Problem-Solving Skills Normal Chess Worksheets for Ages 6-8
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's critical thinking and problem-solving abilities with our chess worksheets designed specifically for ages 6-8. Each engaging activity fosters essential skills like strategic planning, creative reasoning, and decision-making through the fun and interactive game of chess. Our kids-friendly format ensures Bittle attention, featuring colorful designs and relatable scenarios to maintain interest. Perfect for home or classroom use, these downloadable worksheets encourage young learners to tackle challenges, enhancing both their cognitive and social skills. Introduce your child to the timeless game of chess in a supportive learning environment, paving the way for their intellectual development and lifelong love for puzzles and strategy.
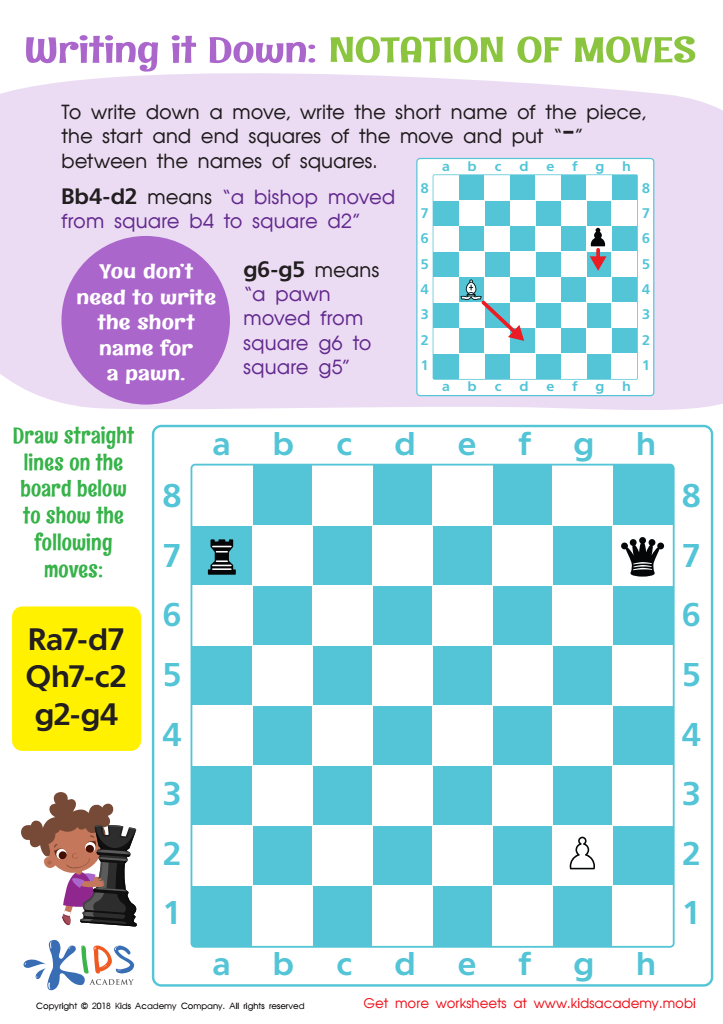

Notation of Moves Writing it Down Worksheet
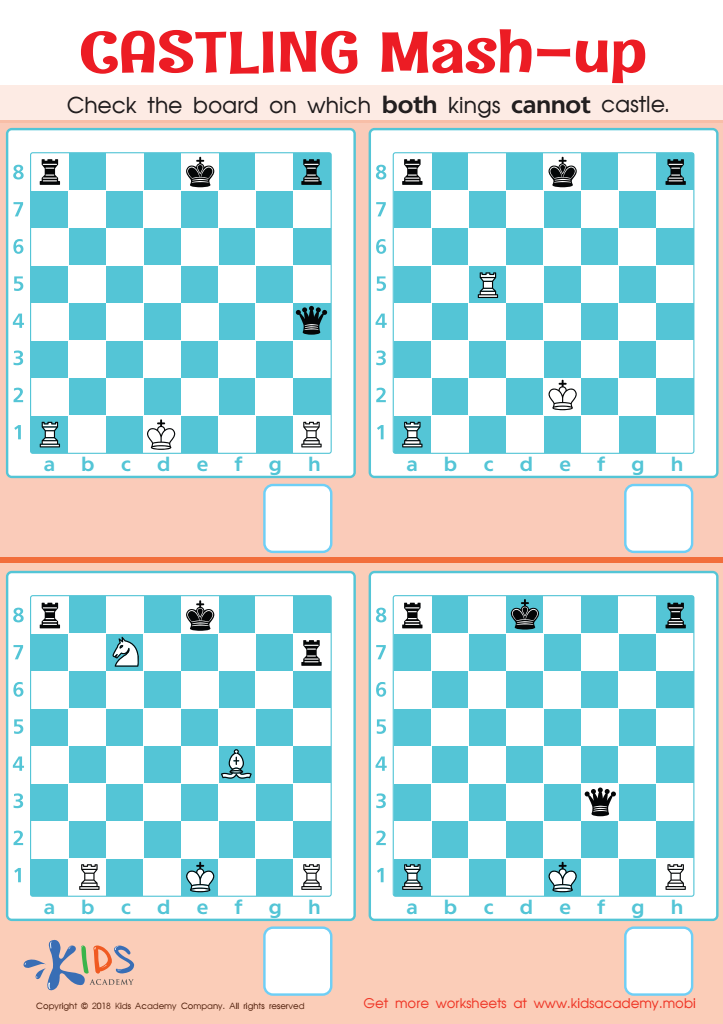

Castling Mash–up Worksheet
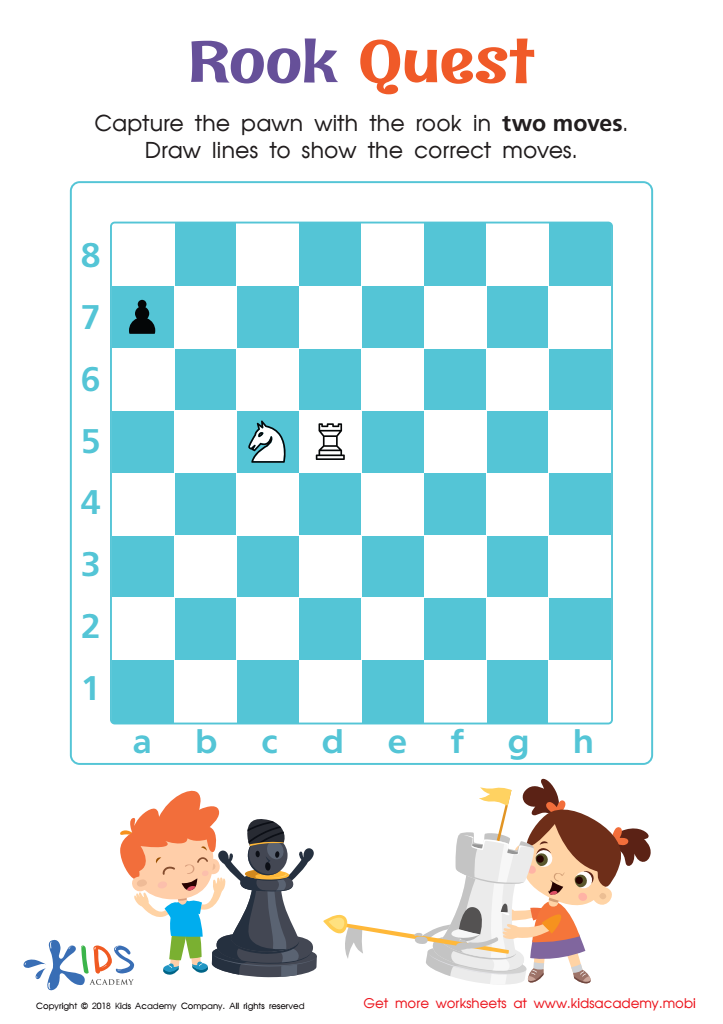

Rook Quest Worksheet
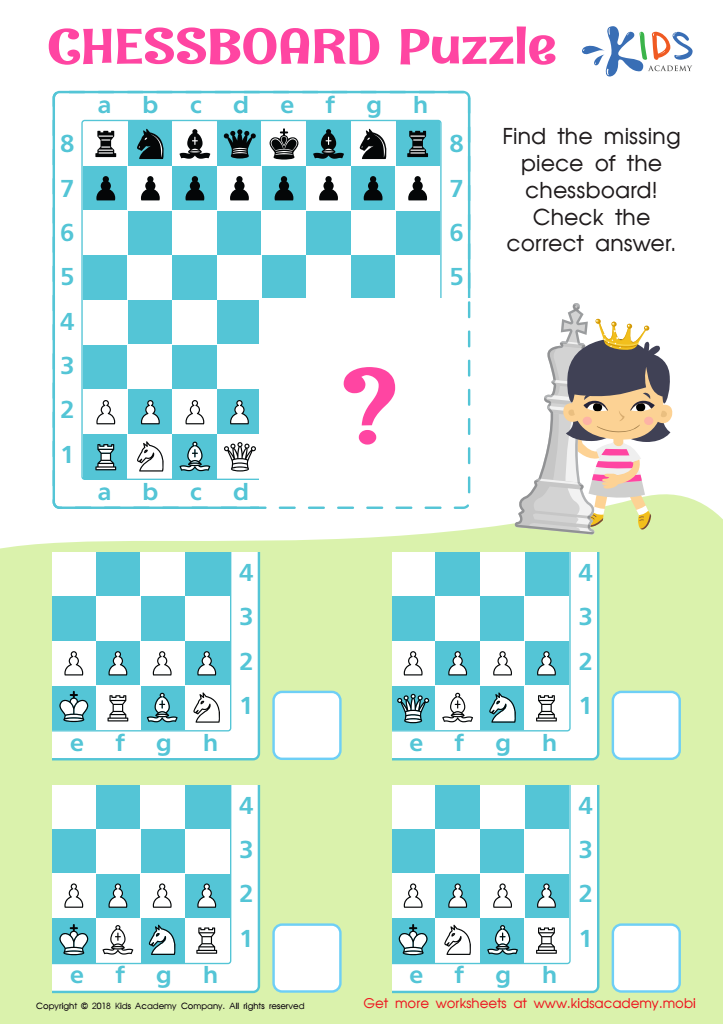

Chessboard Puzzle Worksheet
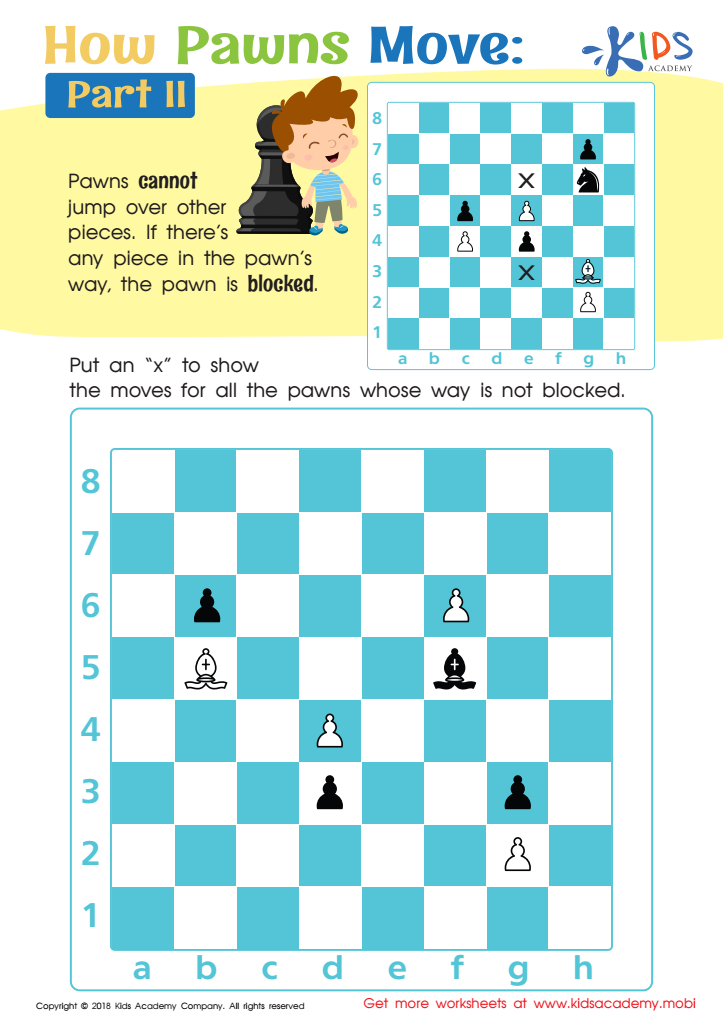

How Pawns Move: Part II Worksheet
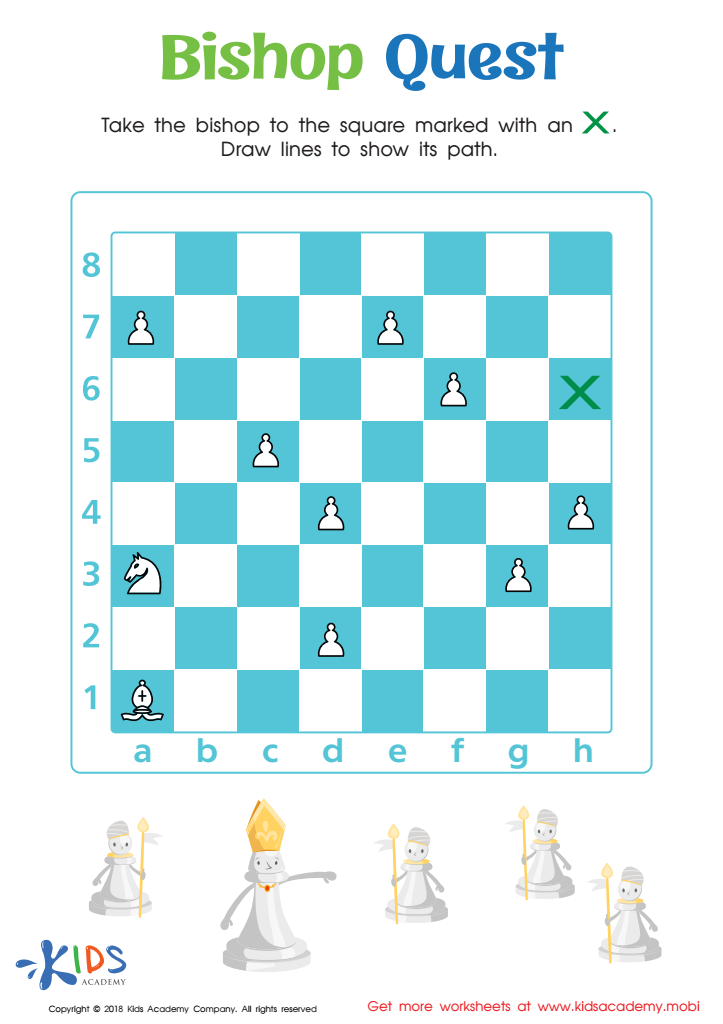

Bishop Quest Worksheet
Parents and teachers should care about teaching problem-solving skills through chess to children aged 6-8 for several vital reasons. First, chess is a game that inherently promotes critical thinking and strategic planning. Players must evaluate various outcomes and make decisions based on limited information, which mirrors real-life problem-solving scenarios.
At this age, children are developing cognitive abilities and learning to think independently. Introducing them to chess can enhance their analytical skills, helping them to learn how to assess situations, foresee consequences, and explore various problem-solving strategies. This foundational skill set not only benefits them in chess but also in their academic pursuits.
Moreover, chess fosters patience and perseverance. As students face challenges on the board, they learn the value of sticking with a task and finding solutions, enriching their emotional resilience—an essential trait in both learning and daily life.
Finally, engagement in chess can promote social skills, as players often collaborate and interact with peers. This interactive aspect can lead to improved communication skills, preparing them for future teamwork and collaborative problem-solving challenges. In summary, cultivating problem-solving skills through chess offers children essential cognitive and interpersonal tools valuable throughout their lives.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students