Counting practice Worksheets for Ages 3-4 - Page 7
304 filtered results
-
From - To
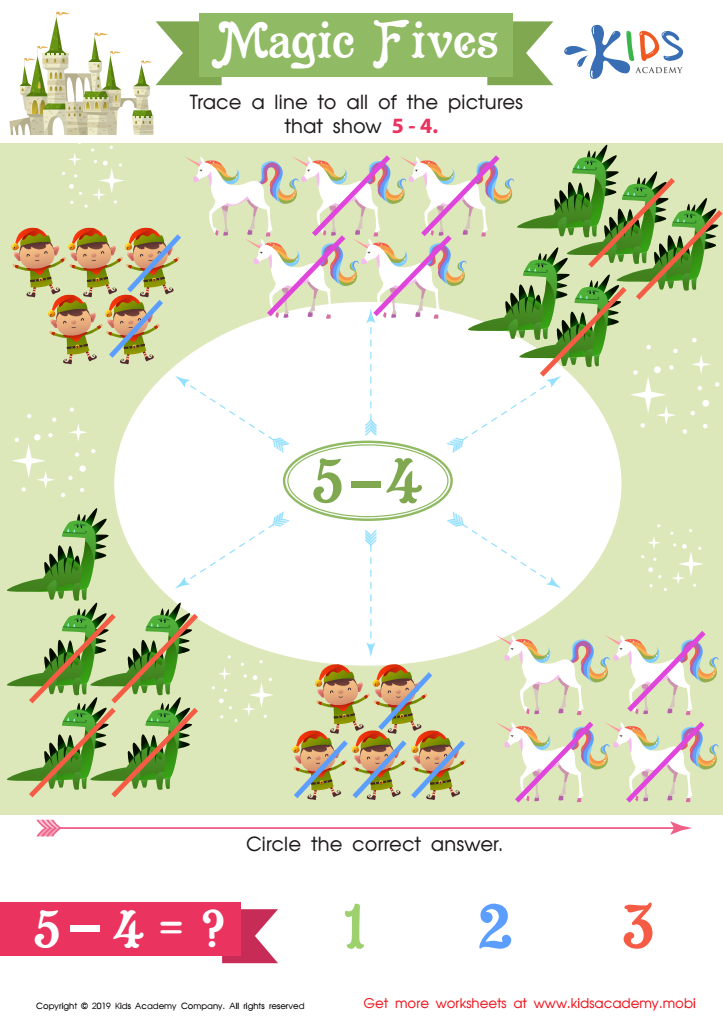

Magic Fives Worksheet


Read from Left to Right: Hats and Spiders Worksheet
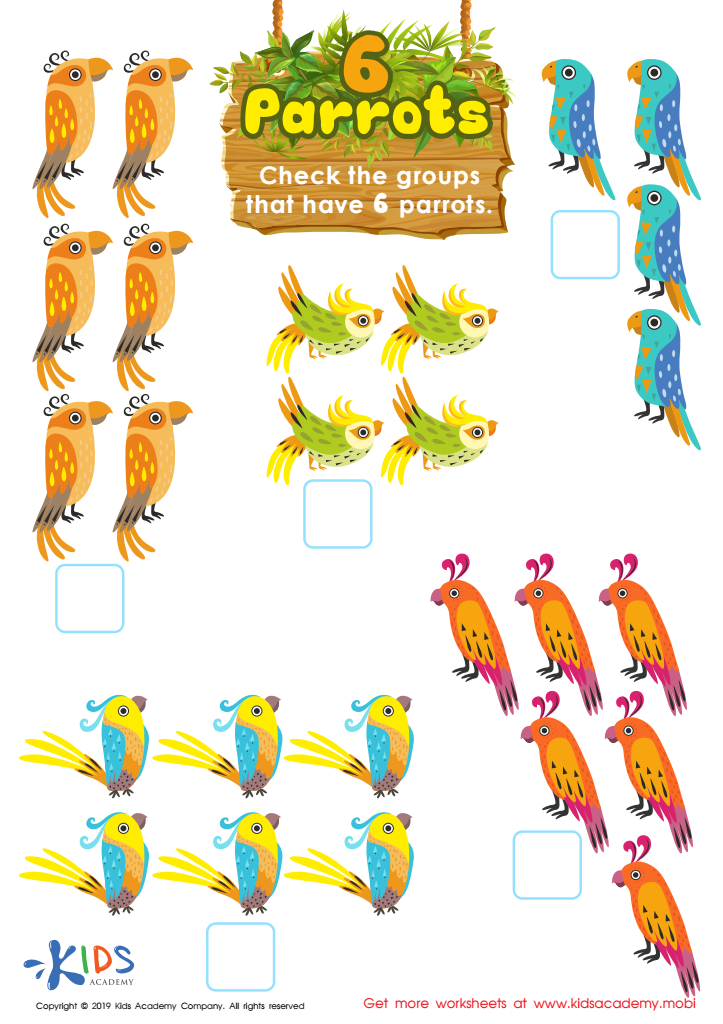

6 Parrots Worksheet
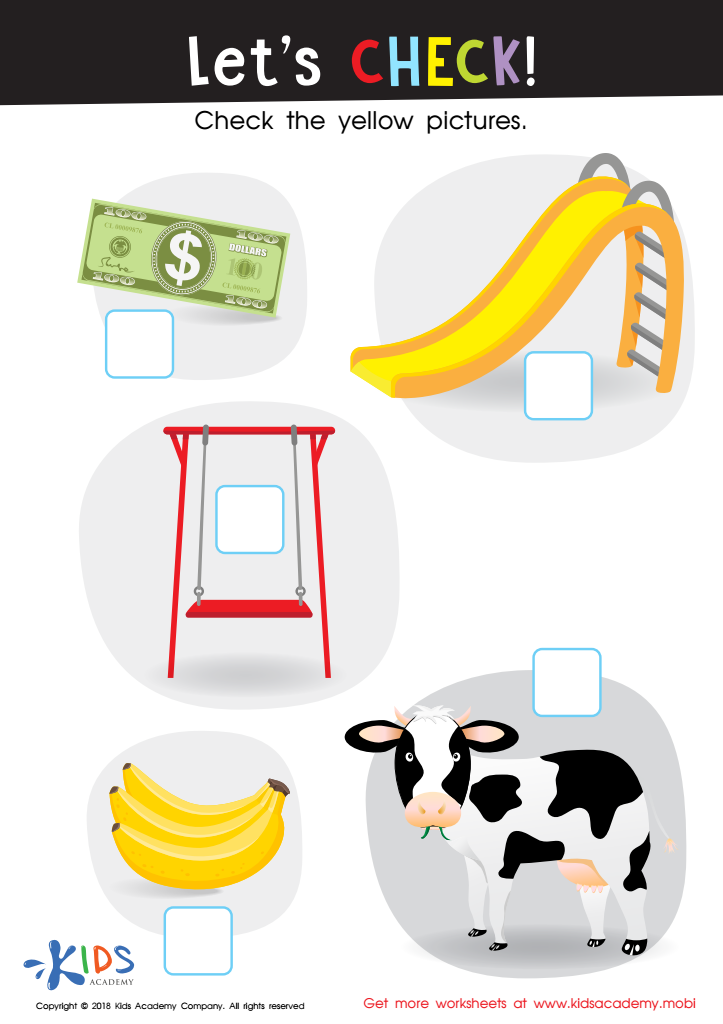


Let's Check! Worksheet


Number 2 Printable
Counting practice is fundamental for young children, particularly those aged 3-4, as it lays the groundwork for future mathematical understanding and cognitive development. At this critical age, children’s brains are highly receptive, and engaging them in counting activities helps nurture several key developmental areas.
First, counting strengthens numerical cognition, allowing children to understand numbers, their order, and their relationships. This early exposure sets the stage for more complex mathematical concepts, such as addition, subtraction, and problem-solving skills, promoting a positive long-term attitude toward math.
Second, counting activities enhance fine motor skills and eye-hand coordination, especially when children use physical objects like blocks, beads, or fingers to count. These skills are crucial for tasks in everyday life and are interlinked with cognitive abilities that impact learning and development.
Furthermore, counting supports the development of language skills. As children recite numbers, they improve their verbal fluency, memory, and listening skills. This practice helps them follow sequences, understand quantity descriptions, and better communicate their thoughts.
Finally, counting practice can be a joyful experience that fosters a sense of achievement. It boosts confidence, encourages curiosity, and creates opportunities for positive interactions between parents, teachers, and peers. Thus, counting practice plays an essential role in holistic early childhood education, emphasizing its importance for parents and teachers.

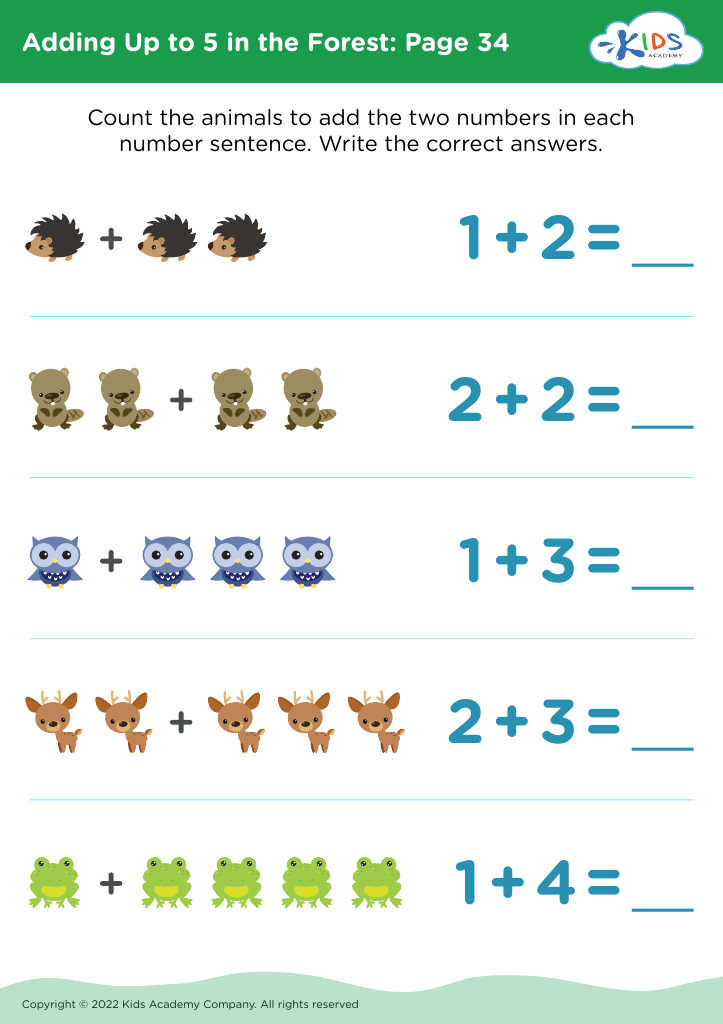

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
































