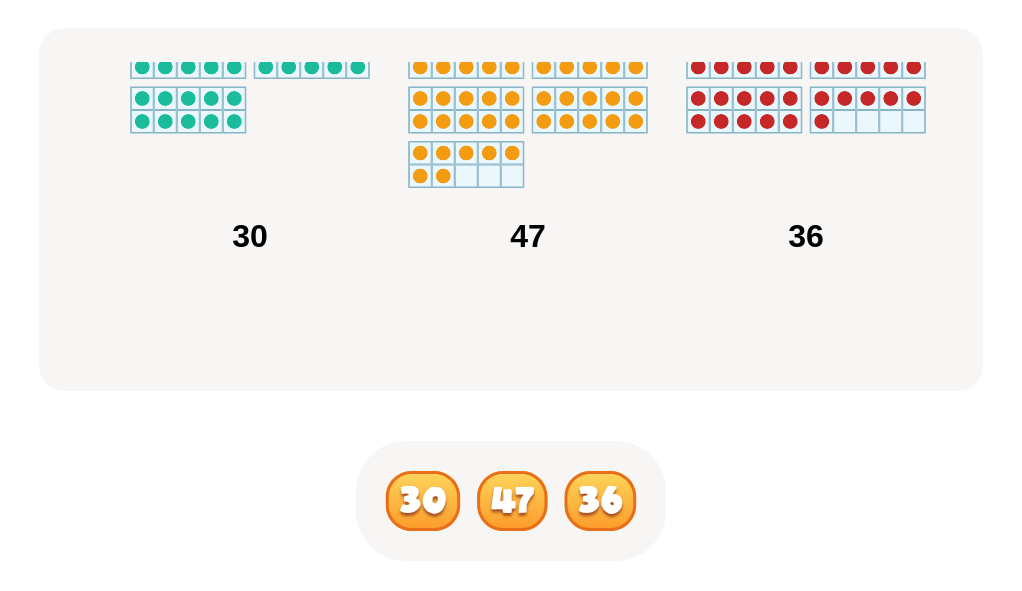
Comparing lengths Comparing Numbers Worksheets for Ages 4-7
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover engaging "Comparing Lengths, Comparing Numbers Worksheets" crafted specifically for children aged 4-7. These educational worksheets provide fun and interactive activities to help kids develop essential early math skills, such as understanding measurements, comparing sizes, and recognizing numerical differences. Designed by experienced educators, the worksheets feature vibrant illustrations and simple, clear instructions that make learning enjoyable and effective. Perfect for both classroom and home use, our worksheets support young learners in building a solid foundation in mathematics, preparing them for future academic success. Boost your child's confidence and proficiency in math with our high-quality resources today!
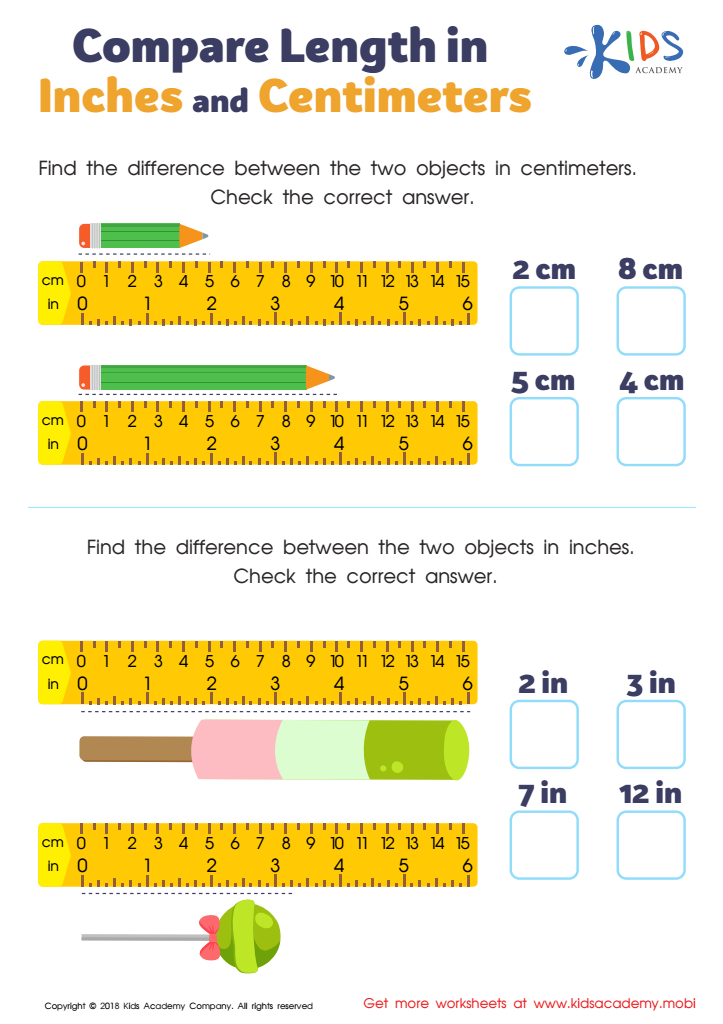

Compare Length in Inches and Centimeters Worksheet
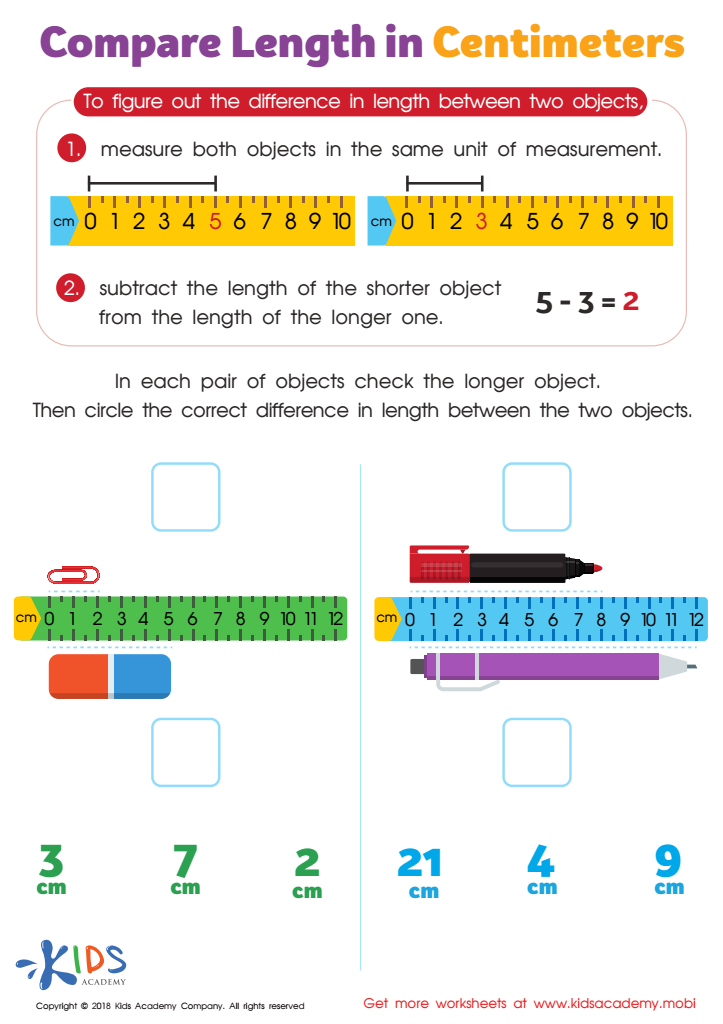

Compare Length in Centimeters Worksheet
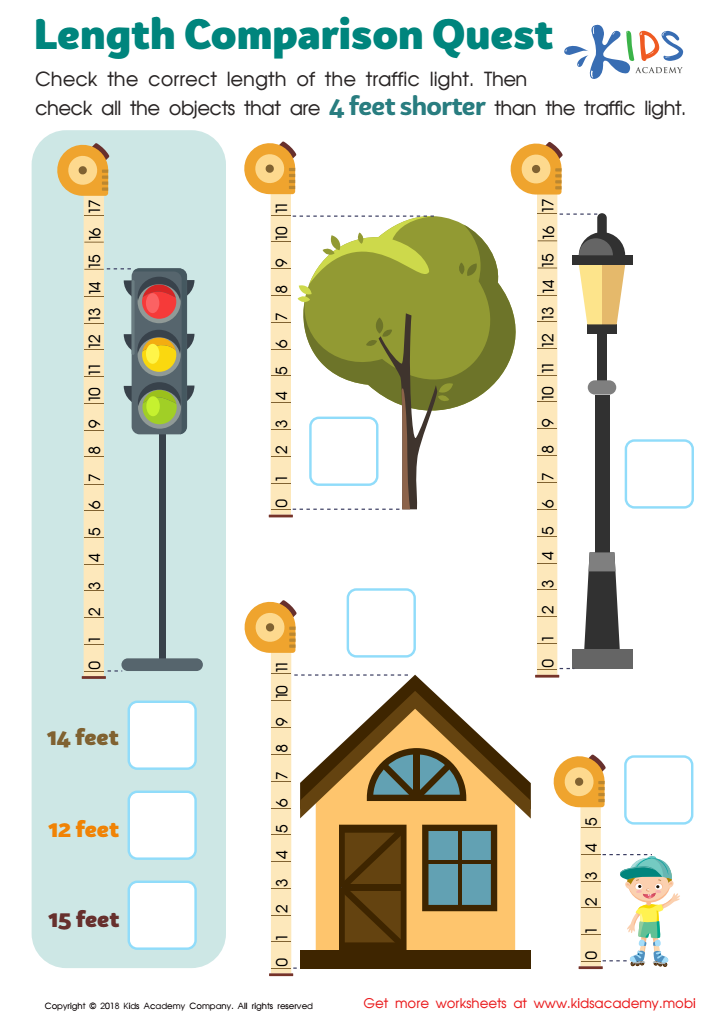

Length Comparison Quest Worksheet


Measuring the Length of Plants Worksheet
Parents and teachers should care about comparing lengths and comparing numbers for children aged 4-7 because these foundational skills are critical in early childhood development and future academic success. Comparing lengths involves measuring and differentiating between objects based on size, which aids in the development of spatial awareness and fine motor skills. For example, by determining which stick is longer or which block is shorter, children begin to understand measurement concepts and the vocabulary associated with them, such as "long," "short," "taller," and "shorter."
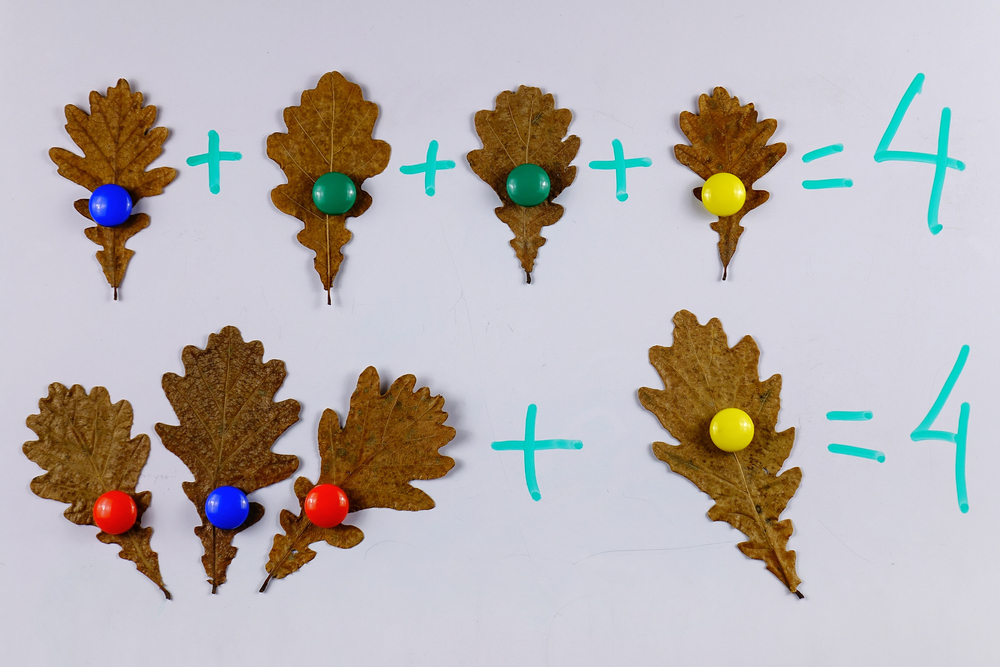
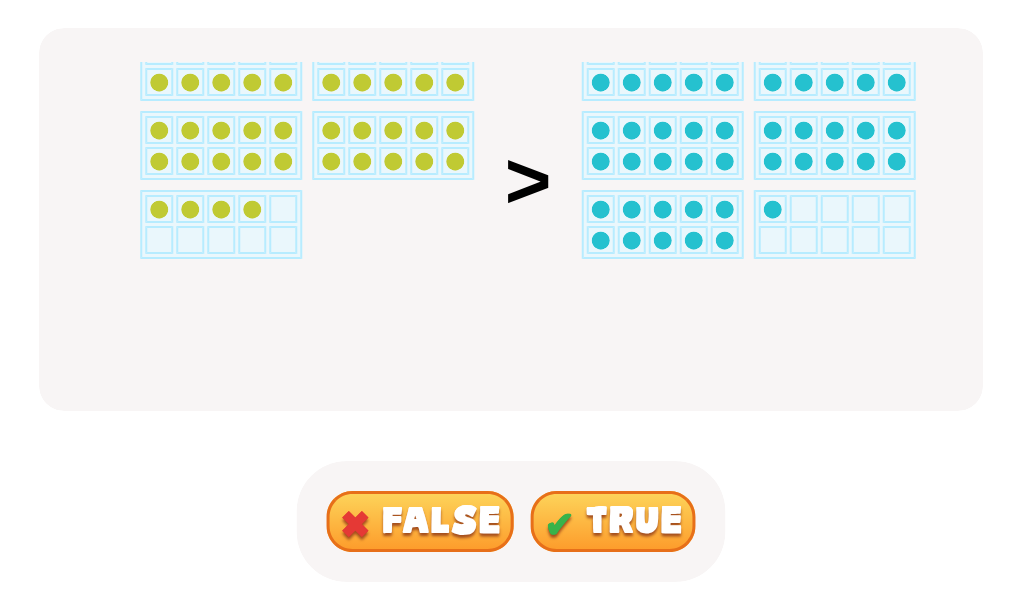
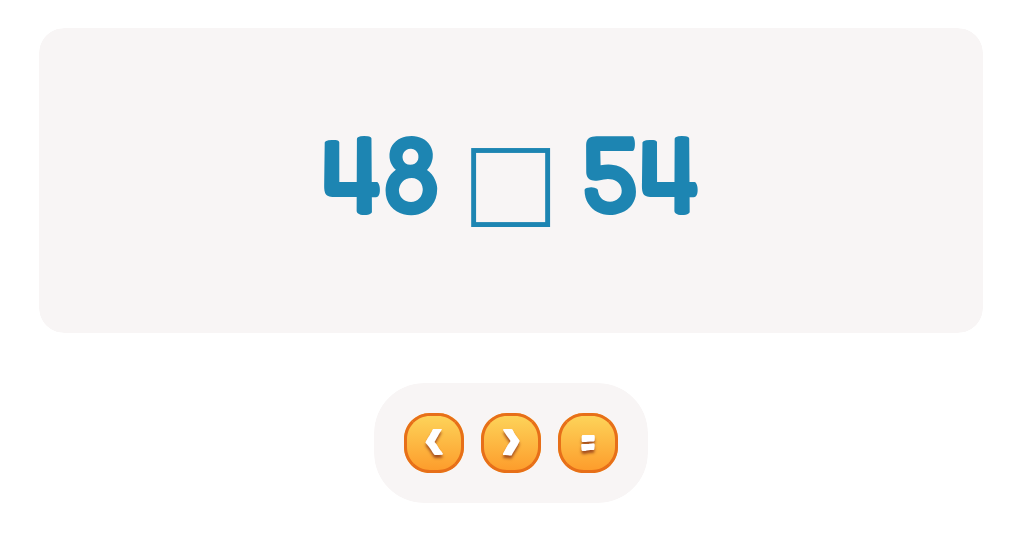
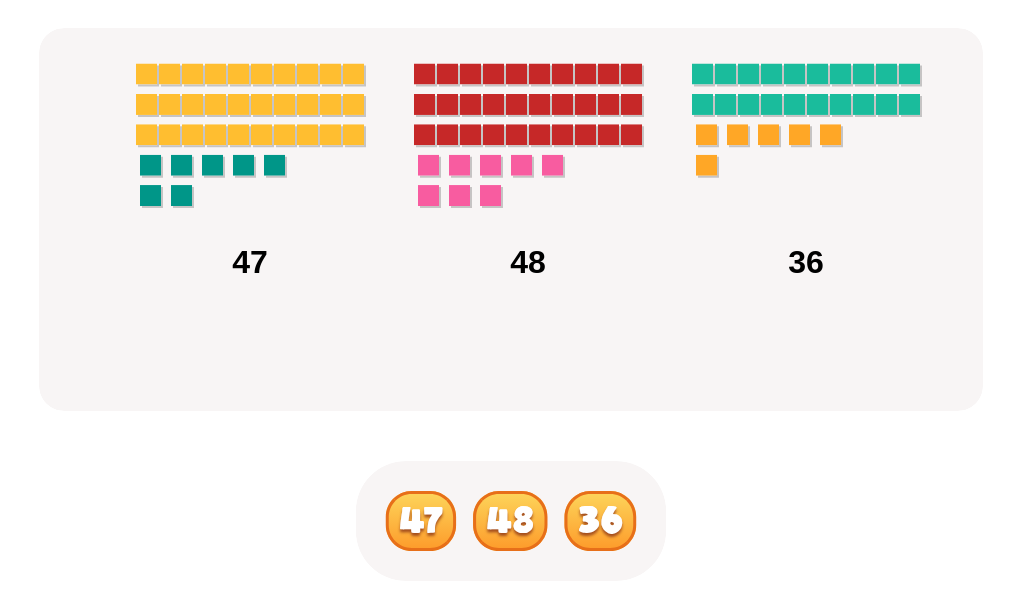
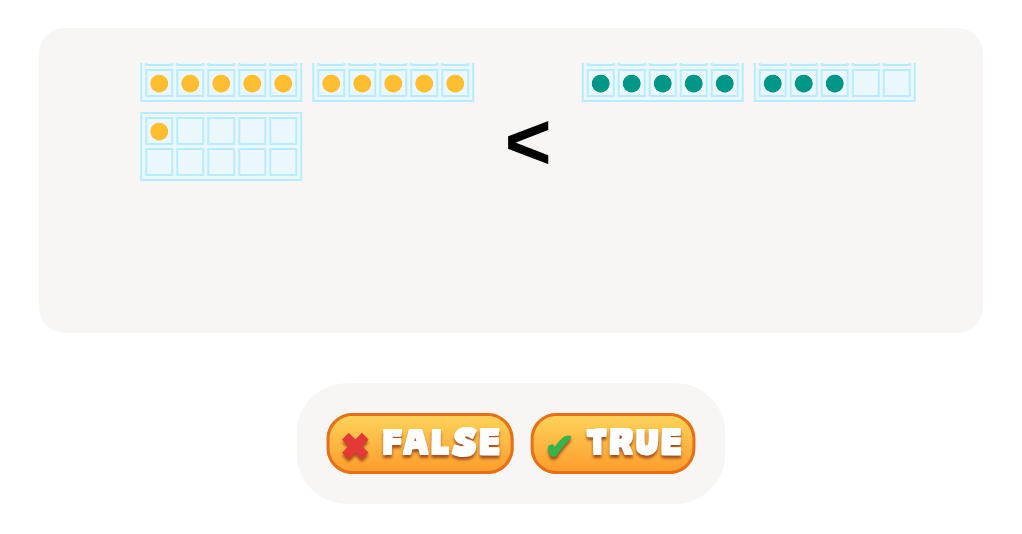
Comparing numbers similarly fosters numerical literacy and critical thinking. When children compare quantities, such as determining whether there are more apples or oranges, they enhance their understanding of numerical relationships and sequences. This process lays the groundwork for more advanced mathematical concepts like addition, subtraction, and place value. Discussing which number is bigger or smaller helps solidify their counting skills and number recognition.
Both comparing lengths and numbers enable children to categorize and organize their world systematically. These activities not only build cognitive skills but also encourage curiosity, problem-solving abilities, and the persistence necessary for lifelong learning. Thus, by supporting these early skills, parents and teachers set the stage for children’s continuing success in mathematics and other areas of education.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students