Fine Motor Skills Geometry Worksheets for Ages 4-8 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To


Patchwork Math Worksheet
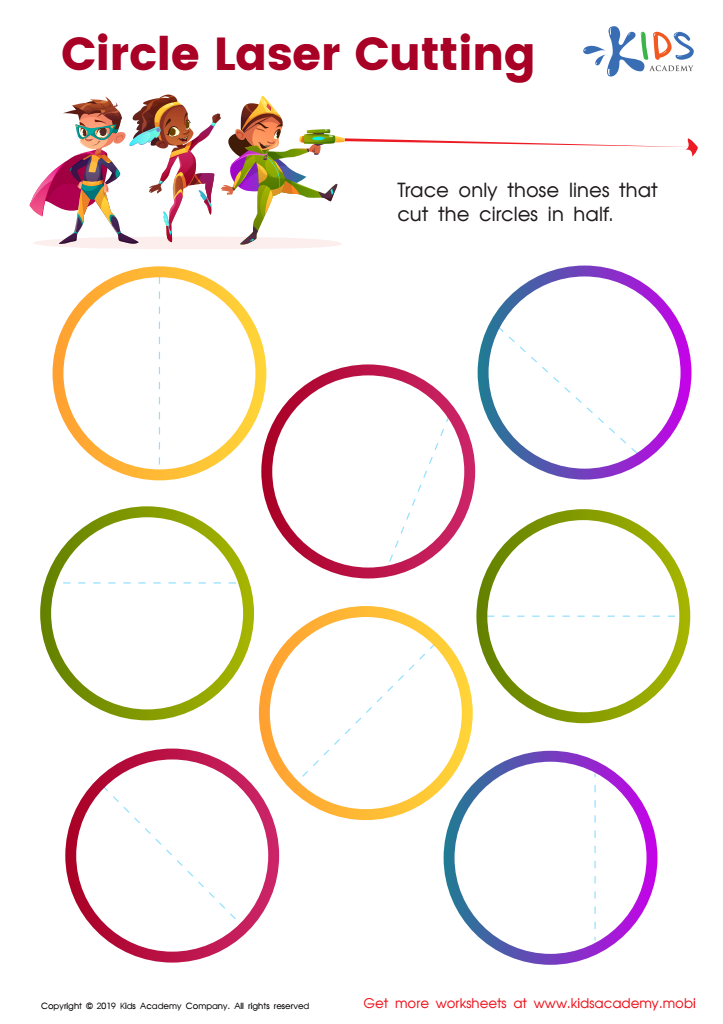

Circle Laser Cutting Worksheet
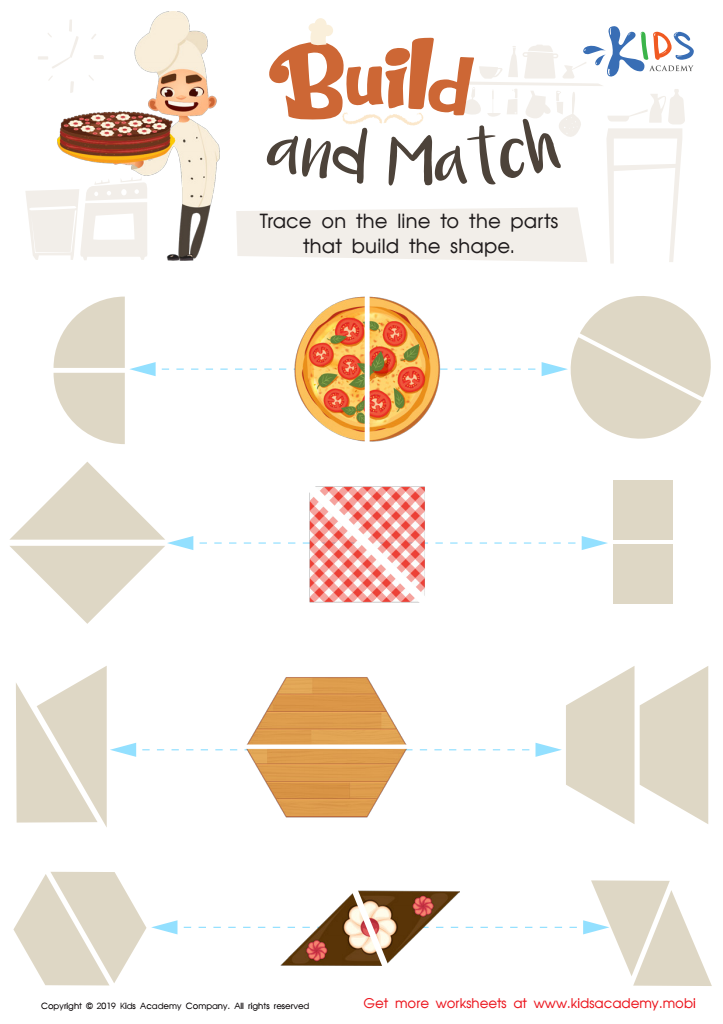

Build and Match Worksheet
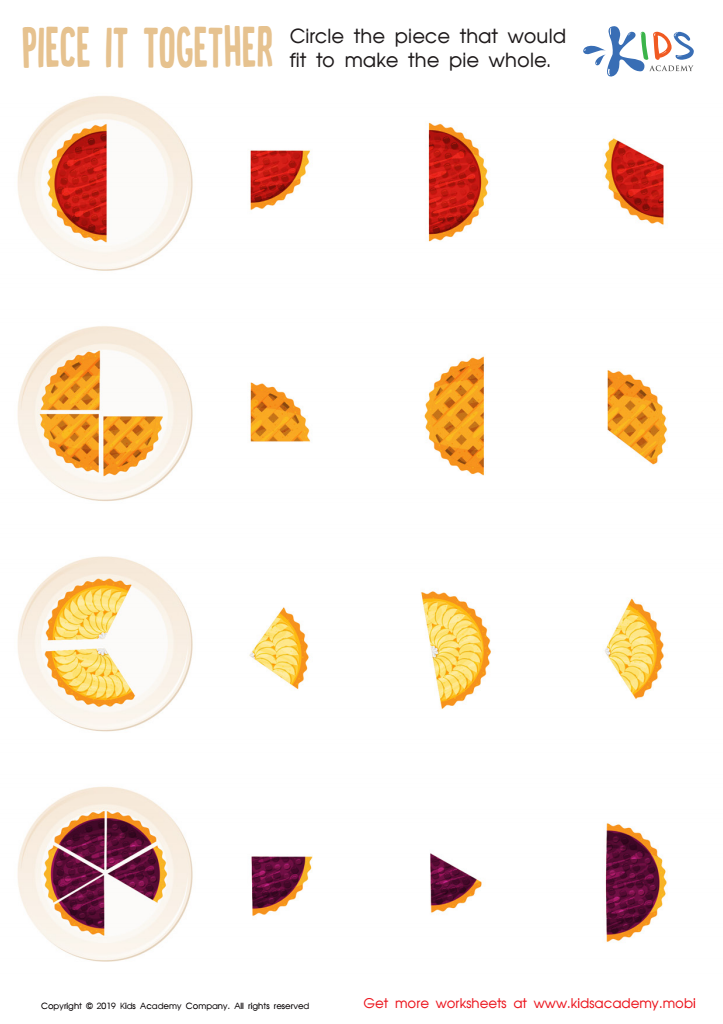


Piece it together Worksheet

Construction Shapes Worksheet
Fine motor skills are critical for young children's development, particularly in the ages of 4-8. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, allowing children to perform precise movements. Fine motor skills are foundational for tasks such as writing, drawing, buttoning clothes, and even during play which is essential for cognitive development.
Integrating geometry into the practice of fine motor skills can exponentially boost a child’s educational foundation. Geometry engages children in spatial reasoning, problem-solving, and logical thinking. Activities such as cutting shapes, arranging patterns, and drawing geometric figures not only enhance fine motor control but also introduce fundamental math concepts. These skills form the foundation for academic success in math and science, fostering a sense of curiosity and enthusiasm for these subjects.
Encouraging development in these areas prepares children for more complex learning and daily activities, increasing their confidence and independence. Educators and parents can incorporate playful, geometry-based motor skills activities—like puzzles or building blocks—into daily routines to support this vital development stage. Consequently, fostering fine motor skills through geometry not only advances children’s physical competencies but also cultivates their intellectual growth, positively impacting their overall learning journey.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students