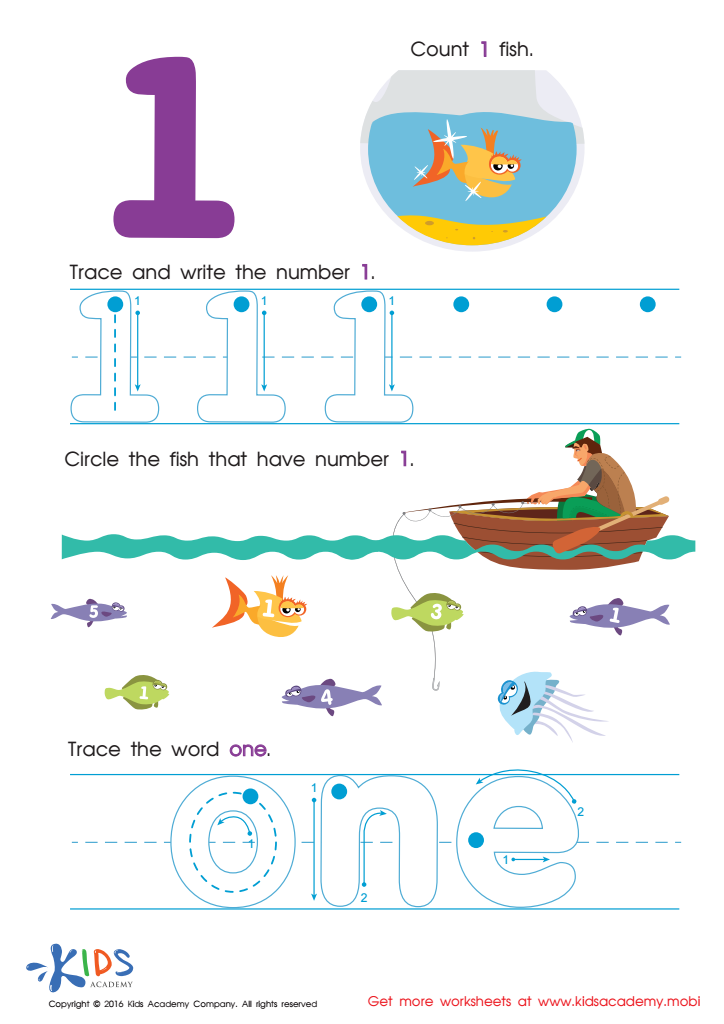

Learning to Write 1 Worksheet
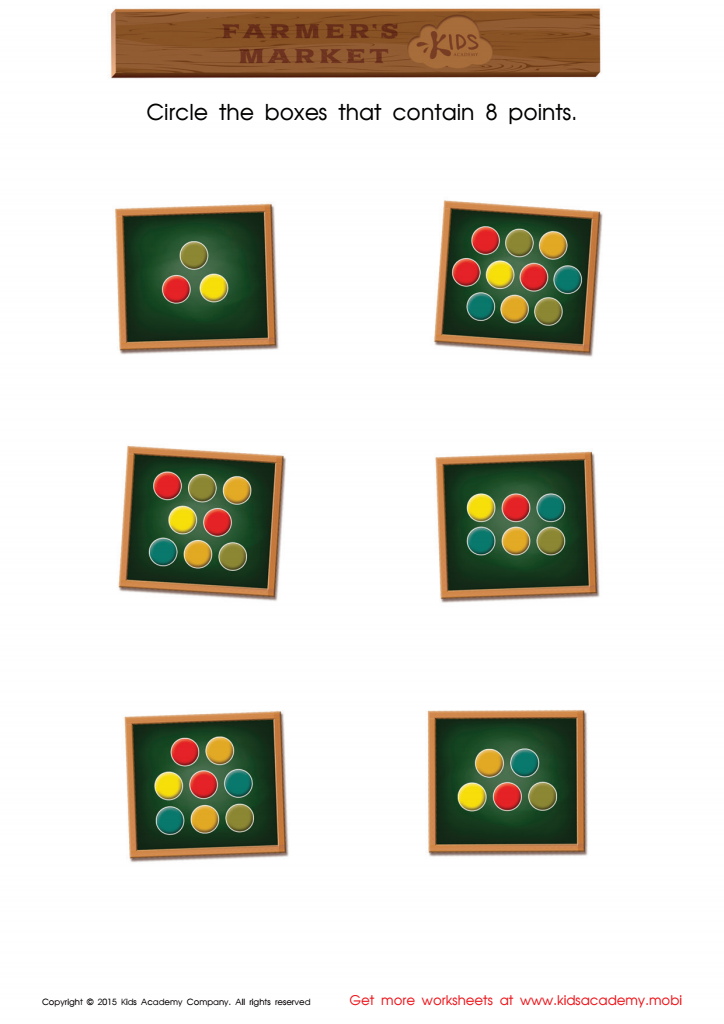

Count and Match Points 8 Math Worksheet
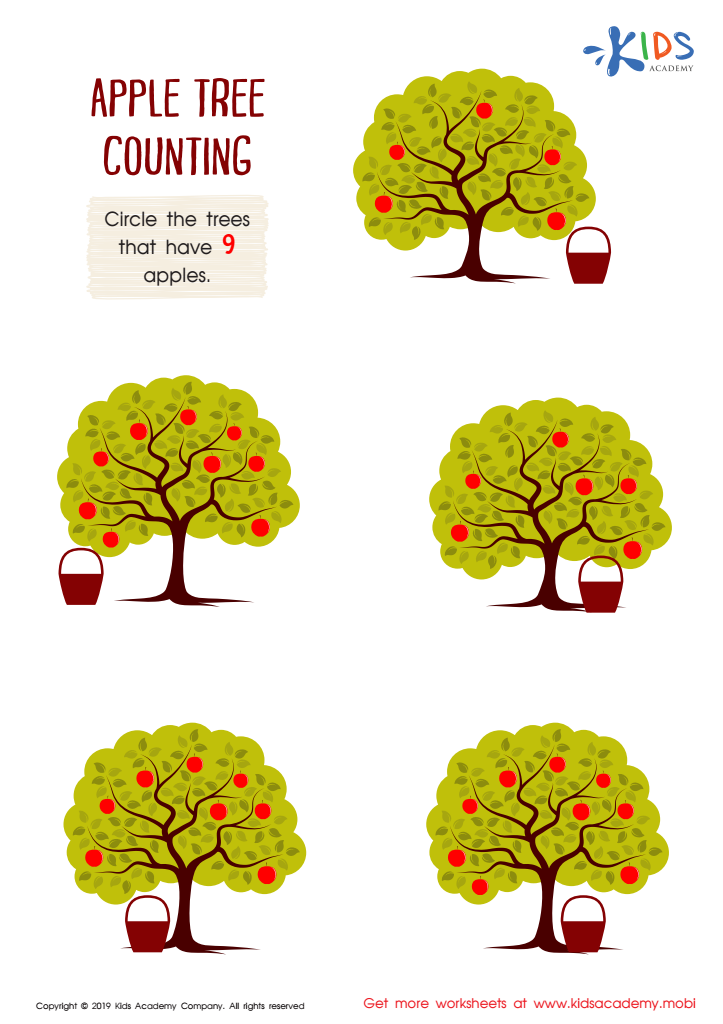

Apple Tree Counting Worksheet
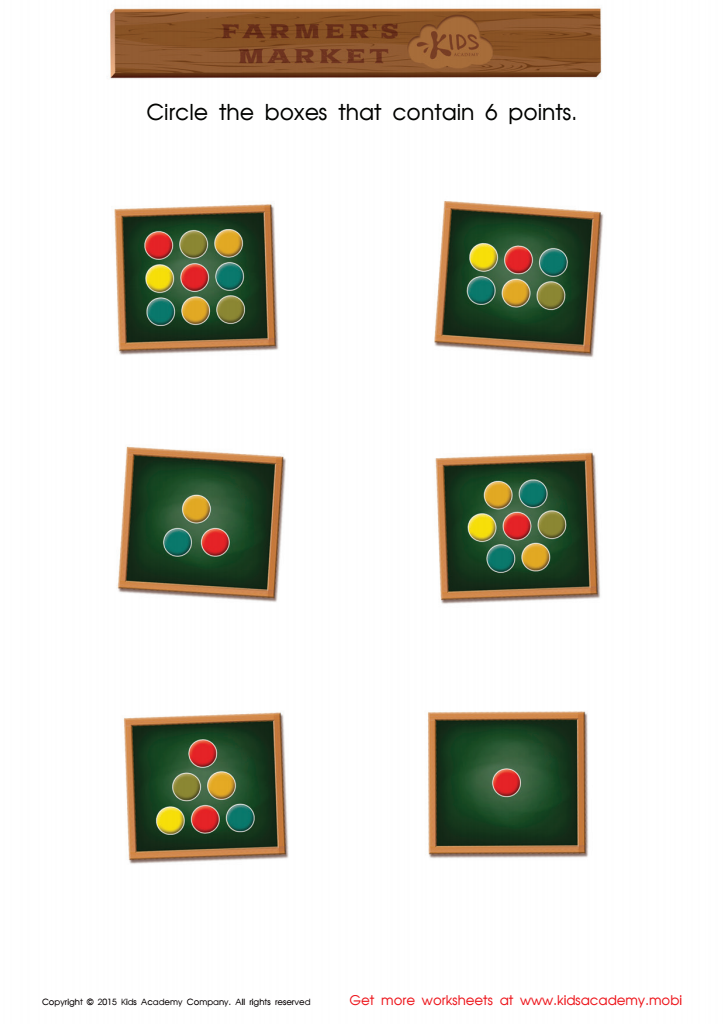

Count and Match Points 6 Math Worksheet


Count with the Captain Connect Dots Worksheet
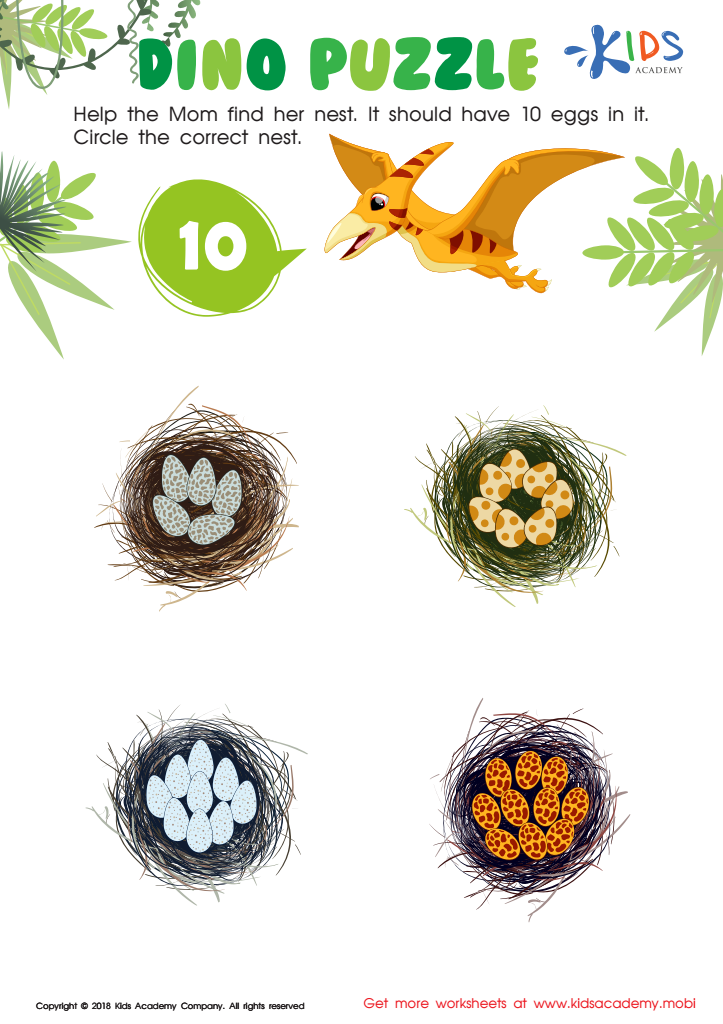


Learn Number For Kindergarten Worksheet
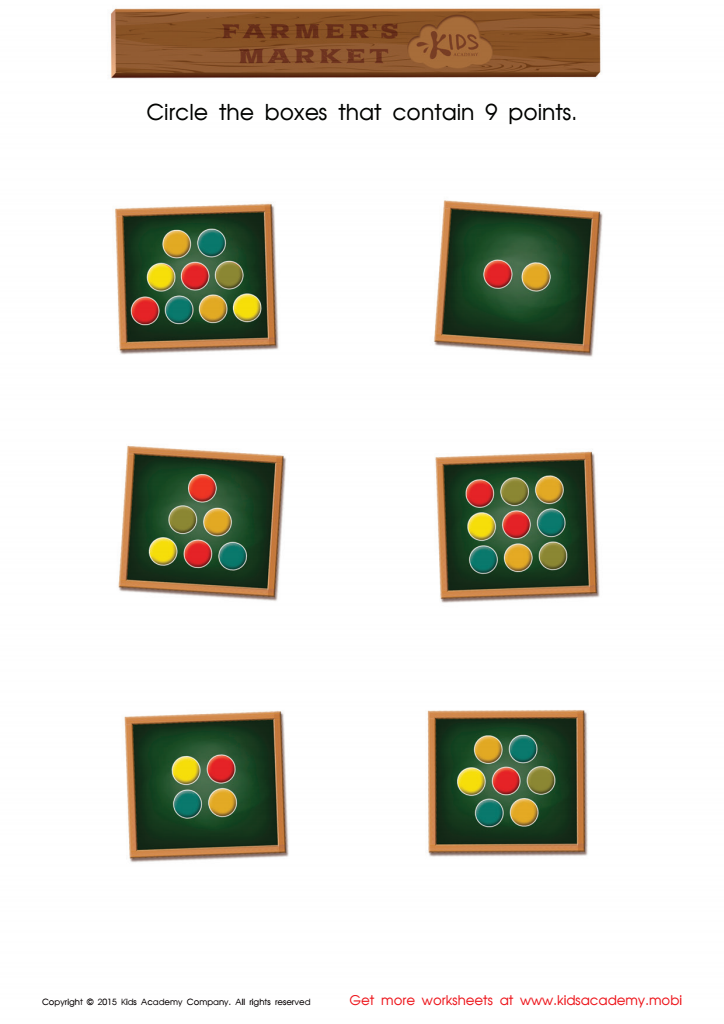

Count and Match Points 9 Math Worksheet
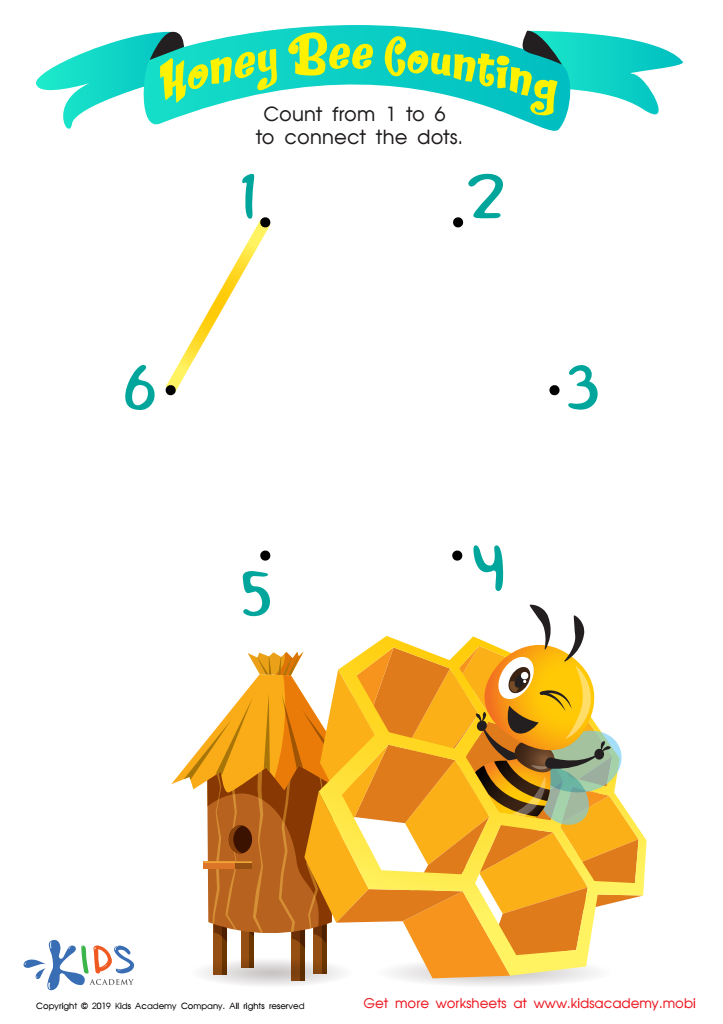


Honey Bee Counting Worksheet
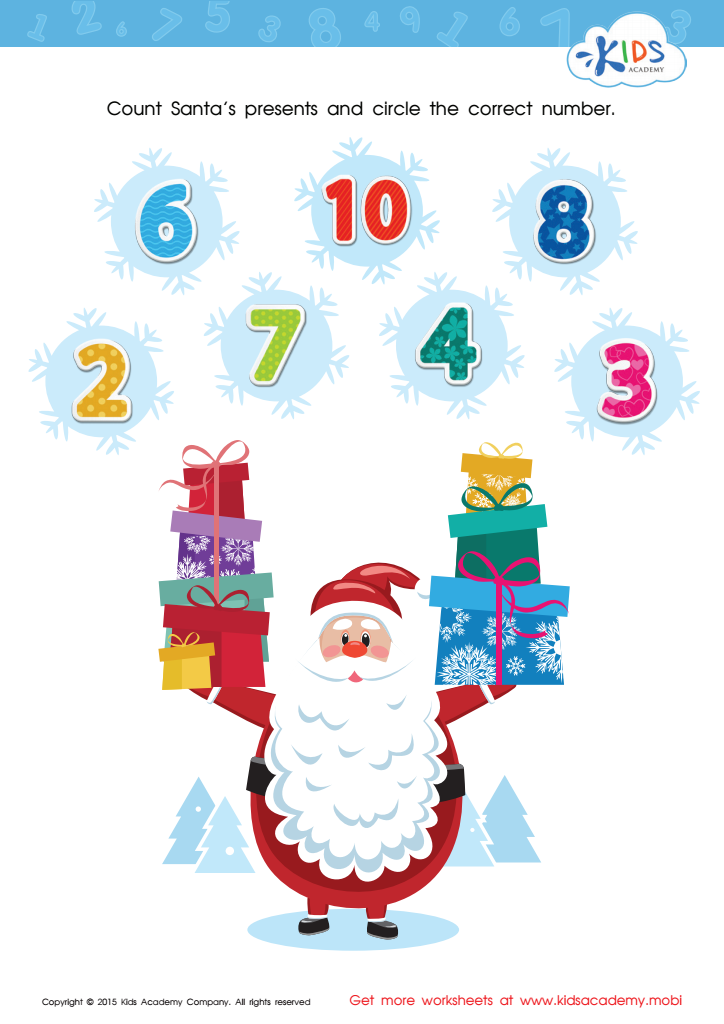


Count Santa's Presents Worksheet
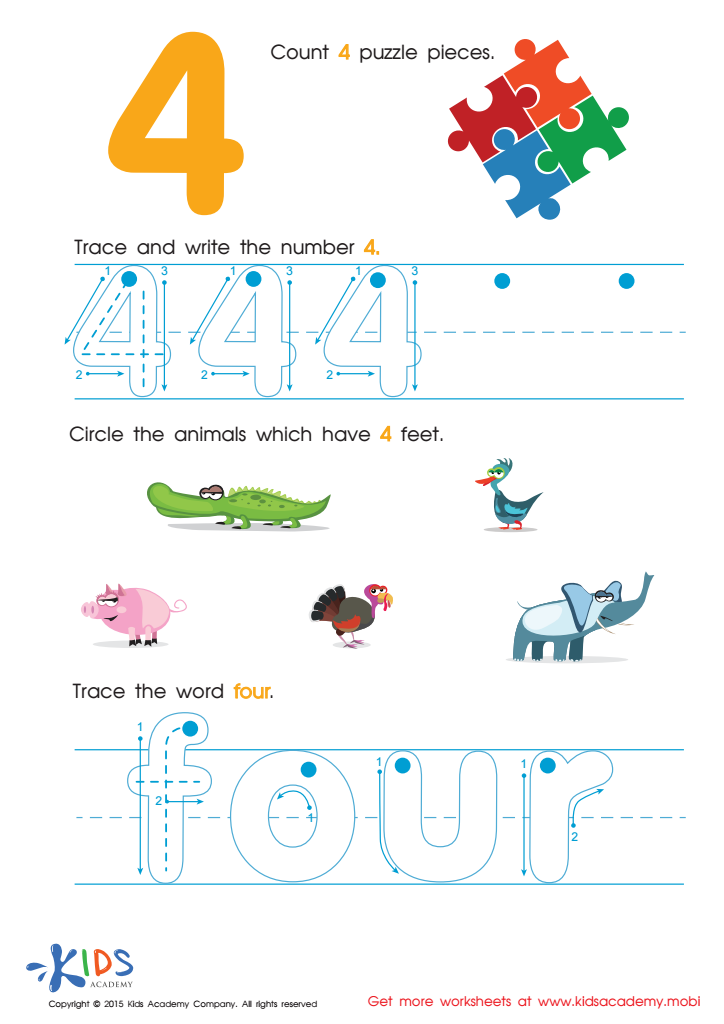

Teaching Children to Write Number 4 Worksheet
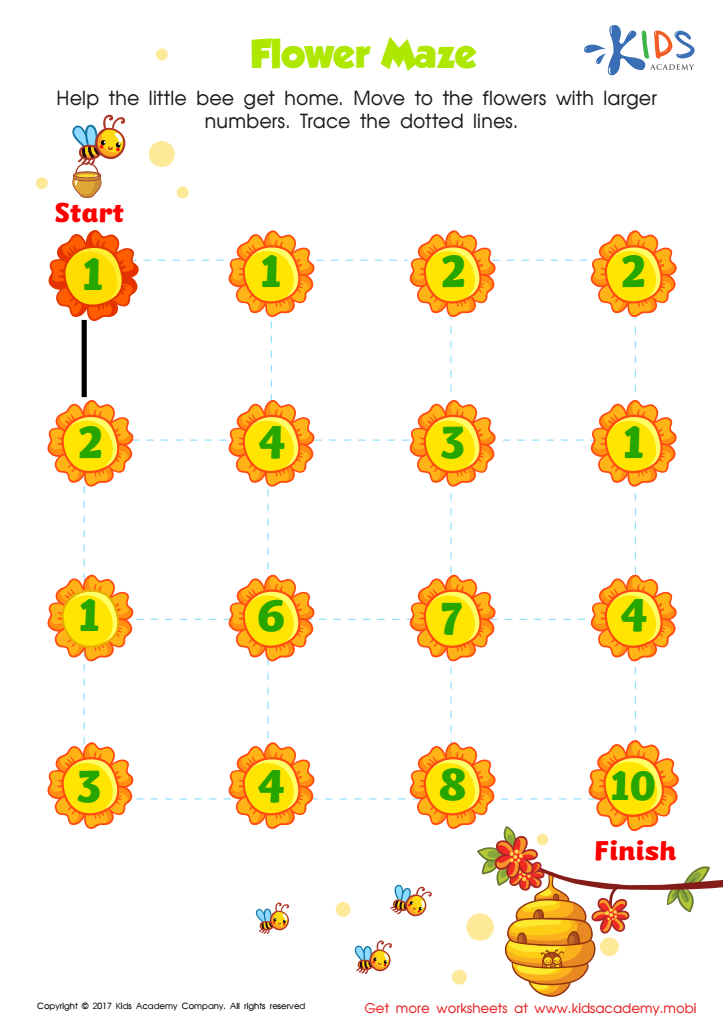


Number Maze For Kindergarten Printable


Counting Butterflies Worksheet


Counting Worksheet


Count with Clowns Worksheet


Number 1 Printable
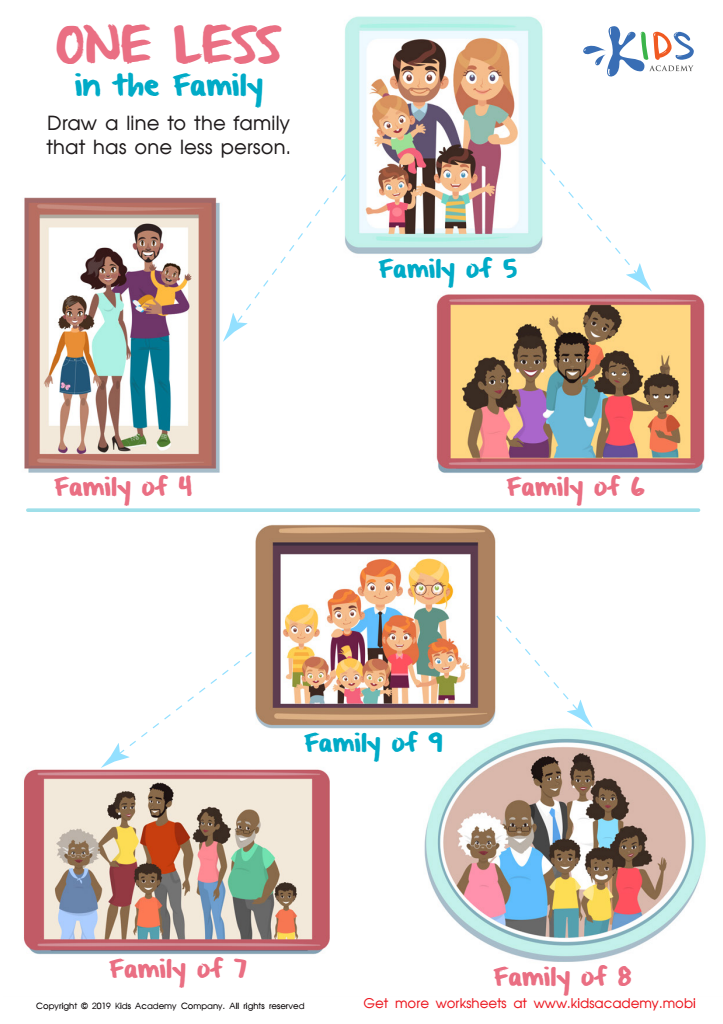

One Less in the Family Worksheet


Jungle Counting Connect Dots Worksheet

Fish Bowl Numbers Worksheet
Counting skills are foundational in early childhood education, especially for children aged 3-4. Developing these skills at a young age lays the groundwork for a child's future mathematical understanding and cognitive development. Parents and teachers should care about counting skills extra challenges because they encourage young learners to think critically and problem-solve in engaging ways.
At this age, children's brains are at a prime stage for learning through play and exploration. Extra challenges can turn counting from a simple rote task into a fun, interactive experience. For instance, activities like counting objects in everyday settings or singing number songs promote both language development and numerical understanding.
Moreover, practicing counting skills helps children develop fine motor skills, as they manipulate objects or use their fingers to trace numbers. By fostering positive attitudes towards math early on, we empower children to approach future mathematical concepts with confidence.
Furthermore, using extra challenges can accommodate various learning styles and encourage parental involvement in schoolwork, creating a supportive learning environment. Ultimately, prioritizing counting skills not only enhances early academic readiness but also instills a lifelong love for learning in children.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students