Fine Motor Skills Normal Math Worksheets for Ages 5-6 - Page 2
37 filtered results
-
From - To


Three–Dimensional Shapes: Cylinder Worksheet


Counting Busy Bees Worksheet

Robot Shapes Worksheet
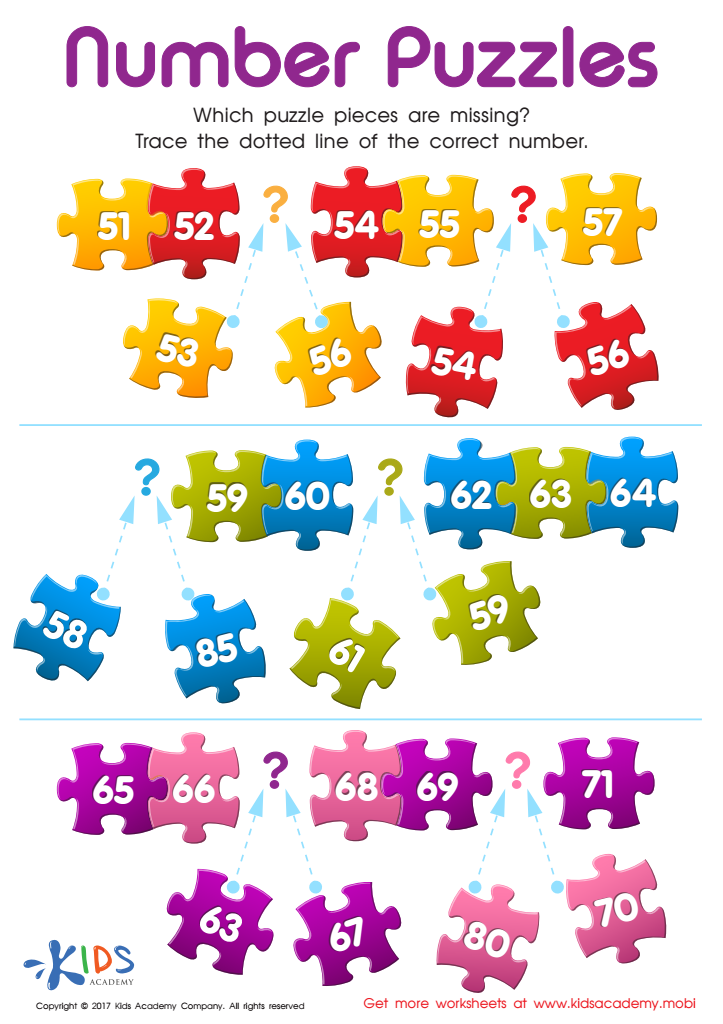

Number Puzzles Worksheet
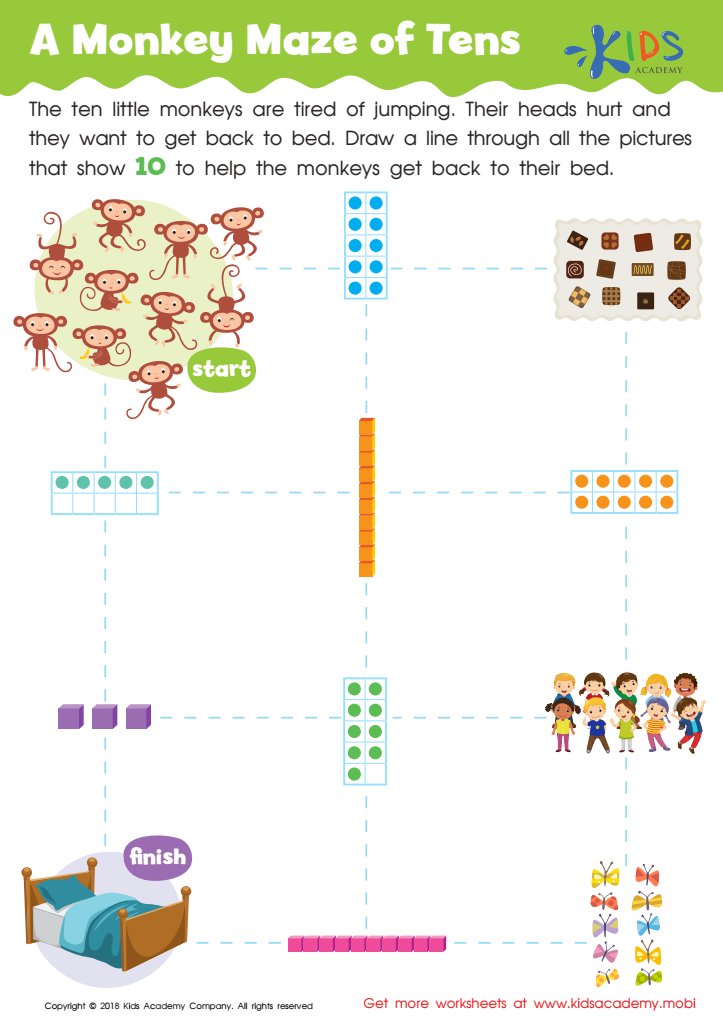

A Monkey Maze of Tens Worksheet


Shapes and Colors Worksheet


Frog Countdown Worksheet


Easy Drawing of Ovals And Rectangles Worksheet


Help the Bee Find 16 Flowers Worksheet


Addition Robot Sorter Worksheet


Bubble Matching Fun Worksheet


Learn to Write the Number 2 Worksheet


Ben Franklin’s Inventions – Count to 120 Worksheet
Parents and teachers should care about fine motor skills development in children aged 5-6 because these skills are fundamental to overall learning and day-to-day activities. Fine motor skills involve the coordinated efforts of small muscles in the hands and fingers that enable children to perform essential tasks such as writing, drawing, buttoning clothes, and manipulating small objects. Developing these skills at an early age sets the foundation for academic success and fosters independence.
Children who have not developed fine motor skills may struggle with tasks that require precision and control, such as forming letters and numbers correctly, which can lead to difficulties in reading and math. For instance, being able to deftly hold a pencil or use scissors not only impacts their ability to complete school assignments but also enhances their confidence and motivation in learning environments. Additionally, fine motor development influences social interactions, allowing children to participate in play that requires dexterity, like building with blocks or playing games.
By engaging children in activities that promote fine motor skills—such as coloring, playing with clay, or using tweezers—parents and teachers support cognitive development and ensure that children are well-prepared for future challenges both in school and in everyday life. This early investment reaps long-term benefits, making it an essential focus during early childhood development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students