Practice sequencing Worksheets for Kids
2 filtered results
-
From - To
Question/Answer
How does the mastery of the Practice sequencing skill affect a student's performance at an early age?
Mastery of the Practice Sequencing skill at an early age significantly enhances a student's ability to organize thoughts, understand chronological order, and improve problem-solving strategies. This foundational skill boosts reading comprehension, mathematical understanding, and the ability to follow instructions accurately, leading to improved academic performance across various subjects and facilitating better cognitive development overall.
Why is the Practice sequencing skill important for Grade 2 students?
The practice sequencing skill is vital for Grade 2 students because it enhances their ability to recognize patterns, organize information logically, and understand the order of events. This foundational skill is crucial for developing reading comprehension, problem-solving abilities, and mathematical concepts, directly contributing to their overall academic success and critical thinking development.
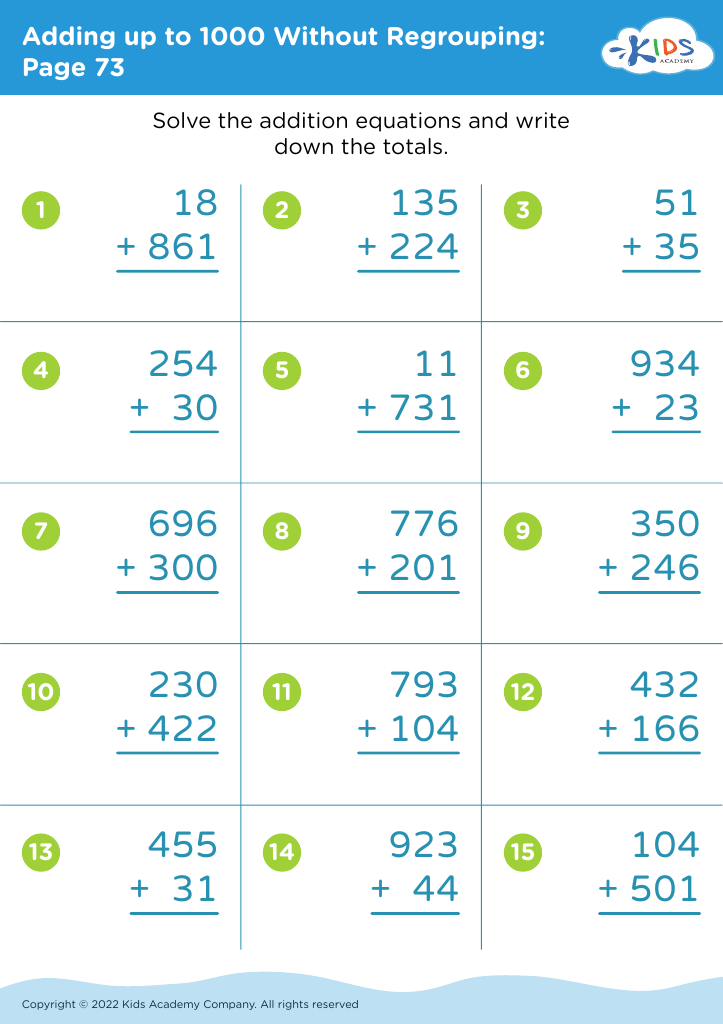
What are some effective activities to train students’ Practice sequencing skill when teaching them about Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping?
To train students in sequencing skills while teaching adding up to 1000 without regrouping, consider the following activities: 1. Number line jumps: Have students use number lines to visually add numbers in sequence. 2. Ordering sums: Give students a set of addition problems and ask them to solve and arrange the sums in ascending or descending order. 3.