Developing fine motor skills Math Worksheets for Ages 4-9
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills with our engaging math worksheets designed for ages 4-9! These carefully crafted resources combine fun and education, helping young learners master essential math concepts while improving hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Our worksheets feature a variety of activities, including tracing numbers, connecting dots, and completing patterns, making math interactive and enjoyable. Tailored to support children's developmental milestones, these printable worksheets are perfect for homeschooling or supplemental practice. Foster your child's confidence in math while nurturing their fine motor skills with our comprehensive collection of worksheets today! Start your learning adventure now!
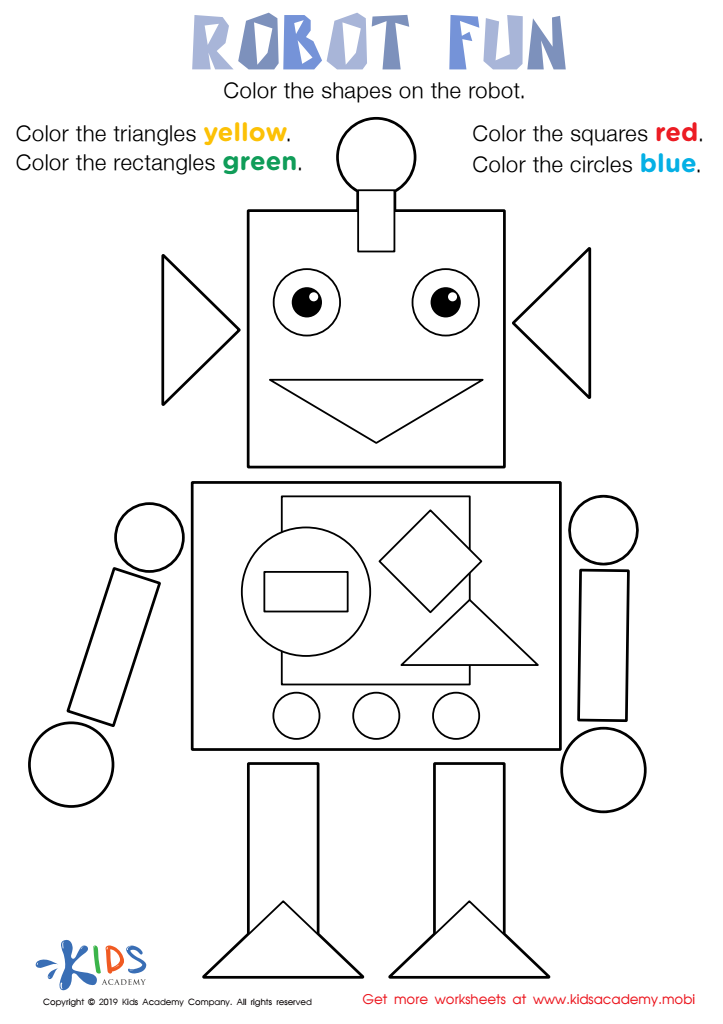

Robot Fun Worksheet
Developing fine motor skills in young children, particularly during the ages of 4 to 9, is crucial as it lays the foundation for various developmental areas, including math. Fine motor skills involve the use of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are essential for tasks such as writing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. As children engage in activities that enhance these skills, such as threading beads, using scissors, or drawing shapes, they begin to develop the precision and control needed to understand mathematical concepts.
Mathematics, especially in early education, often includes tasks that require fine motor skills, such as measuring, counting small items, and creating shapes. Strengthening these skills can support children’s ability to perform more complex math tasks as they progress in their education. Moreover, when children are allowed to engage in activities that combine physical skill with math learning—like counting while playing with blocks or measuring ingredients for a recipe—they connect abstract concepts to tangible experiences, enhancing comprehension and retention.
By prioritizing fine motor development, parents and teachers create an environment where math becomes accessible and enjoyable, fostering a positive attitude towards learning. This foundational support builds confidence and engagement in children’s academic journeys.


 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students