Fine Motor Skills Normal Worksheets for Ages 4-5 - Page 5
105 filtered results
-
From - To
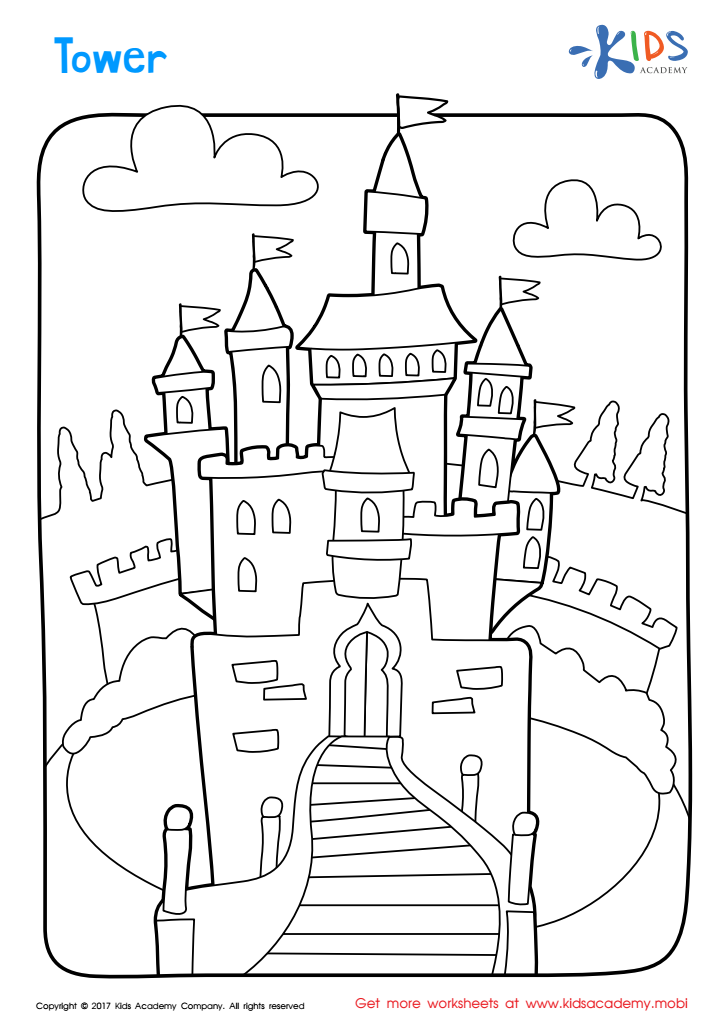


Tower Coloring Page

Letter F Coloring Sheet


Great Hornbill Worksheet


Lowercase Letters v w x Worksheet

Pair Pears Worksheet


Letter N Coloring Sheet

Astronaut Coloring Page


Letter D Tracing Page


Uppercase Letters V, W, and X Worksheet
Fine motor skills are essential for children aged 4-5 because they lay the groundwork for various critical aspects of development and everyday functioning. At this age, children's motor skills mature rapidly, allowing them to perform tasks that require hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and precise movements. Fine motor skills influence a child's ability to write, draw, and manipulate small objects, which are foundational for academic success. For instance, the ability to hold a pencil correctly and form letters shapes their handwriting and literacy skills.
These skills also promote independence in daily activities. Children who develop fine motor skills can dress themselves, button clothes, tie shoelaces, and manage eating utensils, fostering self-reliance and confidence. Fine motor control enhances play and social skills by enabling children to participate in games requiring coordination, such as building blocks, puzzles, and crafts.
Neglecting fine motor skill development can lead to difficulties in school and social settings. Parents and teachers should encourage activities that strengthen these skills through play, arts and crafts, and practical tasks. By caring about fine motor skills, adults support children in gaining the independence, confidence, and competence necessary for academic achievement and personal growth.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















