Problem-Solving Skills Geometry Worksheets for Ages 3-9 - Page 2
30 filtered results
-
From - To
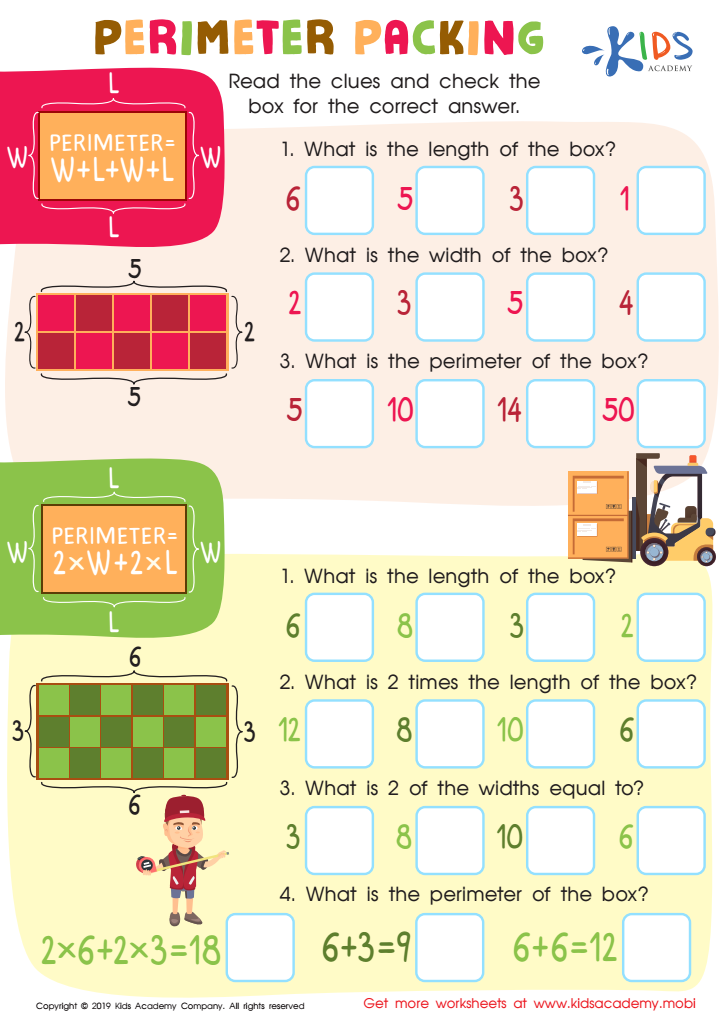

Perimeter Parking Worksheet


The Circle Maze Worksheet
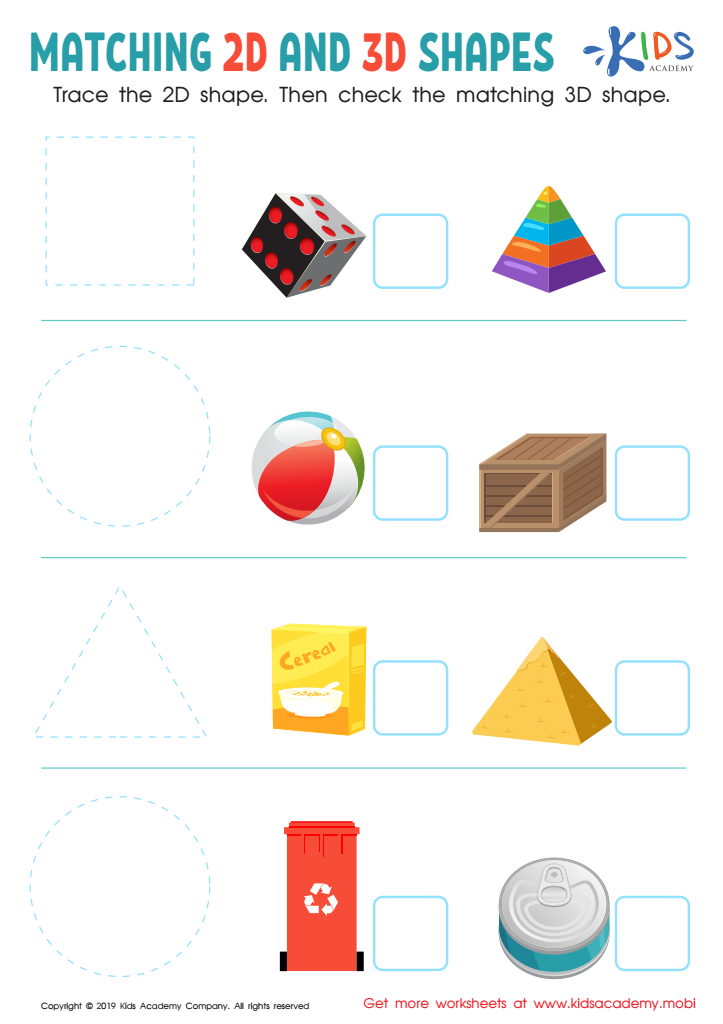


Matching 2D and 3D Shapes Worksheet
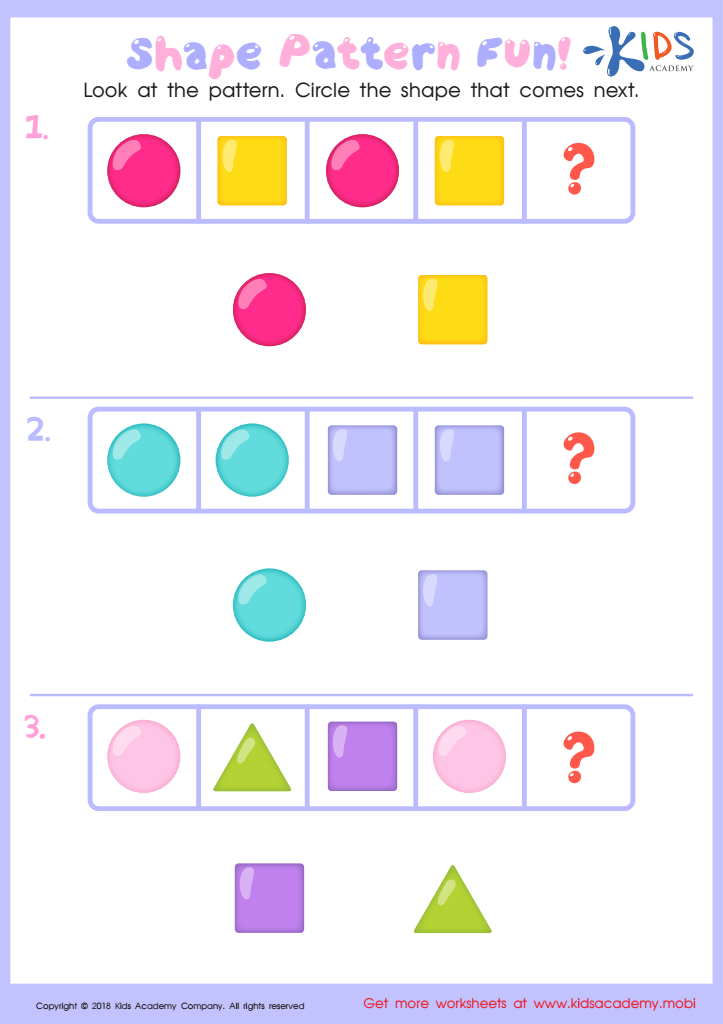

Shape Pattern Fun Worksheet
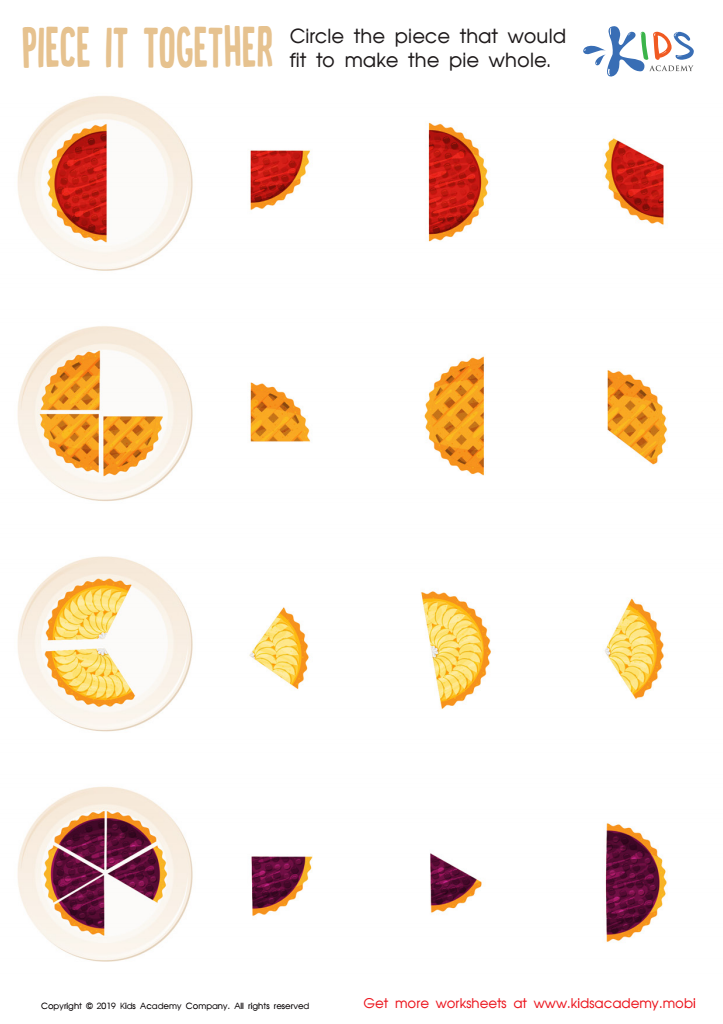


Piece it together Worksheet
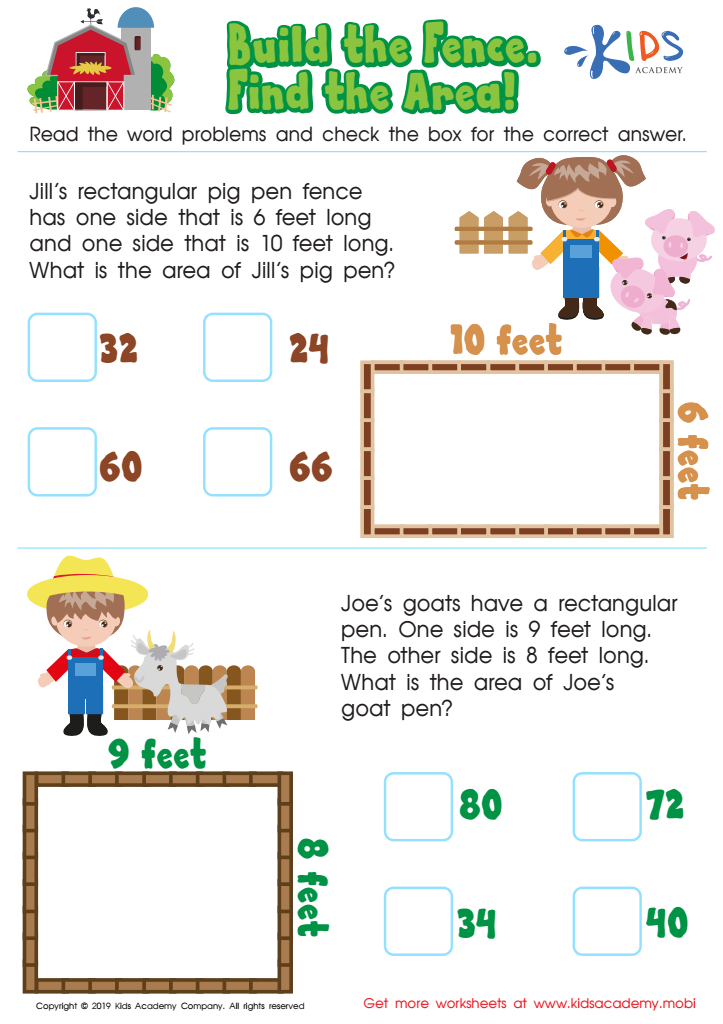

Build the Fence, Find the Area Worksheet
Problem-solving skills in geometry matter significantly for children aged 3-9 because they lay the foundation for critical thinking and cognitive development. At an early age, these skills are integrated through playful learning and hands-on experiences. Engaging with basic shapes and spatial relationships helps children enhance their spatial reasoning, a key component linked to success in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) fields later in life.
Parents and teachers should recognize that geometric play, like building blocks, pattern games, and puzzles, fosters creativity while promoting logical reasoning. Young children who practice solving problems involving shapes demonstrate improved skills in categorization, pattern detection, and visualization, which are fundamental for reading, writing, and arithmetic. By encouraging these activities, adults can not only aid in academic preparedness but also support a child's ability to approach challenges methodically and think critically.
Moreover, problem-solving through geometric activities strengthens a child's attentiveness and perseverance. When children experience the satisfaction of solving puzzles, they develop a growth mindset—believing they can improve through effort. This resilience is invaluable for lifelong learning. Therefore, nurturing problem-solving skills in geometry isn't just about mastering shapes; it is about equipping children with essential tools for intellectual growth and real-world problem-solving.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students